
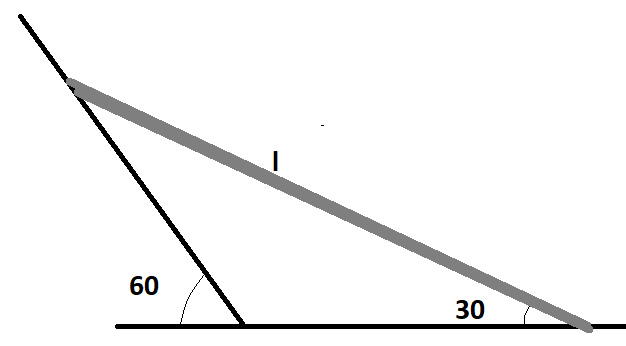
A uniform of length l is released from the rest position shown in the figure. The acceleration due to gravity is g. There is no friction at any surface. find the initial angular acceleration of the rod.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: When the rod is freed to move under gravity two of its end will move in different direction one will move downwards and other will move away from the support but there will be a point about which they will be rotating and this point is called the instantaneous centre of rotation. Here we will use the concept of torque and instantaneous centre to calculate angular acceleration.
Complete step by step solution:
Here a uniform rod is given of length l it is released from the position as shown in the figure.
The acceleration due to gravity is g and all the surface are perfectly smooth and we need to find out the initial angular acceleration of the rod when the rod just starts to rotate,
For solving such questions, we need to draw the free body diagram of the rod
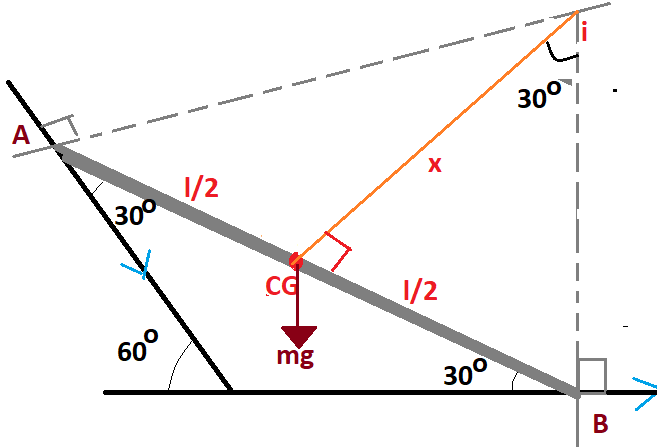
Here the weight of the rod will be acting at the CG in vertically downward direction and Cg will divide the rod into two equal lengths of $\dfrac{l}{2}$ each.
The angle at A will be $30^\circ $ we can find it out at angle addition.
Here it is clear that when the rod slides point A will be moving downwards and point B will move away.
We draw normal to these two motions for drawing normal. We draw two perpendicular lines one from A and other from B. These lines meet at I . This will be the instantaneous centre of rotation of the whole body which means the body is rotating about this point as a whole.
Now we draw a perpendicular from I to CG angle at I will be $30^\circ $ By angle addition property
Now length x will be given by
$\because \cot \theta = \dfrac{{base}}{{perpendicular}}$
$\therefore \cot \theta = \dfrac{x}{{\left( {\dfrac{l}{2}} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{l}{2}\cot \theta $
$\because \theta = 30^\circ $
$x = \dfrac{l}{2}\cot 30^\circ $
$x = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 l}}{2}$
Now as we know torque is the product of the moment of inertia and angular acceleration
$\tau = I\alpha $ ___________________(1)
Where, $I$ Is the moment of inertia of rod about I and $\alpha $ is the angular acceleration
Moment of inertia of a rod about its centre is given by
$\Rightarrow {I_c} = \dfrac{{m{l^2}}}{{12}}$
and since there is a distance between the point of rotation and rod so we will add an offset
So the total moment of inertia in this situation will be
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{m{l^2}}}{{12}} + m{x^2}$
Substituting the value of x we get
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{m{l^2}}}{{12}} + \dfrac{{3m{l^2}}}{4}$
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{5m{l^2}}}{6}$
Now as we know torque is the force times the perpendicular distance
Here the force is g and it acts for a perpendicular distance of $\dfrac{l}{2}\cos \theta $at point CG.
