
If $\alpha $,$\beta $,$\gamma $ are the distance of the vertices of a triangle of $ABC$ from the corresponding point of contact with the incircle, then
$(A)$. $s = \alpha + \beta + \gamma $
$(B)$. ${\gamma ^2} = \dfrac{{\alpha \beta \gamma }}{{\alpha + \beta + \gamma }}$
$(C)$. ${\Delta ^2} = \left( {\alpha + \beta + \gamma } \right)\alpha \beta \gamma $
$(D)$. $2s = \alpha + \beta + \gamma $
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Use theorem tangent to the circle to find sides of the triangle and Heron’s formula to compute the area of the triangle.
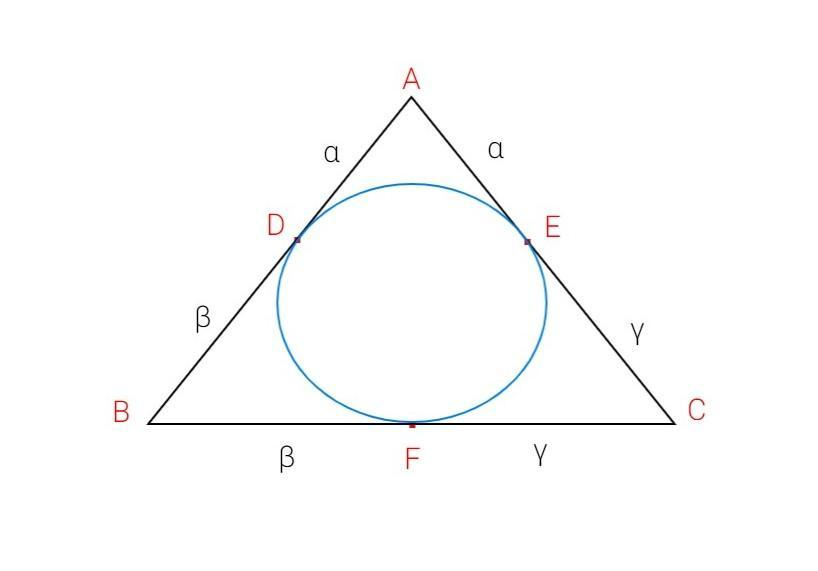
Let ABC be the triangle with incircle inside as given in the problem.
Let the incircle touch the sides of the triangle ABC at points D,E and F respectively .
It is given that $\alpha $,$\beta $,$\gamma $ are the distance of the vertices of a triangle of $ABC$ from the corresponding point of contact with the incircle.
Therefore, we assume,
$
AD = \alpha \\
BD = \beta \\
CE = \gamma \\
$
Theorem tangent to the circle states that a point external to the circle subtends equal tangents to the circle.
Using this theorem in triangle $ABC$,we get
$
AE = \alpha \\
BF = \beta \\
CF = \gamma \\
$
We need to find the area of the triangle $ABC$ using Heron’s formula.
Heron’s formula states that area of the triangle is given by,
\[\Delta = \sqrt {s\left( {s - a} \right)\left( {s - b} \right)\left( {s - c} \right)} {\text{ (1)}}\]
In the above equation, $s$ is the semi-perimeter of the triangle and $a,b,c$ are the sides of the triangle.
Sides of the triangle $ABC$ are given by
$\left(
a = AB = \alpha + \beta \\
b = BC = \beta + \gamma \\
c = AC = \alpha + \gamma \\
\right){\text{ (2)}}$
Semi-perimeter of triangle $ABC$ is given by,
$
s = \dfrac{{a + b + c}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow s = \dfrac{{\alpha + \beta + \beta + \gamma + \alpha + \gamma }}{2} = \alpha + \beta + \gamma {\text{ (3)}} \\
$
Using equation $(2)$and $(3)$ in $(1)$,we get
\[
\Delta = \sqrt {\left( {\alpha + \beta + \gamma } \right)\left( {\alpha + \beta + \gamma - \alpha - \beta } \right)\left( {\alpha + \beta + \gamma - \beta - \gamma } \right)\left( {\alpha + \beta + \gamma - \alpha - \gamma } \right)} \\
\Rightarrow \Delta = \sqrt {\left( {\alpha + \beta + \gamma } \right)\alpha \beta \gamma } {\text{ }} \\
\]
Squaring both sides of the above equation, we get
\[{\Delta ^2} = \left( {\alpha + \beta + \gamma } \right)\alpha \beta \gamma {\text{ }}\]
Hence option $(C)$. ${\Delta ^2} = \left( {\alpha + \beta + \gamma } \right)\alpha \beta \gamma $ is the correct answer.
Note: Always try to draw the diagram in problems related to incircle. Try to remember the properties of incircle. Geometrical theorems should also be kept in mind while solving similar problems.

