
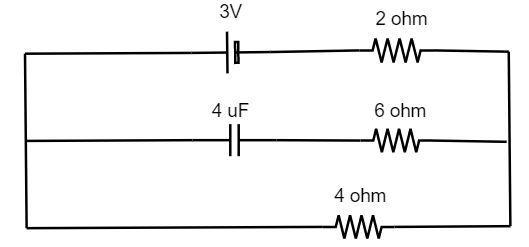
Find the potential drop across $4\,\mu F$ capacitor and $6\,\Omega $ resistor in figure.
(A) $0,\,0$
(B) $0,\,3V$
(C) $0,\,2V$
(D) $2V,\,0$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint Find the total current of the given circuit from the rearranged ohm’s law. Again substitute the value of the resistance and the calculated current in it to find the potential drop across the two branches with the capacitor and the $6\,\Omega $ resistor.
Useful formula:
The ohm’s law is given by
$V = IR$
Where $V$ is the potential difference, $I$ is the current and $R$ is the resistance developed in the circuit.
Complete step by step answer
From the given circuit diagram, it is understood that it possesses three branches with the capacitor at the middle branch. Let us use the formula of the ohm’s law,
$V = IR$
Let us find the total current through the circuit, by rearranging the above formula, we get
$I = \dfrac{V}{R}$
Let us consider that the capacitor is fully charged. Since it is fully charged, it will not draw any current from the total current. Hence the current through the branch of the capacitor is zero. Let us substitute this in the above formula, we get
$I = \dfrac{3}{{2 + 4}}$
By performing basic arithmetic operations, we get
$I = \dfrac{1}{2}\,A$
The potential drop across the $6\,\Omega $ resistor is found using the ohm’s law.
$V = IR = 0 \times 6$
$V = 0$
Hence the potential drop across the capacitor circuit is zero.
The potential drop across the $4\,\Omega $ resistor is calculated using the ohm’s law.
$V = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 4$
By simplification of the above step, we get
$V = 2\,V$
Hence the potential drop across the $4\,\Omega $ resistor is calculated as $2$ volt. Since the voltage drop across the parallel circuit is the same, the potential drop in the branch of $4\,\Omega $ resistor must be equal to that of the potential drop across the $4\,\mu F$ capacitor.
Thus the option (D) is correct.
Note: Remember that in the parallel circuit, the total current through the circuit will be equal to the sum of the current through the resistors. The voltage drop across each branch will be equal to the voltage drop across other branches and also the total voltage drop.
Useful formula:
The ohm’s law is given by
$V = IR$
Where $V$ is the potential difference, $I$ is the current and $R$ is the resistance developed in the circuit.
Complete step by step answer
From the given circuit diagram, it is understood that it possesses three branches with the capacitor at the middle branch. Let us use the formula of the ohm’s law,
$V = IR$
Let us find the total current through the circuit, by rearranging the above formula, we get
$I = \dfrac{V}{R}$
Let us consider that the capacitor is fully charged. Since it is fully charged, it will not draw any current from the total current. Hence the current through the branch of the capacitor is zero. Let us substitute this in the above formula, we get
$I = \dfrac{3}{{2 + 4}}$
By performing basic arithmetic operations, we get
$I = \dfrac{1}{2}\,A$
The potential drop across the $6\,\Omega $ resistor is found using the ohm’s law.
$V = IR = 0 \times 6$
$V = 0$
Hence the potential drop across the capacitor circuit is zero.
The potential drop across the $4\,\Omega $ resistor is calculated using the ohm’s law.
$V = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 4$
By simplification of the above step, we get
$V = 2\,V$
Hence the potential drop across the $4\,\Omega $ resistor is calculated as $2$ volt. Since the voltage drop across the parallel circuit is the same, the potential drop in the branch of $4\,\Omega $ resistor must be equal to that of the potential drop across the $4\,\mu F$ capacitor.
Thus the option (D) is correct.
Note: Remember that in the parallel circuit, the total current through the circuit will be equal to the sum of the current through the resistors. The voltage drop across each branch will be equal to the voltage drop across other branches and also the total voltage drop.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Why does capacitor block DC and allow AC class 12 physics JEE_Main

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

CBSE Class 12 Physics Set 2 (55/2/2) 2025 Question Paper & Solutions

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Units and Measurements Mock Test for JEE Main 2025-26 Preparation

Chemistry Question Papers for JEE Main, NEET & Boards (PDFs)




