
Consider the following statements. Choose the correct ones:
(This question has multiple correct options.)
A) CM of a uniform semi-circular disc of radius R is $2R\pi $ from the centre.
B) CM of a uniform semi-circular ring of radius $\dfrac{{2R}}{3}$ is $\dfrac{{4R}}{{3\pi }}$ from the centre.
C) CM of a solid hemisphere of radius R is $\dfrac{{4R}}{{3\pi }}$ from the centre.
D) CM of a solid hemisphere shell of radius R is $\dfrac{R}{2}$ from the centre.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Centre of mass of a system is the point where mass of the system is concentrated. For a system of mass m, the centre of mass can be calculated using mass and the position coordinates. We find the coordinates of the centre of mass using the corresponding formula depending on which axis is the symmetry axis. The number of coordinates that describe the centre of mass will depend on the dimension of the object.
Formula used:
The coordinates of the centre of mass are approximately given by
i) $X = \dfrac{1}{M}\int {xdm} $(X stands for the X-coordinate of the centre of mass, M stands for the mass of the particle, x stands for the x coordinate of the particle)
ii) $Y = \dfrac{1}{M}\int {ydm} $ (Y stands for the y coordinate of the centre of mass, y stands for the y coordinate of the particle)
iii) $Z = \dfrac{1}{M}\int {zdm} $(Z stands for the z coordinate of the centre of mass, z stands for the z coordinate of the particle)
Complete step by step solution:
A) CM of a uniform semi-circular disc of radius R:
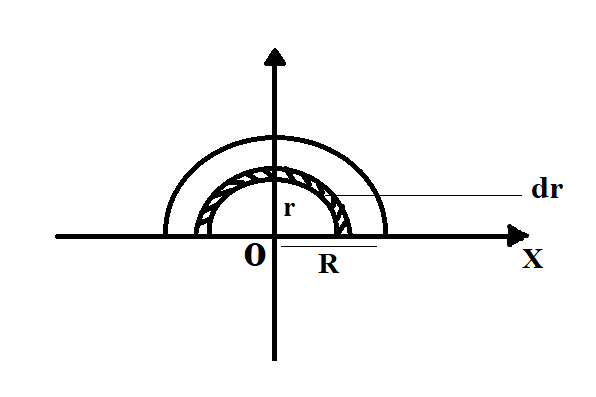
Let us consider a semi-circular disc of mass M and radius R.
Area of the disc = $\dfrac{{\pi {R^2}}}{2}$
Mass per unit area of the disc, $m = \dfrac{M}{{\dfrac{{\pi {R^2}}}{2}}} = \dfrac{{2M}}{{\pi {R^2}}}$
Area of the small element, dr = $\dfrac{1}{2}(\pi r{(r + dr)^2} - \pi {r^2})$ (calculating the area of the small element)
$\Rightarrow dr = \dfrac{1}{2}(\pi ({r^2} + d{r^2} + 2rdr) - \pi {r^2}) $
$\Rightarrow dr= \dfrac{1}{2}(2\pi rdr),(\because d{r^2} < < 1)$ ($\pi {r^2}$ is cancelled and $\pi d{r^2}$ is neglected because $d{r^2} \ll 1$)
$\Rightarrow dr= \pi rdr$
Mass of the small element dm is obtained by multiplying the mass per unit area and the area of the small element
The mass of the small element, $dm = \left( {\pi rdr} \right) \times \left( {\dfrac{{2M}}{{\pi {R^2}}}} \right)$ (on the calculation, we get)
$ \Rightarrow dm= \dfrac{{2Mr}}{{{R^2}}}dr$
The coordinates of the small element dr $(x,y)$= $\left( {0,\dfrac{{2r}}{\pi }} \right)$ $(x = 0,y = \dfrac{{2r}}{\pi })$
Let us take X and Y to be the coordinates for centre of mass,
$X = 0$(Due to the symmetry of the disc)
$Y = \dfrac{1}{M}\int {ydm} $
