
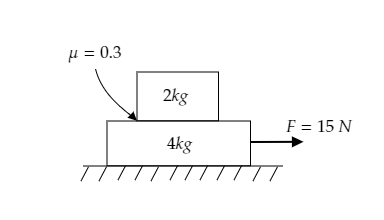
Find the frictional force between the two blocks in the given figure.
A) ${\text{6N}}$
B) ${\text{17}} \cdot {\text{6N}}$
C) ${\text{5N}}$
D) $12{\text{N}}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: When the force is applied on the lower block of mass, the upper block will slide only when it receives a force greater than the maximum frictional force acting on it. If the two blocks were to slide then they would have a common acceleration and this would be equal to the acceleration of the lower block in the presence of friction.
Formula Used:
The maximum frictional force acting on a block of mass is given by, ${f_{\max }} = \mu N$ where $\mu $ is the coefficient of friction and $N$ is the normal force acting on the block.
The common acceleration of a system of two blocks is given by, ${a_{common}} = \dfrac{F}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}}$ where $F$ is the applied force and ${m_1}$, ${m_2}$ are the masses of the two blocks.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1: List the parameters obtained from the figure.
The arrangement of two blocks, one on top of the other, on a horizontal surface is given below.
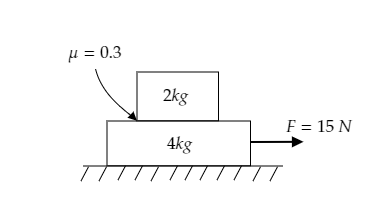
The force applied to the lower block is given to be $F = 15{\text{N}}$ .
The mass of the lower block is ${m_L} = 4{\text{kg}}$ and that of the upper block is given to be ${m_U} = 2{\text{kg}}$ .
The coefficient of friction is $\mu = 0 \cdot 3$ .
Step 2: Express the relation for the common acceleration of the system.
The common acceleration of the given system of two blocks is given by,
${a_{common}} = \dfrac{F}{{{m_U} + {m_L}}}$ -------- (1)
Substituting for $F = 15{\text{N}}$, ${m_L} = 4{\text{kg}}$ and ${m_U} = 2{\text{kg}}$ in equation (1) we get, ${a_{common}} = \dfrac{{15}}{{2 + 4}} = 2 \cdot 5{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}$
Thus the common acceleration of the system is ${a_{common}} = 2 \cdot 5{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}$.
Step 3: Sketch a figure depicting the forces acting on the upper block and find the maximum friction of the block.
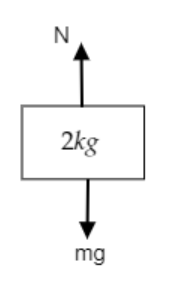
In the above figure, the force of gravity $W = mg$ acts downwards and an equal normal force $N$ acts upwards.
The normal force acting on the upper block will be $N = mg = 2 \times 10 = 20{\text{N}}$ .
Now, the maximum frictional force acting on the upper block is given by, ${f_{\max }} = \mu N$ ------ (2)
Substituting for $\mu = 0 \cdot 3$ and $N = 20{\text{N}}$ in equation (2) we get, ${f_{\max }} = 0 \cdot 3 \times 20 = 6{\text{N}}$
i.e., the upper block will slide only when it receives a force greater than ${f_{\max }} = 6{\text{N}}$ .
When the upper block receives this force its acceleration will be ${a_{\max }} = \dfrac{{{f_{\max }}}}{{{m_U}}} = \dfrac{6}{2} = 3{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}$ .
Step 4: Using the obtained value for the maximum friction find the acceleration of the lower block.
As the lower block receives a force $F = 15{\text{N}}$ to slide, the force of friction $f$ will try to oppose the sliding.
Hence the total force acting on the lower block in the horizontal direction will be $F - f$ .
The acceleration of the lower block is given by, ${a_L} = \dfrac{{F - f}}{{{m_L}}}$
$ \Rightarrow f = F - \left( {{a_L} \times {m_L}} \right)$ ------- (3)
The lower block moves with the common acceleration of the system i.e., ${a_L} = {a_{common}} = 2 \cdot 5{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$
Substituting values for $F = 15{\text{N}}$, ${a_L} = 2 \cdot 5{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}$ and ${m_L} = 4{\text{kg}}$ in equation (3) we get, $f = 15 - \left( {2 \cdot 5 \times 4} \right) = 5{\text{N}}$
Thus the frictional force between the blocks will be $f = 5{\text{N}}$ .
