
Lactose is made up of:
A. Galactose and glucose unit
B. Glucose unit and fructose
C. Both glucose units
D. Glucose and arabinose unit
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Lactose is basically a reducing sugar, it is known as milk sugar, because it is found to occur in the milk of cows and also in other mammals. Lactose is found to be lowest in sweetness among all others found in nature.
Step by step solution:
-Structure of lactose is found as:
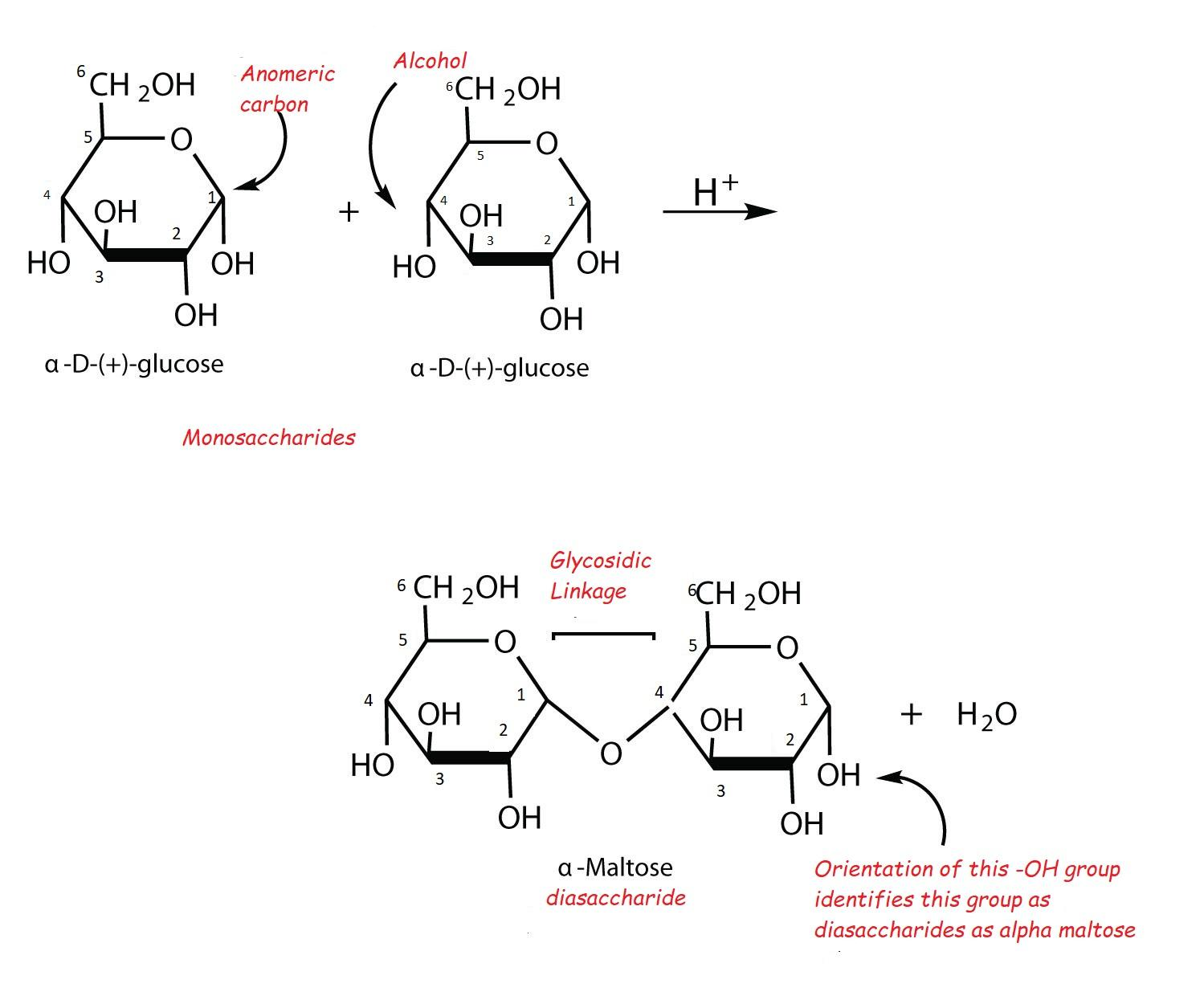
-When lactose undergoes acid hydrolysis then two monosaccharides are formed, one molecule of D-glucose and one molecule of D-galactose.
- They are found to be joined by a $\beta -1,4-\text{ }gly\cos idic$ bond , the bond from the anomeric carbon of the first monosaccharide unit is in upward direction.
- This process also involves the catalytic action of enzyme lactase.
- Hence, we can conclude that the option (a)is correct that lactose is made up of galactose and glucose units.
Additional information:
- We can see that there is lactose intolerance found in most adults. Lactose intolerance means when a body is not able to digest the lactose which is found in milk and various dairy products.
- There are various symptoms of lactose intolerance depending on the amount of lactose that our body can make. Some of them are like: gas, pain or cramps and mostly diarrhoea.
- It is found that the reason for lactose intolerance is when the small intestine can’t produce sufficient enzymes that are called lactose. Our body basically needs lactose to digest lactose.
- Those people who are lactose intolerant should eat calcium rich food that can make their bones healthy.
Note:
- Galactose and glucose both have the same chemical formula that is ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}$. Also, both of them have the same structure but the difference is only in the position of one hydroxyl group.
Step by step solution:
-Structure of lactose is found as:

-When lactose undergoes acid hydrolysis then two monosaccharides are formed, one molecule of D-glucose and one molecule of D-galactose.
- They are found to be joined by a $\beta -1,4-\text{ }gly\cos idic$ bond , the bond from the anomeric carbon of the first monosaccharide unit is in upward direction.
- This process also involves the catalytic action of enzyme lactase.
- Hence, we can conclude that the option (a)is correct that lactose is made up of galactose and glucose units.
Additional information:
- We can see that there is lactose intolerance found in most adults. Lactose intolerance means when a body is not able to digest the lactose which is found in milk and various dairy products.
- There are various symptoms of lactose intolerance depending on the amount of lactose that our body can make. Some of them are like: gas, pain or cramps and mostly diarrhoea.
- It is found that the reason for lactose intolerance is when the small intestine can’t produce sufficient enzymes that are called lactose. Our body basically needs lactose to digest lactose.
- Those people who are lactose intolerant should eat calcium rich food that can make their bones healthy.
Note:
- Galactose and glucose both have the same chemical formula that is ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}$. Also, both of them have the same structure but the difference is only in the position of one hydroxyl group.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




