
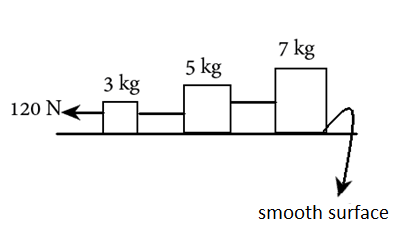
\[{T_1}\] and \[{T_2}\] in the given figure are
(A) 28 N, 48 N
(B) 48 N, 28 N
(C) 96 N, 56 N
(D) 56 N, 96 N
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: We need to identify the force acting on each block. Perform a Newton’s second law analysis on each of the blocks separately. The acceleration of each object is equal to the acceleration of the system.
Formula used: In this solution we will be using the following formulae;
\[{F_{NET}} = ma\] where \[{F_{NET}}\] is the net force acting on a body, \[m\] is the mass of the body, and \[a\] is the acceleration of the body.
Complete Step-by-Step Answer:
A particular amount of force is acting upon a chain of objects, the tensions in the cords are asked to be determined. To do this, we must analyse the forces on each block independently and link them with the acceleration. The acceleration of the system is the acceleration of the blocks, hence, they are equal.
Newton’s second law can be written as
\[{F_{NET}} = ma\] where \[{F_{NET}}\] is the net force acting on a body, \[m\] is the mass of the body, and \[a\] is the acceleration of the body.
Applying on the 3kg body, we have
\[120 - {T_1} = ma\]
\[ \Rightarrow 120 - {T_1} = 3a\]
Similarly, on the 5kg block
\[{T_1} - {T_2} = 5a\]
And on the 7kg block
\[{T_2} = 7a\]
We shall solve this three equations simultaneously, hence,
Insert \[{T_2} = 7a\] into \[{T_1} - {T_2} = 5a\], then,
\[{T_1} - 7a = 5a\]
\[ \Rightarrow {T_1} = 12a\]
Inserting this into \[120 - {T_1} = 3a\], we have
\[120 - 12a = 3a\]
\[ \Rightarrow 120 = 15a\]
Dividing both sides by 10, we get
\[a = 8m{s^{ - 2}}\]
Then, \[{T_1}\] can be calculated from
\[120 - {T_1} = 3 \times 8\]
\[ \Rightarrow {T_1} = 120 - 24 = 96N\]
Then the tension in the second cord \[{T_2}\] can be calculated from
\[{T_2} = 7a\] as
\[{T_2} = 7 \times 8 = 56N\]
Hence, the correct option is C
Note: Alternatively, one could take the entire system as one block which will be the sum of all three blocks and calculate the acceleration as thus
\[a = \dfrac{{120}}{M} = \dfrac{{120}}{{3 + 5 + 7}} = \dfrac{{120}}{{15}}\]
Hence, by computation,
\[a = 8m{s^{ - 2}}\]
Formula used: In this solution we will be using the following formulae;
\[{F_{NET}} = ma\] where \[{F_{NET}}\] is the net force acting on a body, \[m\] is the mass of the body, and \[a\] is the acceleration of the body.
Complete Step-by-Step Answer:
A particular amount of force is acting upon a chain of objects, the tensions in the cords are asked to be determined. To do this, we must analyse the forces on each block independently and link them with the acceleration. The acceleration of the system is the acceleration of the blocks, hence, they are equal.
Newton’s second law can be written as
\[{F_{NET}} = ma\] where \[{F_{NET}}\] is the net force acting on a body, \[m\] is the mass of the body, and \[a\] is the acceleration of the body.
Applying on the 3kg body, we have
\[120 - {T_1} = ma\]
\[ \Rightarrow 120 - {T_1} = 3a\]
Similarly, on the 5kg block
\[{T_1} - {T_2} = 5a\]
And on the 7kg block
\[{T_2} = 7a\]
We shall solve this three equations simultaneously, hence,
Insert \[{T_2} = 7a\] into \[{T_1} - {T_2} = 5a\], then,
\[{T_1} - 7a = 5a\]
\[ \Rightarrow {T_1} = 12a\]
Inserting this into \[120 - {T_1} = 3a\], we have
\[120 - 12a = 3a\]
\[ \Rightarrow 120 = 15a\]
Dividing both sides by 10, we get
\[a = 8m{s^{ - 2}}\]
Then, \[{T_1}\] can be calculated from
\[120 - {T_1} = 3 \times 8\]
\[ \Rightarrow {T_1} = 120 - 24 = 96N\]
Then the tension in the second cord \[{T_2}\] can be calculated from
\[{T_2} = 7a\] as
\[{T_2} = 7 \times 8 = 56N\]
Hence, the correct option is C
Note: Alternatively, one could take the entire system as one block which will be the sum of all three blocks and calculate the acceleration as thus
\[a = \dfrac{{120}}{M} = \dfrac{{120}}{{3 + 5 + 7}} = \dfrac{{120}}{{15}}\]
Hence, by computation,
\[a = 8m{s^{ - 2}}\]
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