So the correct option is C.
Note: If the frictional force between the two blocks $f = {f_{\max }} = 6{\text{N}}$ then the acceleration of the lower block would be ${a_L} = \dfrac{{15 - 6}}{4} = 2 \cdot 25{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}$ .
But we know that the acceleration of the lower block will be ${a_{common}} = 2 \cdot 5{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}$ .
So the frictional force between the blocks, $f \ne {f_{\max }}$ .
Formula Used:
The maximum frictional force acting on a block of mass is given by, ${f_{\max }} = \mu N$ where $\mu $ is the coefficient of friction and $N$ is the normal force acting on the block.
The common acceleration of a system of two blocks is given by, ${a_{common}} = \dfrac{F}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}}$ where $F$ is the applied force and ${m_1}$, ${m_2}$ are the masses of the two blocks.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1: List the parameters obtained from the figure.
The arrangement of two blocks, one on top of the other, on a horizontal surface is given below.

The force applied to the lower block is given to be $F = 15{\text{N}}$ .
The mass of the lower block is ${m_L} = 4{\text{kg}}$ and that of the upper block is given to be ${m_U} = 2{\text{kg}}$ .
The coefficient of friction is $\mu = 0 \cdot 3$ .
Step 2: Express the relation for the common acceleration of the system.
The common acceleration of the given system of two blocks is given by,
${a_{common}} = \dfrac{F}{{{m_U} + {m_L}}}$ -------- (1)
Substituting for $F = 15{\text{N}}$, ${m_L} = 4{\text{kg}}$ and ${m_U} = 2{\text{kg}}$ in equation (1) we get, ${a_{common}} = \dfrac{{15}}{{2 + 4}} = 2 \cdot 5{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}$
Thus the common acceleration of the system is ${a_{common}} = 2 \cdot 5{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}$.
Step 3: Sketch a figure depicting the forces acting on the upper block and find the maximum friction of the block.

In the above figure, the force of gravity $W = mg$ acts downwards and an equal normal force $N$ acts upwards.
The normal force acting on the upper block will be $N = mg = 2 \times 10 = 20{\text{N}}$ .
Now, the maximum frictional force acting on the upper block is given by, ${f_{\max }} = \mu N$ ------ (2)
Substituting for $\mu = 0 \cdot 3$ and $N = 20{\text{N}}$ in equation (2) we get, ${f_{\max }} = 0 \cdot 3 \times 20 = 6{\text{N}}$
i.e., the upper block will slide only when it receives a force greater than ${f_{\max }} = 6{\text{N}}$ .
When the upper block receives this force its acceleration will be ${a_{\max }} = \dfrac{{{f_{\max }}}}{{{m_U}}} = \dfrac{6}{2} = 3{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}$ .
Step 4: Using the obtained value for the maximum friction find the acceleration of the lower block.
As the lower block receives a force $F = 15{\text{N}}$ to slide, the force of friction $f$ will try to oppose the sliding.
Hence the total force acting on the lower block in the horizontal direction will be $F - f$ .
The acceleration of the lower block is given by, ${a_L} = \dfrac{{F - f}}{{{m_L}}}$
$ \Rightarrow f = F - \left( {{a_L} \times {m_L}} \right)$ ------- (3)
The lower block moves with the common acceleration of the system i.e., ${a_L} = {a_{common}} = 2 \cdot 5{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}$
Substituting values for $F = 15{\text{N}}$, ${a_L} = 2 \cdot 5{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}$ and ${m_L} = 4{\text{kg}}$ in equation (3) we get, $f = 15 - \left( {2 \cdot 5 \times 4} \right) = 5{\text{N}}$
Thus the frictional force between the blocks will be $f = 5{\text{N}}$ .
So the correct option is C.
Note: If the frictional force between the two blocks $f = {f_{\max }} = 6{\text{N}}$ then the acceleration of the lower block would be ${a_L} = \dfrac{{15 - 6}}{4} = 2 \cdot 25{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}$ .
But we know that the acceleration of the lower block will be ${a_{common}} = 2 \cdot 5{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}$ .
So the frictional force between the blocks, $f \ne {f_{\max }}$ .
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




