
In the figure below is shown the flow of liquid through a horizontal pipe. Three tubes $A$, $B$ and $C$ are connected to the pipe. The radii of the tubes $A$, $B$ and $C$ at the junction are respectively $2\,cm$, $1\,cm$ and $2\,cm$. It can be said that the:
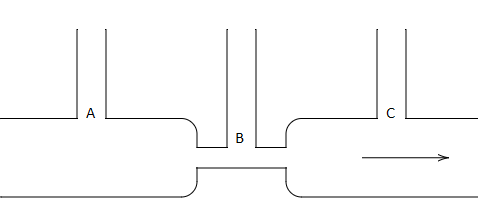
(A) The height of the liquid in the tube $A$ is maximum
(B) The height of the liquid in the tube $A$ and $B$ is the same
(C) The height of the liquid in all the three tubes is the same
(D) The height of the liquid in the tube $A$ and $C$ is the same.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: By using the theory of the Bernoulli’s theorem and the venturi meter concepts, the height of the liquid in the pipe $A$, pipe $B$ and pipe $C$ are determined. In venturi meters the height is determined by the relation of the pressure in the pipe and density of the liquids.
Complete step by step solution:
Given that,
The radius of the pipe $A$, ${r_A} = 2\,cm$
The radius of the pipe $B$, ${r_B} = 1\,cm$
The radius of the pipe $C$, ${r_C} = 2\,cm$
Bernoulli’s theorem:
Bernoulli’s theorem states that the total mechanical energy of the fluid flowing having the energy associated with fluid pressure, the gravitational potential energy of elevation, and the kinetic energy of fluid motion will remain constant.
Assuming that the pressure of the liquid is flowing near the junction of the pipe $A$ and the liquid is flowing near the junction of the pipe $C$ are the same pressure. Because the diameter of the horizontal pipe is the same in both the junctions.
The pressure is different near the junction of the pipe $B$, because the diameter of the horizontal pipe near the junction of pipe $B$ is different from the diameter of the horizontal pipe near the junction of the pipe $A$ and pipe $C$. The height of the liquid in the venturi meter depends on the pressure of the fluid flowing in the horizontal pipe.
So, the pressure of the pipe $A$ and the pressure of the pipe $C$ is the same, then the height of the liquid in the tube $A$ and the height of the liquid in the tube $C$ is the same.
Hence, the option (D) is the correct answer.
Note: Near the junction of the pipe $B$, the pressure is greater than the pressure of the liquid near the junction of the pipe $A$ and the junction of the pipe $C$. Due to the high pressure and the small diameter of the pipe $B$, the height of the liquid in the pipe $B$ is little small when compared to the height of the liquid in the pipe $A$ and pipe $C$.
Complete step by step solution:
Given that,
The radius of the pipe $A$, ${r_A} = 2\,cm$
The radius of the pipe $B$, ${r_B} = 1\,cm$
The radius of the pipe $C$, ${r_C} = 2\,cm$
Bernoulli’s theorem:
Bernoulli’s theorem states that the total mechanical energy of the fluid flowing having the energy associated with fluid pressure, the gravitational potential energy of elevation, and the kinetic energy of fluid motion will remain constant.
Assuming that the pressure of the liquid is flowing near the junction of the pipe $A$ and the liquid is flowing near the junction of the pipe $C$ are the same pressure. Because the diameter of the horizontal pipe is the same in both the junctions.
The pressure is different near the junction of the pipe $B$, because the diameter of the horizontal pipe near the junction of pipe $B$ is different from the diameter of the horizontal pipe near the junction of the pipe $A$ and pipe $C$. The height of the liquid in the venturi meter depends on the pressure of the fluid flowing in the horizontal pipe.
So, the pressure of the pipe $A$ and the pressure of the pipe $C$ is the same, then the height of the liquid in the tube $A$ and the height of the liquid in the tube $C$ is the same.
Hence, the option (D) is the correct answer.
Note: Near the junction of the pipe $B$, the pressure is greater than the pressure of the liquid near the junction of the pipe $A$ and the junction of the pipe $C$. Due to the high pressure and the small diameter of the pipe $B$, the height of the liquid in the pipe $B$ is little small when compared to the height of the liquid in the pipe $A$ and pipe $C$.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