$Y = \dfrac{1}{M}\int\limits_0^R {\left( {\dfrac{{2r}}{\pi }} \right)} \left( {\dfrac{{2Mr}}{{{R^2}}}} \right)dr$
Integrating the above equation and applying the limits we get,
$Y = \left( {\dfrac{4}{{\pi {R^2}}}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{{R^3}}}{3}} \right)$
$Y = \dfrac{{4R}}{{3\pi }}$
B) CM of a uniform semi-circular ring of radius R:
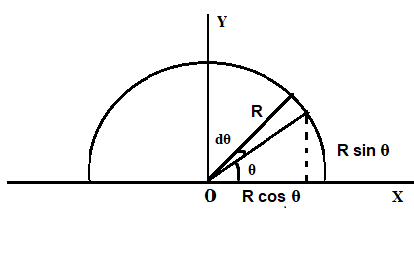
First we calculate the radius of a semi-circular ring with radius R and mass M
Total length of semi-circular ring $ = \dfrac{{2\pi R}}{2} = \pi R$
Mass per unit length of the semi-circular ring $ = \dfrac{M}{{\pi R}}$
The length of the small element is $ = Rd\theta $
Multiplying the mass per unit length and the length of the small element
The mass of the small element $dm = \left( {\dfrac{M}{{\pi R}}} \right)\left( {Rd\theta } \right) = \dfrac{M}{\pi }d\theta $
According to symmetry the x coordinate is zero
$X = \dfrac{1}{M}\int {xdm} $$ = \dfrac{1}{M}\int\limits_0^\pi {\left( {R\cos \theta } \right)} \dfrac{M}{\pi }d\theta = 0$
The y coordinate can be calculated using the above equation
$Y = \dfrac{1}{M}\int {ydm} $$ = \dfrac{1}{M}\int\limits_0^\pi {\left( {R\sin \theta } \right)} \left( {\dfrac{M}{\pi }} \right)d\theta = \dfrac{{2R}}{\pi }$……………………………(1)
To find the centre of mass of semi-circular ring with radius $\dfrac{{2R}}{3}$ can be obtained by substituting this value instead of R in (A)
$Y = \dfrac{2}{\pi } \times \dfrac{{2R}}{3} = \dfrac{{4R}}{{3\pi }}$
C) CM of a solid hemisphere:
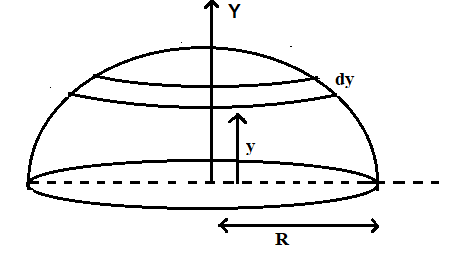
Consider a hemisphere of mass M and radius R
The radius of the disc, $r = \sqrt {{R^2} - {y^2}} $………………………………………(1)
Mass of the disc at a height y, $ = $$dM = \left( {\dfrac{{3M}}{{2\pi {R^3}}}} \right)\left( {\pi {r^2}dy} \right)$……………………………………..(2)
(r is the radius of the small disc at a height y)
Substitute equation $(1)$ in equation $(2)$
\[dM = \left( {\dfrac{{3M}}{{2\pi {R^3}}}} \right) \times \left( {\pi \left( {{R^2} - {y^2}} \right)dy} \right)\]
The Y coordinate can be obtained by the equation $Y = \dfrac{1}{M}\int {ydm} $
$Y = \dfrac{1}{M}\int {y\left( {\dfrac{{3M}}{{2{R^3}}}} \right) \times \left( {{R^2} - {y^2}} \right)dy} $
We have to integrate the above equation from 0 to R
\[Y = \dfrac{1}{M}\int\limits_0^R {\dfrac{{3M}}{{{R^3}}}\left( {{R^2} - {y^2}} \right) \times y} \]
$Y = \dfrac{3}{{2{R^3}}}\int\limits_0^R {\left( {{R^2}y - {y^3}} \right)dy} $
After integrating and applying the limits,
$Y = \left( {\dfrac{3}{{2{R^2}}}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{{R^4}}}{2}} \right) - \dfrac{{{R^4}}}{4} $
$Y = \dfrac{{3R}}{8} $
D) CM of a solid hemisphere shell of radius R:
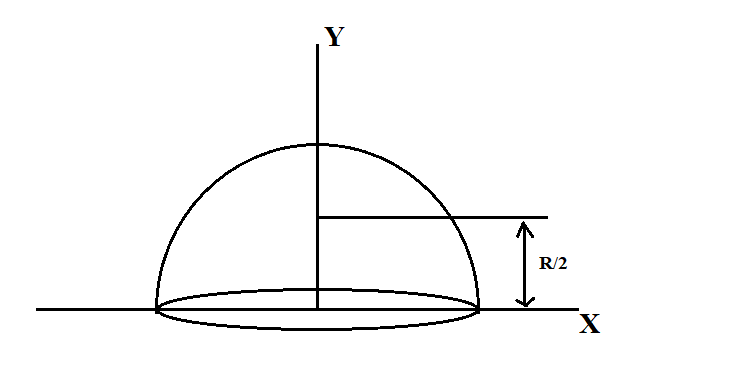
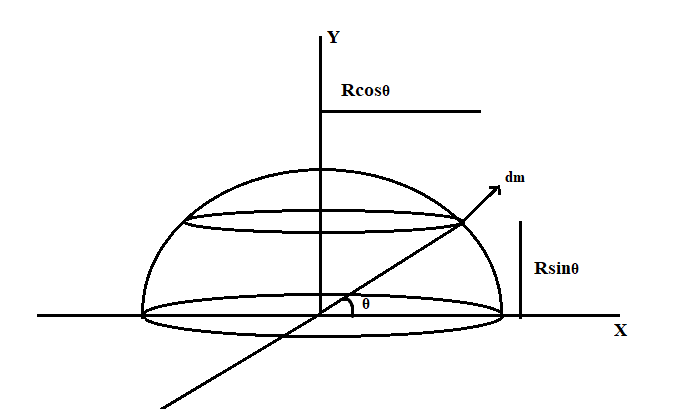
Consider a hemispherical shell of radius R and mass M.
