
When the switch \[S\] , in the circuit shows, is closed, then the value of current \[i\] will be:
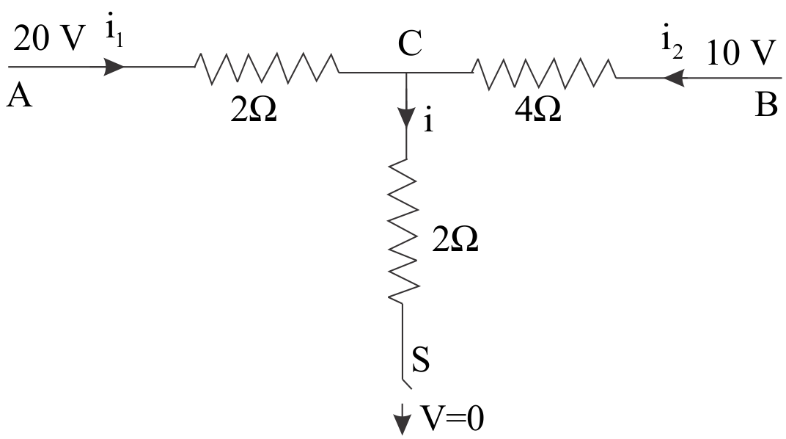
(A) \[3A\]
(B) \[5A\]
(C) \[4A\]
(D) \[2A\]
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Let the potential across terminal C be \[xV\] and apply the Kirchoff’s Current Law at point C i.e. the current incoming is equal to the current outgoing . And first find the value of \[x\] and this will ultimately help us in finding the value of \[i\] .
Complete step by step solution:
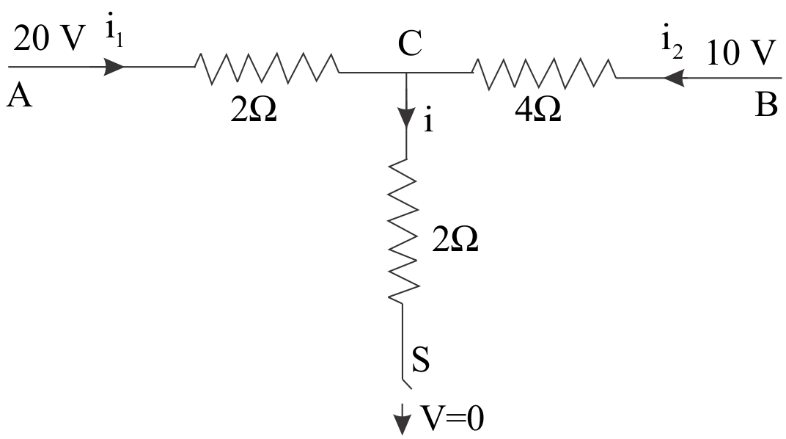
One end of the terminal C is grounded as we can clearly see and it has a potential of zero volts. As soon as the switch is closed the current will start running in that arm and we are required to find that value .
Let the potential at point C be \[xV\] .
At point C , we will apply Kirchoff’s First Law or we can say Kirchoff’s Current law which states that: the sum of currents entering the junction is equal to the sum of currents leaving the junction . It is based on the principle of conservation of charge.
This means that: \[i = {i_1} + {i_2}\] ……..(i)
We know from Ohm’s Law that -
\[
current = \dfrac{{voltage}}{
resistor \\
\\
} \\
i = \dfrac{V}{R} \\
\]
Writing the respective values of \[i,{i_1},{i_2}\] in eq(i) in terms of voltage and resistance across them .
\[
i = {i_1} + {i_2} \\
\dfrac{{x - 0}}{2} = \dfrac{{20 - x}}{2} + \dfrac{{10 - x}}{4} \\
2x = (40 - 2x) + (10 - x) \\
2x + 2x + x = 50 \\
5x = 50 \\
x = 10V \\
\]
Now we know that-
\[
i = \dfrac{{x - 0}}{2} \\
i = \dfrac{{10}}{2} \\
i = 5A \\
\]
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: We have to keep in mind that we have taken $x$ as the potential across C and not potential drop ( which is the difference in potential between two points) while in the ohm’s law we always take potential difference across any two terminals . So that is why while writing the values of current we have written potential differences.
Complete step by step solution:

One end of the terminal C is grounded as we can clearly see and it has a potential of zero volts. As soon as the switch is closed the current will start running in that arm and we are required to find that value .
Let the potential at point C be \[xV\] .
At point C , we will apply Kirchoff’s First Law or we can say Kirchoff’s Current law which states that: the sum of currents entering the junction is equal to the sum of currents leaving the junction . It is based on the principle of conservation of charge.
This means that: \[i = {i_1} + {i_2}\] ……..(i)
We know from Ohm’s Law that -
\[
current = \dfrac{{voltage}}{
resistor \\
\\
} \\
i = \dfrac{V}{R} \\
\]
Writing the respective values of \[i,{i_1},{i_2}\] in eq(i) in terms of voltage and resistance across them .
\[
i = {i_1} + {i_2} \\
\dfrac{{x - 0}}{2} = \dfrac{{20 - x}}{2} + \dfrac{{10 - x}}{4} \\
2x = (40 - 2x) + (10 - x) \\
2x + 2x + x = 50 \\
5x = 50 \\
x = 10V \\
\]
Now we know that-
\[
i = \dfrac{{x - 0}}{2} \\
i = \dfrac{{10}}{2} \\
i = 5A \\
\]
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: We have to keep in mind that we have taken $x$ as the potential across C and not potential drop ( which is the difference in potential between two points) while in the ohm’s law we always take potential difference across any two terminals . So that is why while writing the values of current we have written potential differences.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




