
The maximum compression in the spring if the lower block is shifted rightwards with acceleration ‘a’. All surfaces are smooth:
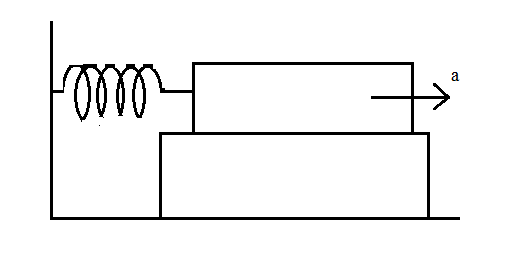
A) \[\dfrac{{ma}}{{2k}}\]
B) \[\dfrac{{2ma}}{k}\]
C) \[\dfrac{{ma}}{k}\]
D) \[\dfrac{{4ma}}{k}\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Draw the free body diagram of upper block
Apply work energy kinetic theory for the system.
Complete step by step answer:
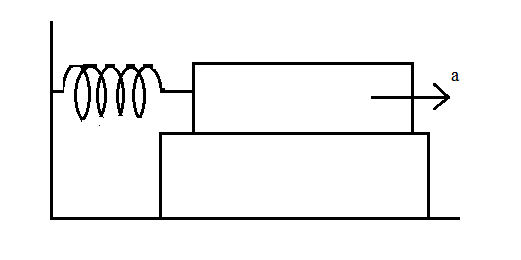
As shown in the figure, when the lower block is accelerated in the given direction, the upper block will move in the opposite direction and displacement of the block will be towards the spring.
Let \[k\] be the spring constant.
Let the displacement caused in the spring be \[x\] and force is \[kx\].
Given all surfaces are smooth, therefore, neglecting frictional forces:
When the lower block is moved, a pseudo force of ma acts on the upper block. This force acts in the opposite direction to which the lower block moves.
We know, when there is maximum compression in the spring, final velocity becomes zero.
Initially the block was at rest, thus initial velocity is also zero.
Therefore, we can say change in kinetic energy is also zero.
Now, applying work kinetic energy theorem, we can say:
Work done by all forces must be equal to the change in kinetic energy, which is equal to zero.
Therefore,
The equation becomes:
\[{W_{Sring}} + {W_{pseudo}} = 0\]
Where,
\[{W_{Sring}}\] is the work done due to the spring
\[{W_{pseudo}}\] is the work done due to pseudo force
As shown in the diagram, they are opposite in direction,
So,
\[ - \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2} + ma = 0\]
As, is the work done due to the spring is= \[\dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}\]
Therefore,
\[x = \dfrac{{2ma}}{k}\]
So, option (B) is correct.
Note: Pseudo force is referred to as apparent force.
Spring constant determines the stiffness of the spring. When a spring is stretched, it exerts a force which is proportional to the displacement caused in the spring. This constant of proportionality is called the spring constant.
Apply work energy kinetic theory for the system.
Complete step by step answer:

As shown in the figure, when the lower block is accelerated in the given direction, the upper block will move in the opposite direction and displacement of the block will be towards the spring.
Let \[k\] be the spring constant.
Let the displacement caused in the spring be \[x\] and force is \[kx\].
Given all surfaces are smooth, therefore, neglecting frictional forces:
When the lower block is moved, a pseudo force of ma acts on the upper block. This force acts in the opposite direction to which the lower block moves.
We know, when there is maximum compression in the spring, final velocity becomes zero.
Initially the block was at rest, thus initial velocity is also zero.
Therefore, we can say change in kinetic energy is also zero.
Now, applying work kinetic energy theorem, we can say:
Work done by all forces must be equal to the change in kinetic energy, which is equal to zero.
Therefore,
The equation becomes:
\[{W_{Sring}} + {W_{pseudo}} = 0\]
Where,
\[{W_{Sring}}\] is the work done due to the spring
\[{W_{pseudo}}\] is the work done due to pseudo force
As shown in the diagram, they are opposite in direction,
So,
\[ - \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2} + ma = 0\]
As, is the work done due to the spring is= \[\dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}\]
Therefore,
\[x = \dfrac{{2ma}}{k}\]
So, option (B) is correct.
Note: Pseudo force is referred to as apparent force.
Spring constant determines the stiffness of the spring. When a spring is stretched, it exerts a force which is proportional to the displacement caused in the spring. This constant of proportionality is called the spring constant.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Derive an expression for maximum speed of a car on class 11 physics JEE_Main

Understanding Elastic Collisions in Two Dimensions

Class 11 JEE Main Physics Mock Test 2025

Other Pages
NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory (2025-26)

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Define thermal expansion for alpha beta and gamma A class 11 physics JEE_Main

Happy New Year Wishes 2026 – 100+ Messages, Quotes, Shayari, Images & Status in All Languages

Valentine Week 2026 List | Valentine Week Days, Dates & Meaning




