
What is the axis of rotation of a purely rotating body?
A. Must pass through the center of mass
B. May pass through the center of mass
C. Must pass through the particle of the body
D. May pass through the particle of the body
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: It is important to know about the axis of rotation and center of mass. The point or axis around which the object rotates is known as the axis of rotation. If you consider a point in a body or system of bodies at which the whole mass is concentrated at the center of the body known as the center of mass. Now let’s find the answer to the question given.
Complete step by step solution:
A body is said to be in the pure rotation when it rotates about a certain fixed axis and this axis could be anywhere. It is not necessary that it must pass through the center of mass or through some particle or a body. It can also be outside the body. Purely rotating means if a body is in pure rotation, then each point of the body must go in a circle. To understand this, consider an example.
Take a disc ‘a’ and the axis of rotation ‘x’ doesn’t pass through the center of mass.
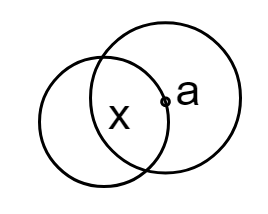
Image: Disc
Here we can see that point ‘a’ rotates purely in a circle. Hence, the axis of rotation may pass through the center of mass.
Now, if the axis of rotation passes through the center of the mass, then points also rotate in a circle. Hence, the axis of rotation may pass through the particle of the body. Therefore, the axis of rotation of a purely rotating body may pass through the center of mass and also through the particle of the body.
Hence, Option B and D both are the correct answer.
Note: If the axis passes through the body’s center of mass, the body is said to rotate upon itself or spin. Objects that cannot rotate or spin completely can nonetheless be thought to be revolving around an axis. Ankles and knees, as well as mechanical pieces and a variety of other things, may rotate in a restricted circle around an internal line.
Complete step by step solution:
A body is said to be in the pure rotation when it rotates about a certain fixed axis and this axis could be anywhere. It is not necessary that it must pass through the center of mass or through some particle or a body. It can also be outside the body. Purely rotating means if a body is in pure rotation, then each point of the body must go in a circle. To understand this, consider an example.
Take a disc ‘a’ and the axis of rotation ‘x’ doesn’t pass through the center of mass.

Image: Disc
Here we can see that point ‘a’ rotates purely in a circle. Hence, the axis of rotation may pass through the center of mass.
Now, if the axis of rotation passes through the center of the mass, then points also rotate in a circle. Hence, the axis of rotation may pass through the particle of the body. Therefore, the axis of rotation of a purely rotating body may pass through the center of mass and also through the particle of the body.
Hence, Option B and D both are the correct answer.
Note: If the axis passes through the body’s center of mass, the body is said to rotate upon itself or spin. Objects that cannot rotate or spin completely can nonetheless be thought to be revolving around an axis. Ankles and knees, as well as mechanical pieces and a variety of other things, may rotate in a restricted circle around an internal line.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