Consider a small element as shown in the figure having radius $R\cos \theta $
The mass per unit length is given by $\dfrac{m}{{2\pi {R^2}}}$
The mass of the small element is,$dm = \left( {2\pi \cos \theta } \right)Rd\theta \times \dfrac{m}{{2\pi {R^2}}}$
$dm = m\cos \theta d\theta $
To find the coordinate of centre of mass, we use the equation ,$Y = \dfrac{1}{M}\int {ydm} $
Integrating from $0$to $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
$Y = \dfrac{1}{M}\int\limits_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}} {R\sin \theta \cos \theta md\theta } $ (use the identity $\left( {\sin \theta \cos \theta = \dfrac{{\sin 2\theta }}{2}} \right)$ in the equation)
$Y = \dfrac{R}{2}\int\limits_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}} {\sin 2\theta d\theta } $
$Y = \dfrac{R}{2}\left[ {\dfrac{{ - \cos 2\theta }}{2}} \right]_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}}$
Substituting the limits, we get
$Y = \dfrac{R}{2}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{2} + \dfrac{1}{2}} \right] $
$Y = \dfrac{R}{2} \times 1 = \dfrac{R}{2} $
Hence, the correct options are (B) and (D).
Note:Since in question we have semi-circular and hemispherical geometry we take the area and volume to be half of the value of circular and spherical geometry. Consider a small element and calculate its mass. Substitute in the equation for a coordinate to find the coordinate of the centre of mass. Due to symmetry, the x coordinate is usually zero for geometries with their centre at the origin.
Formula used:
The coordinates of the centre of mass are approximately given by
i) $X = \dfrac{1}{M}\int {xdm} $(X stands for the X-coordinate of the centre of mass, M stands for the mass of the particle, x stands for the x coordinate of the particle)
ii) $Y = \dfrac{1}{M}\int {ydm} $ (Y stands for the y coordinate of the centre of mass, y stands for the y coordinate of the particle)
iii) $Z = \dfrac{1}{M}\int {zdm} $(Z stands for the z coordinate of the centre of mass, z stands for the z coordinate of the particle)
Complete step by step solution:
A) CM of a uniform semi-circular disc of radius R:

Let us consider a semi-circular disc of mass M and radius R.
Area of the disc = $\dfrac{{\pi {R^2}}}{2}$
Mass per unit area of the disc, $m = \dfrac{M}{{\dfrac{{\pi {R^2}}}{2}}} = \dfrac{{2M}}{{\pi {R^2}}}$
Area of the small element, dr = $\dfrac{1}{2}(\pi r{(r + dr)^2} - \pi {r^2})$ (calculating the area of the small element)
$\Rightarrow dr = \dfrac{1}{2}(\pi ({r^2} + d{r^2} + 2rdr) - \pi {r^2}) $
$\Rightarrow dr= \dfrac{1}{2}(2\pi rdr),(\because d{r^2} < < 1)$ ($\pi {r^2}$ is cancelled and $\pi d{r^2}$ is neglected because $d{r^2} \ll 1$)
$\Rightarrow dr= \pi rdr$
Mass of the small element dm is obtained by multiplying the mass per unit area and the area of the small element
The mass of the small element, $dm = \left( {\pi rdr} \right) \times \left( {\dfrac{{2M}}{{\pi {R^2}}}} \right)$ (on the calculation, we get)
$ \Rightarrow dm= \dfrac{{2Mr}}{{{R^2}}}dr$
The coordinates of the small element dr $(x,y)$= $\left( {0,\dfrac{{2r}}{\pi }} \right)$ $(x = 0,y = \dfrac{{2r}}{\pi })$
Let us take X and Y to be the coordinates for centre of mass,
$X = 0$(Due to the symmetry of the disc)
$Y = \dfrac{1}{M}\int {ydm} $
$Y = \dfrac{1}{M}\int\limits_0^R {\left( {\dfrac{{2r}}{\pi }} \right)} \left( {\dfrac{{2Mr}}{{{R^2}}}} \right)dr$
Integrating the above equation and applying the limits we get,
$Y = \left( {\dfrac{4}{{\pi {R^2}}}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{{R^3}}}{3}} \right)$
$Y = \dfrac{{4R}}{{3\pi }}$
B) CM of a uniform semi-circular ring of radius R:

First we calculate the radius of a semi-circular ring with radius R and mass M
