
An equimolar solution of ${\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ and ${\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ can act as :
A. Strong Reductant
B. Strong Oxidant
C. Buffer Solution
D. None of these
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: To know whether ${\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ and ${\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ makes an equimolar solution or not, we should whether both the compounds are strong or weak base and acid respectively. Once we know that, we can analyse the characteristics to term them as one among the mentioned options.
Complete step-by-step answer:
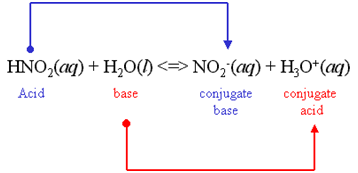
We all know that, ${\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is a weak acid. ${\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ partially dissociates in the aqueous solution. Here is the equation of the dissociation of ${\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ :
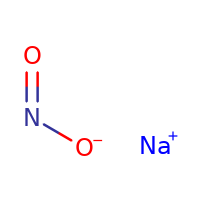
${\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is the example of a salt, which is formed by the reaction between weak acid and strong base. The weak acid is ${\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ and the strong base is NaOH. Here is the structure of ${\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$:
The equation for the formation of ${\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is :
$\text{HN}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+NaOH}\xrightarrow{{}}\text{NaN}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}$
We know, a buffer solution is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice versa. Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it. Therefore, an equimolar solution of ${\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ and ${\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ can act as a buffer solution.
So the correct answer is Option C.
Note: Buffer solutions have pH more than 7, are known as acidic buffer solutions.
A buffer is a solution that can resist pH change upon the addition of acidic or basic components. It is able to neutralize small amounts of added acid or base, does maintain the pH of the solution relatively stable. This is important for the processes and or reactions which requires specific and stable pH ranges.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We all know that, ${\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is a weak acid. ${\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ partially dissociates in the aqueous solution. Here is the equation of the dissociation of ${\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ :

${\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is the example of a salt, which is formed by the reaction between weak acid and strong base. The weak acid is ${\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ and the strong base is NaOH. Here is the structure of ${\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$:

The equation for the formation of ${\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is :
$\text{HN}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+NaOH}\xrightarrow{{}}\text{NaN}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}$
We know, a buffer solution is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice versa. Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it. Therefore, an equimolar solution of ${\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ and ${\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ can act as a buffer solution.
So the correct answer is Option C.
Note: Buffer solutions have pH more than 7, are known as acidic buffer solutions.
A buffer is a solution that can resist pH change upon the addition of acidic or basic components. It is able to neutralize small amounts of added acid or base, does maintain the pH of the solution relatively stable. This is important for the processes and or reactions which requires specific and stable pH ranges.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




