
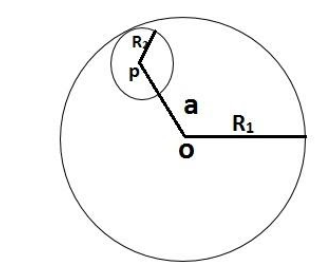
Consider a uniform spherical charge distribution of radius ${R_1}$ centred at the origin O. In this distribution a spherical cavity of radius${R_2}$, centred at P with distance $OP = a = {R_1} = {R_2}$ is made. If the electric field inside the cavity at position $\vec r$ is $\vec E\left( {\vec r} \right)$, then the correct statement is
(A) $\vec E$ is uniform, its magnitude is independent of ${R_2}$ but its direction depends on $\vec r$
(B) $\vec E$ is uniform, its magnitude is dependent of ${R_2}$ but its direction depends on $\vec r$
(C) $\vec E$ is uniform, its magnitude is independent of $a$ but its direction depends on $\vec a$
(D) $\vec E$ is uniform and both its magnitude and direction depend on $\vec a$.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Due to the larger sphere without the cavity and a smaller sphere with opposite charge density, the principle of superposition of electric fields can be applied. We need to apply Gauss’s Law to get the final answer.
Complete Step by Step Solution: Every charged particle creates an electric field in the universe in the space surrounding it. The electric field created due to the charge is independent of the presence or absence of all other charges. The electric field created can be calculated with the help of Coulomb’s law. The principle of superposition allows for the combination of two or more electric fields.
Superposition Principle gives the total force on a given charge due to any number of point charges acting on it. The principle of superposition states that every charge in space creates an electric field at a point independent of the presence of other charges in that medium. The resultant electric field is a vector sum of the electric field due to individual charges.
Since it has been given that, a uniform spherical charge distribution centred at the origin O has a radius ${R_1}$. In this distribution a spherical cavity of radius${R_2}$, centred at P with distance $OP = a = {R_1} = {R_2}$ is made and the electric field inside the cavity at position $\vec r$ is $\vec E\left( {\vec r} \right)$.
The problem can be considered as a superposition of electric fields due to the larger sphere without the cavity and a smaller sphere with opposite charge density.
By application of Gauss’ Law, for an internal point inside the spherical charge distribution, we have,
$\vec E\left( {\vec r} \right) = \dfrac{{\rho r}}{{3{ \in _r}}}$ where $\rho $ is the density.
By principle of superposition, $\vec E = {\vec E_1} + {\vec E_2}$.
$\dfrac{\rho }{{3{ \in _0}}}O\vec A + \dfrac{\rho }{{3{ \in _0}}}\vec AP + \dfrac{\rho }{{3{ \in _0}}}\left( {O\vec A + \vec AP} \right)$
We can write,
$\vec E = \dfrac{\rho }{{3{ \in _0}}}O\vec A = \dfrac{\rho }{{3{ \in _0}}}\vec a$
Hence, $\vec E$ is uniform and both its magnitude and direction depend on $\vec a$.
The correct answer is Option D.
Note: Gauss Law states that the total electric flux out of a closed surface is equal to the charge enclosed divided by the permittivity. The electric flux in an area is defined as the electric field multiplied by the area of the surface projected in a plane and perpendicular to the field.
Complete Step by Step Solution: Every charged particle creates an electric field in the universe in the space surrounding it. The electric field created due to the charge is independent of the presence or absence of all other charges. The electric field created can be calculated with the help of Coulomb’s law. The principle of superposition allows for the combination of two or more electric fields.
Superposition Principle gives the total force on a given charge due to any number of point charges acting on it. The principle of superposition states that every charge in space creates an electric field at a point independent of the presence of other charges in that medium. The resultant electric field is a vector sum of the electric field due to individual charges.
Since it has been given that, a uniform spherical charge distribution centred at the origin O has a radius ${R_1}$. In this distribution a spherical cavity of radius${R_2}$, centred at P with distance $OP = a = {R_1} = {R_2}$ is made and the electric field inside the cavity at position $\vec r$ is $\vec E\left( {\vec r} \right)$.
The problem can be considered as a superposition of electric fields due to the larger sphere without the cavity and a smaller sphere with opposite charge density.
By application of Gauss’ Law, for an internal point inside the spherical charge distribution, we have,
$\vec E\left( {\vec r} \right) = \dfrac{{\rho r}}{{3{ \in _r}}}$ where $\rho $ is the density.
By principle of superposition, $\vec E = {\vec E_1} + {\vec E_2}$.
$\dfrac{\rho }{{3{ \in _0}}}O\vec A + \dfrac{\rho }{{3{ \in _0}}}\vec AP + \dfrac{\rho }{{3{ \in _0}}}\left( {O\vec A + \vec AP} \right)$
We can write,
$\vec E = \dfrac{\rho }{{3{ \in _0}}}O\vec A = \dfrac{\rho }{{3{ \in _0}}}\vec a$
Hence, $\vec E$ is uniform and both its magnitude and direction depend on $\vec a$.
The correct answer is Option D.
Note: Gauss Law states that the total electric flux out of a closed surface is equal to the charge enclosed divided by the permittivity. The electric flux in an area is defined as the electric field multiplied by the area of the surface projected in a plane and perpendicular to the field.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