Total length of semi-circular ring $ = \dfrac{{2\pi R}}{2} = \pi R$
Mass per unit length of the semi-circular ring $ = \dfrac{M}{{\pi R}}$
The length of the small element is $ = Rd\theta $
Multiplying the mass per unit length and the length of the small element
The mass of the small element $dm = \left( {\dfrac{M}{{\pi R}}} \right)\left( {Rd\theta } \right) = \dfrac{M}{\pi }d\theta $
According to symmetry the x coordinate is zero
$X = \dfrac{1}{M}\int {xdm} $$ = \dfrac{1}{M}\int\limits_0^\pi {\left( {R\cos \theta } \right)} \dfrac{M}{\pi }d\theta = 0$
The y coordinate can be calculated using the above equation
$Y = \dfrac{1}{M}\int {ydm} $$ = \dfrac{1}{M}\int\limits_0^\pi {\left( {R\sin \theta } \right)} \left( {\dfrac{M}{\pi }} \right)d\theta = \dfrac{{2R}}{\pi }$……………………………(1)
To find the centre of mass of semi-circular ring with radius $\dfrac{{2R}}{3}$ can be obtained by substituting this value instead of R in (A)
$Y = \dfrac{2}{\pi } \times \dfrac{{2R}}{3} = \dfrac{{4R}}{{3\pi }}$
C) CM of a solid hemisphere:

Consider a hemisphere of mass M and radius R
The radius of the disc, $r = \sqrt {{R^2} - {y^2}} $………………………………………(1)
Mass of the disc at a height y, $ = $$dM = \left( {\dfrac{{3M}}{{2\pi {R^3}}}} \right)\left( {\pi {r^2}dy} \right)$……………………………………..(2)
(r is the radius of the small disc at a height y)
Substitute equation $(1)$ in equation $(2)$
\[dM = \left( {\dfrac{{3M}}{{2\pi {R^3}}}} \right) \times \left( {\pi \left( {{R^2} - {y^2}} \right)dy} \right)\]
The Y coordinate can be obtained by the equation $Y = \dfrac{1}{M}\int {ydm} $
$Y = \dfrac{1}{M}\int {y\left( {\dfrac{{3M}}{{2{R^3}}}} \right) \times \left( {{R^2} - {y^2}} \right)dy} $
We have to integrate the above equation from 0 to R
\[Y = \dfrac{1}{M}\int\limits_0^R {\dfrac{{3M}}{{{R^3}}}\left( {{R^2} - {y^2}} \right) \times y} \]
$Y = \dfrac{3}{{2{R^3}}}\int\limits_0^R {\left( {{R^2}y - {y^3}} \right)dy} $
After integrating and applying the limits,
$Y = \left( {\dfrac{3}{{2{R^2}}}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{{R^4}}}{2}} \right) - \dfrac{{{R^4}}}{4} $
$Y = \dfrac{{3R}}{8} $
D) CM of a solid hemisphere shell of radius R:


Consider a hemispherical shell of radius R and mass M.
Consider a small element as shown in the figure having radius $R\cos \theta $
The mass per unit length is given by $\dfrac{m}{{2\pi {R^2}}}$
The mass of the small element is,$dm = \left( {2\pi \cos \theta } \right)Rd\theta \times \dfrac{m}{{2\pi {R^2}}}$
$dm = m\cos \theta d\theta $
To find the coordinate of centre of mass, we use the equation ,$Y = \dfrac{1}{M}\int {ydm} $
Integrating from $0$to $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$
$Y = \dfrac{1}{M}\int\limits_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}} {R\sin \theta \cos \theta md\theta } $ (use the identity $\left( {\sin \theta \cos \theta = \dfrac{{\sin 2\theta }}{2}} \right)$ in the equation)
$Y = \dfrac{R}{2}\int\limits_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}} {\sin 2\theta d\theta } $
$Y = \dfrac{R}{2}\left[ {\dfrac{{ - \cos 2\theta }}{2}} \right]_0^{\dfrac{\pi }{2}}$
Substituting the limits, we get
$Y = \dfrac{R}{2}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{2} + \dfrac{1}{2}} \right] $
$Y = \dfrac{R}{2} \times 1 = \dfrac{R}{2} $
Hence, the correct options are (B) and (D).
Note:Since in question we have semi-circular and hemispherical geometry we take the area and volume to be half of the value of circular and spherical geometry. Consider a small element and calculate its mass. Substitute in the equation for a coordinate to find the coordinate of the centre of mass. Due to symmetry, the x coordinate is usually zero for geometries with their centre at the origin.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