So $\tau = mg\dfrac{l}{2}\cos \theta $
$\because \theta = 30^\circ $
$\therefore \tau = mg\dfrac{l}{2}\cos 30^\circ $
$ \Rightarrow \tau = mgl\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}$
$\because \theta = 30^\circ $
So we have got the value of I and $\tau $
Now substituting these in equation 1 we get
$\because \tau = I\alpha $
$\Rightarrow \alpha = \dfrac{\tau }{I}$
$\Rightarrow \alpha = \dfrac{{\left( {mgl\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}} \right)}}{{\left( {\dfrac{{5m{l^2}}}{6}} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \alpha = \dfrac{{6g\sqrt 3 }}{{20l}}$
$ \Rightarrow \alpha = \dfrac{{3g\sqrt 3 }}{{10l}}$
The initial angular acceleration will be $\dfrac{{3g\sqrt 3 }}{{10l}}$.
Note: Torque is always at the perpendicular direction. The instantaneous centre is the point where both the points seem to be in rotational motion about that point. Whenever a body is rotating at an offset always adds its effect on moment of inertia.
Complete step by step solution:
Here a uniform rod is given of length l it is released from the position as shown in the figure.
The acceleration due to gravity is g and all the surface are perfectly smooth and we need to find out the initial angular acceleration of the rod when the rod just starts to rotate,
For solving such questions, we need to draw the free body diagram of the rod

Here the weight of the rod will be acting at the CG in vertically downward direction and Cg will divide the rod into two equal lengths of $\dfrac{l}{2}$ each.
The angle at A will be $30^\circ $ we can find it out at angle addition.
Here it is clear that when the rod slides point A will be moving downwards and point B will move away.
We draw normal to these two motions for drawing normal. We draw two perpendicular lines one from A and other from B. These lines meet at I . This will be the instantaneous centre of rotation of the whole body which means the body is rotating about this point as a whole.
Now we draw a perpendicular from I to CG angle at I will be $30^\circ $ By angle addition property
Now length x will be given by
$\because \cot \theta = \dfrac{{base}}{{perpendicular}}$
$\therefore \cot \theta = \dfrac{x}{{\left( {\dfrac{l}{2}} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{l}{2}\cot \theta $
$\because \theta = 30^\circ $
$x = \dfrac{l}{2}\cot 30^\circ $
$x = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 l}}{2}$
Now as we know torque is the product of the moment of inertia and angular acceleration
$\tau = I\alpha $ ___________________(1)
Where, $I$ Is the moment of inertia of rod about I and $\alpha $ is the angular acceleration
Moment of inertia of a rod about its centre is given by
$\Rightarrow {I_c} = \dfrac{{m{l^2}}}{{12}}$
and since there is a distance between the point of rotation and rod so we will add an offset
So the total moment of inertia in this situation will be
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{m{l^2}}}{{12}} + m{x^2}$
Substituting the value of x we get
$\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{m{l^2}}}{{12}} + \dfrac{{3m{l^2}}}{4}$
$ \Rightarrow I = \dfrac{{5m{l^2}}}{6}$
Now as we know torque is the force times the perpendicular distance
Here the force is g and it acts for a perpendicular distance of $\dfrac{l}{2}\cos \theta $at point CG.
So $\tau = mg\dfrac{l}{2}\cos \theta $
$\because \theta = 30^\circ $
$\therefore \tau = mg\dfrac{l}{2}\cos 30^\circ $
$ \Rightarrow \tau = mgl\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}$
$\because \theta = 30^\circ $
So we have got the value of I and $\tau $
Now substituting these in equation 1 we get
$\because \tau = I\alpha $
$\Rightarrow \alpha = \dfrac{\tau }{I}$
$\Rightarrow \alpha = \dfrac{{\left( {mgl\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{4}} \right)}}{{\left( {\dfrac{{5m{l^2}}}{6}} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \alpha = \dfrac{{6g\sqrt 3 }}{{20l}}$
$ \Rightarrow \alpha = \dfrac{{3g\sqrt 3 }}{{10l}}$
The initial angular acceleration will be $\dfrac{{3g\sqrt 3 }}{{10l}}$.
Note: Torque is always at the perpendicular direction. The instantaneous centre is the point where both the points seem to be in rotational motion about that point. Whenever a body is rotating at an offset always adds its effect on moment of inertia.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