Let ABC be the triangle with incircle inside as given in the problem.
Let the incircle touch the sides of the triangle ABC at points D,E and F respectively .
It is given that $\alpha $,$\beta $,$\gamma $ are the distance of the vertices of a triangle of $ABC$ from the corresponding point of contact with the incircle.
Therefore, we assume,
$
AD = \alpha \\
BD = \beta \\
CE = \gamma \\
$
Theorem tangent to the circle states that a point external to the circle subtends equal tangents to the circle.
Using this theorem in triangle $ABC$,we get
$
AE = \alpha \\
BF = \beta \\
CF = \gamma \\
$
We need to find the area of the triangle $ABC$ using Heron’s formula.
Heron’s formula states that area of the triangle is given by,
\[\Delta = \sqrt {s\left( {s - a} \right)\left( {s - b} \right)\left( {s - c} \right)} {\text{ (1)}}\]
In the above equation, $s$ is the semi-perimeter of the triangle and $a,b,c$ are the sides of the triangle.
Sides of the triangle $ABC$ are given by
$\left(
a = AB = \alpha + \beta \\
b = BC = \beta + \gamma \\
c = AC = \alpha + \gamma \\
\right){\text{ (2)}}$
Semi-perimeter of triangle $ABC$ is given by,
$
s = \dfrac{{a + b + c}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow s = \dfrac{{\alpha + \beta + \beta + \gamma + \alpha + \gamma }}{2} = \alpha + \beta + \gamma {\text{ (3)}} \\
$
Using equation $(2)$and $(3)$ in $(1)$,we get
\[
\Delta = \sqrt {\left( {\alpha + \beta + \gamma } \right)\left( {\alpha + \beta + \gamma - \alpha - \beta } \right)\left( {\alpha + \beta + \gamma - \beta - \gamma } \right)\left( {\alpha + \beta + \gamma - \alpha - \gamma } \right)} \\
\Rightarrow \Delta = \sqrt {\left( {\alpha + \beta + \gamma } \right)\alpha \beta \gamma } {\text{ }} \\
\]
Squaring both sides of the above equation, we get
\[{\Delta ^2} = \left( {\alpha + \beta + \gamma } \right)\alpha \beta \gamma {\text{ }}\]
Hence option $(C)$. ${\Delta ^2} = \left( {\alpha + \beta + \gamma } \right)\alpha \beta \gamma $ is the correct answer.
Note: Always try to draw the diagram in problems related to incircle. Try to remember the properties of incircle. Geometrical theorems should also be kept in mind while solving similar problems.
Recently Updated Pages
Mutually Exclusive vs Independent Events: Key Differences Explained

Area vs Volume: Key Differences Explained for Students

Area of an Octagon Formula Explained Simply

Absolute Pressure Formula Explained: Key Equation & Examples

Central Angle of a Circle Formula Explained Quickly

Difference Between Vapor and Gas: JEE Main 2026

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Jan 21 Shift 1 Question Papers with Solutions & Answer Keys – Detailed Day 1 Analysis

JEE Main Response Sheet 2026 Released – Key Dates and Official Updates by NTA

JEE Main 2026 Answer Key OUT – Download Session 1 PDF, Response Sheet & Challenge Link

JEE Main Marks vs Percentile 2026: Calculate Percentile and Rank Using Marks

JEE Main 2026 Jan 22 Shift 1 Today Paper Live Analysis With Detailed Solutions

Other Pages
NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 9 Circles (2025-26)

Fuel Cost Calculator – Estimate Your Journey Expenses Easily

NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 11 Surface Areas and Volumes (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 11 Surface Areas And Volumes Exercise 11.3 (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 12 Statistics (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Heron's Formula (2025-26)




