
Among the following compounds most basic amino acid is :
A. Lysine
B. Asparagine
C. Serine
D. Histidine
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Amino acids are organic compounds containing amine and carboxyl functional groups along with a side chain specific to each amino acid. So amino acid is made up of Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and other elements are found in side chains of some amino acids. Side chain of amino acid resembles ammonia which is a base.
Complete step by step solution:
> There are three amino acids that have basic side chains at neutral \[pH\] . These are arginine, histidine, lysine. Their side chains contain nitrogen. Lysine is used in the biosynthesis of proteins, It contains an $\alpha - $ amino group , $\alpha - $ carboxylic acid group, and a side chain lysyl. Lysyl is a basic charged aliphatic amino acid. It has two amine groups.
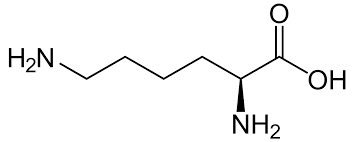 Lysine
Lysine
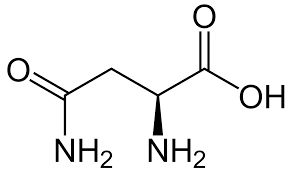 Asparagine
Asparagine
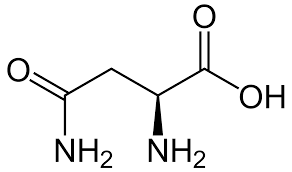 Serine
Serine
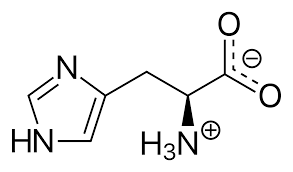 Histidine
Histidine
> Asparagine is an $\alpha $- amino acid that is also used in biosynthesis of proteins. A side chain of carboxamide distributes it as a polar aliphatic amino acid. Serine contains an alcohol and is functionally important in many proteins. It is useful for metabolism of fat, fatty acid and cell membranes and a healthy immune system. Histidine is an alpha-amino acid with an imidazole functional group. So as it contains the most basic nitrogen atom, it is the most basic amino acid. Hence option D is correct.
Note: We know that amino acids are known as ‘building blocks’ of proteins. It assists in the growth of muscles, connective tissues, tissue strength and maintains healthy skin. It has healing and repair capabilities in our body. Here histidine is most basic among all the given options because it contains imidazole.
Complete step by step solution:
> There are three amino acids that have basic side chains at neutral \[pH\] . These are arginine, histidine, lysine. Their side chains contain nitrogen. Lysine is used in the biosynthesis of proteins, It contains an $\alpha - $ amino group , $\alpha - $ carboxylic acid group, and a side chain lysyl. Lysyl is a basic charged aliphatic amino acid. It has two amine groups.
 Lysine
Lysine  Asparagine
Asparagine Serine
Serine Histidine
Histidine> Asparagine is an $\alpha $- amino acid that is also used in biosynthesis of proteins. A side chain of carboxamide distributes it as a polar aliphatic amino acid. Serine contains an alcohol and is functionally important in many proteins. It is useful for metabolism of fat, fatty acid and cell membranes and a healthy immune system. Histidine is an alpha-amino acid with an imidazole functional group. So as it contains the most basic nitrogen atom, it is the most basic amino acid. Hence option D is correct.
Note: We know that amino acids are known as ‘building blocks’ of proteins. It assists in the growth of muscles, connective tissues, tissue strength and maintains healthy skin. It has healing and repair capabilities in our body. Here histidine is most basic among all the given options because it contains imidazole.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




