
When the bob of a pendulum is at the mean position (minimum displacement) of its motion, its total energy is
(A) All potential
(B) Zero
(C) All kinetic
(D) Partly kinetic partly potential
Answer
526k+ views
Hint A pendulum possesses both the kinetic energy and the potential energy when it is undergoing oscillations about its mean position. The variation of one energy is inverse to the variation of the other energy such that the total energy remains conserved.
Complete Step by step solution
Kinetic energy is defined as the energy possessed by an object by the virtue of its motion while potential energy is the energy possessed by an object by the virtue of its position. When a pendulum undergoes oscillatory motion about its mean position then it possesses both the kinetic energy and the potential energy.
The kinetic energy of the bob of the pendulum is zero at the extreme positions while its value is maximum when it passes through its mean position.
The behaviour of the potential energy is opposite to that of the kinetic energy. The potential energy of the bob of the pendulum is maximum at the extreme positions and zero when it passes through its mean position.
The following graph shows the variation of the kinetic energy and the potential energy of a pendulum oscillating about its mean position.
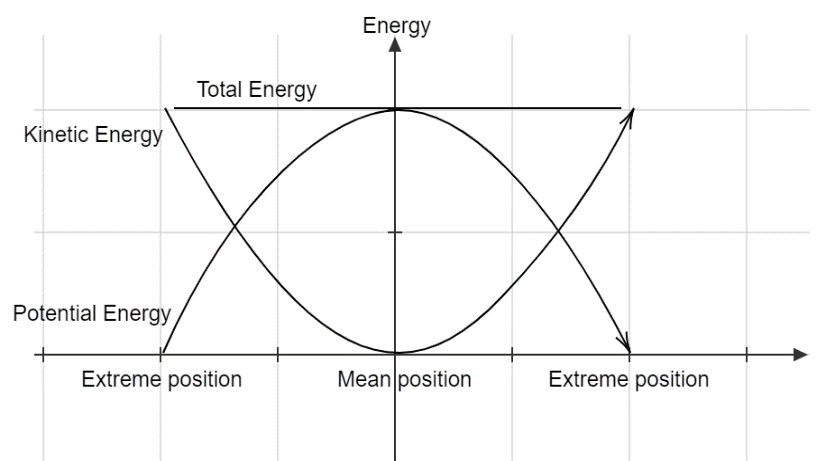
The total energy of the pendulum is equal to the sum of the kinetic energy and potential energy and its value remains constant throughout the motion of the pendulum.
Based on the above discussion we say that the correct answer is option (C) All kinetic.
Note The opposite variation of the kinetic energy and the potential energy ensures that the total energy of the pendulum remains constant. When the pendulum is at its extreme position, it momentarily comes to rest due to which the kinetic energy becomes zero at the extreme positions.
Complete Step by step solution
Kinetic energy is defined as the energy possessed by an object by the virtue of its motion while potential energy is the energy possessed by an object by the virtue of its position. When a pendulum undergoes oscillatory motion about its mean position then it possesses both the kinetic energy and the potential energy.
The kinetic energy of the bob of the pendulum is zero at the extreme positions while its value is maximum when it passes through its mean position.
The behaviour of the potential energy is opposite to that of the kinetic energy. The potential energy of the bob of the pendulum is maximum at the extreme positions and zero when it passes through its mean position.
The following graph shows the variation of the kinetic energy and the potential energy of a pendulum oscillating about its mean position.

The total energy of the pendulum is equal to the sum of the kinetic energy and potential energy and its value remains constant throughout the motion of the pendulum.
Based on the above discussion we say that the correct answer is option (C) All kinetic.
Note The opposite variation of the kinetic energy and the potential energy ensures that the total energy of the pendulum remains constant. When the pendulum is at its extreme position, it momentarily comes to rest due to which the kinetic energy becomes zero at the extreme positions.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




