
The weakest Lewis base?
(a) \[{{H}^{-}}\]
(b) \[O{{H}^{-}}\]
(c) \[C{{l}^{-}}\]
(d) \[HCO_{3}^{-}\]
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Bases are those compounds that tend to donate a pair of electrons. Therefore, any compound which can donate electrons or negative charge easily, will be a strong base. Similarly, the compounds which lack the tendency to donate are weak bases.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us try to solve this question by understanding the basic concept of Lewis bases.
According to the Lewis theory of acid-base reactions, bases are those compounds which donate a pair of electrons and acid are those which accept electron pairs. Therefore, a Lewis base is defined as any substance, such as the hydroxyl ion\[(O{{H}^{-}})\], that can donate a pair of nonbonding electrons. A Lewis base is therefore called an electron-pair donor.
Keep in mind that the more stable compound will not react fast.
Also, if negative charge is present on a more electronegative element, it will be less reactive, and hence be less basic.
Let us look at the given options and check the reactivity of the following bases.
The increasing order of basicity for the given compounds is: \[C{{l}^{-}}\]<\[HCO_{3}^{-}\]<\[O{{H}^{-}}\]<\[{{H}^{-}}\].
Therefore, the answer is – option (c).
Additional Information:
The conjugate of a strong acid is a weak base.Hydrochloric acid is a very strong acid, but its conjugate base – Chloride ion is a weak base.
Note: Just like Lewis base, a Lewis acid is defined as any substance, such as proton -\[{{H}^{+}}\]ion, which can accept a pair of nonbonding electrons. A Lewis acid can therefore be called an ‘electron-pair acceptor’. For example – iron (Ferrous - \[F{{e}^{+2}}\], Ferric - \[F{{e}^{+3}}\]).
Complete step by step answer:
Let us try to solve this question by understanding the basic concept of Lewis bases.
According to the Lewis theory of acid-base reactions, bases are those compounds which donate a pair of electrons and acid are those which accept electron pairs. Therefore, a Lewis base is defined as any substance, such as the hydroxyl ion\[(O{{H}^{-}})\], that can donate a pair of nonbonding electrons. A Lewis base is therefore called an electron-pair donor.
Keep in mind that the more stable compound will not react fast.
Also, if negative charge is present on a more electronegative element, it will be less reactive, and hence be less basic.
Let us look at the given options and check the reactivity of the following bases.
\[{{H}^{-}}\]
Hydride ion is a very strong base, since it has a high reactivity. Even though it has a complete duet (2 valence shell electrons), it is reactive as it has a small size.
\[O{{H}^{-}}\]
Hydroxyl ion has a comparatively lower reactivity than hydride due to the presence of oxygen. Oxygen, being the more electronegative element, has the tendency to pull the negative charge towards itself and stabilize the compound. Still, it reacts fast since oxygen has two lone pairs.
\[HCO_{3}^{-}\]
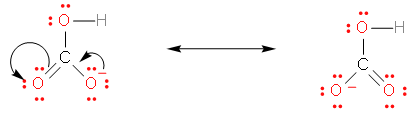
This compound has three oxygens. It can, therefore, form resonating structures, which provides it stability. The resonating structures are given below –

\[C{{l}^{-}}\]
Chlorine has a high electronegativity. It, therefore, is stable with a negative charge, since it has a tendency to pull electrons towards itself. Therefore, amongst all the given options, the chloride ion is the most stable.
The increasing order of basicity for the given compounds is: \[C{{l}^{-}}\]<\[HCO_{3}^{-}\]<\[O{{H}^{-}}\]<\[{{H}^{-}}\].
Therefore, the answer is – option (c).
Additional Information:
The conjugate of a strong acid is a weak base.Hydrochloric acid is a very strong acid, but its conjugate base – Chloride ion is a weak base.
Note: Just like Lewis base, a Lewis acid is defined as any substance, such as proton -\[{{H}^{+}}\]ion, which can accept a pair of nonbonding electrons. A Lewis acid can therefore be called an ‘electron-pair acceptor’. For example – iron (Ferrous - \[F{{e}^{+2}}\], Ferric - \[F{{e}^{+3}}\]).
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

In Carius method of estimation of halogens 015g of class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Chapter 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Chapter 8 Redox Reactions (2025-26)

An ideal gas is at pressure P and temperature T in class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses




