How Can Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 NCERT Solutions Help With Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles And Techniques Questions and Answers
Organic chemistry some basic principles and techniques class 11 questions and answers help students understand carbon compounds. This chapter introduces important concepts like hybridization, isomerism, and organic reactions. Class 11 chemistry chapter 8 NCERT solutions explain each topic with simple examples.
 Table of Content
Table of ContentVedantu provides clear solutions for every exercise question in this chapter. Students learn about IUPAC naming, functional groups, and reaction mechanisms step by step.
These solutions help students solve problems easily and build strong concepts. Each answer is written in simple language with proper explanations. Download the NCERT Solutions PDF for free and practice organic chemistry effectively.
How Can Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 NCERT Solutions Help With Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles And Techniques Questions and Answers
1. What are hybridization states of each carbon atom in the following compounds?
${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ = C = O, C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH = C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}},{\text{ }}{\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)_{\text{2}}}{\text{CO, C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ = CHCN, }}{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$
Ans:
$\mathop {\text{C}}\limits^1 {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ = }}\mathop {\text{C}}\limits^2 {\text{ = O}}$
In the given compound, carbon-1 is bonded to two hydrogen atoms and one carbon atom. So, according to the VSEPR theory, the steric number is 3 which corresponds to $s{p^2}$ hybridization. Carbon-2 is bonded to one carbon atom and one oxygen atom. So, the steric number is 2 which corresponds to $sp$ hybridization.
$\mathop {\text{C}}\limits^1 {{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\mathop {\text{C}}\limits^2 {\text{H = }}\mathop {\text{C}}\limits^3 {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$
In the given compound, carbon-1 is bonded to three hydrogen atoms and one carbon atom. So, according to the VSEPR theory, the steric number is 4 which corresponds to $s{p^3}$ hybridization. Carbon-2 is bonded to two carbon atoms and one hydrogen atom. So, the steric number is 3 which corresponds to $s{p^2}$ hybridization.
$\mathop {\text{C}}\limits^1 {{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\mathop {\text{C}}\limits^2 {\text{O}}\mathop {\text{C}}\limits^3 {{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$
In the given compound, carbon-1 and carbon-3 are bonded to three hydrogen atoms and one carbon atom. So, according to the VSEPR theory, the steric number is 4 which corresponds to $s{p^3}$ hybridization. Carbon-2 is bonded to two carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. So, the steric number is 3 which corresponds to $s{p^2}$ hybridization.
$\mathop {\text{C}}\limits^1 {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ = }}\mathop {\text{C}}\limits^2 {\text{H}}\mathop {\text{C}}\limits^3 {\text{N}}$
In the given compound, carbon-1 is bonded to two hydrogen atoms and one carbon atom. So, according to the VSEPR theory, the steric number is 3 which corresponds to $s{p^2}$ hybridization. Carbon-2 is bonded to two carbon atoms and one hydrogen atom. So, the steric number is 3 which corresponds to $s{p^2}$ hybridization. Carbon-3 is bonded to one carbon atom and one nitrogen atom. So, the steric number is 2 which corresponds to $sp$ hybridization.
${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$
In the given compound, all carbon atoms are bonded to two carbon atoms and one hydrogen atom. So, according to the VSEPR theory, the steric number is 3 which corresponds to $s{p^2}$ hybridization.
2. Indicate the $\sigma {\text{ and }}\pi $ bonds in the following molecules:
${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{, }}{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}{\text{, C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{, C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ = C = C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{, C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{, HCONHC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$
Ans: The structure of ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}$ is shown below.
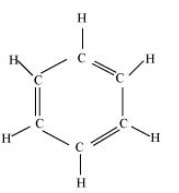
Single bond contains only one sigma bond and double bond contains one sigma and one pi bond. In this structure, nine single bonds and three double bonds are present. So, there are $12{\text{ }}\sigma {\text{ and 3 }}\pi $ bonds present.
The structure of ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}$ is shown below.
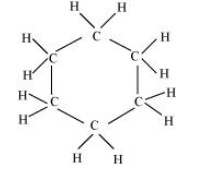
In this structure, eighteen single bonds are present. So, there are only $18{\text{ }}\sigma {\text{ }}$ bonds present.
The structure of ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ is shown below.
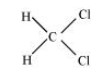
In this structure, four single bonds are present. So, there are only $4{\text{ }}\sigma {\text{ }}$ bonds present.
The structure of ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ = C = C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$ is shown below.
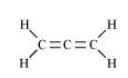
In this structure, four single bonds and two double bonds are present. So, there are $6{\text{ }}\sigma {\text{ and 2 }}\pi $ bonds present.
The structure of ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is shown below.
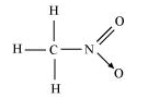
In this structure, five single bonds and one double bond are present. So, there are $6{\text{ }}\sigma {\text{ and 1 }}\pi $ bonds present.
The structure of ${\text{HCONHC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ is shown below.
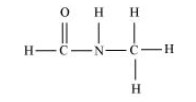
In this structure, seven single bonds and one double bond are present. So, there are $8{\text{ }}\sigma {\text{ and 1 }}\pi $ bonds present.
3. Write bond line formulas for:
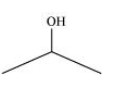
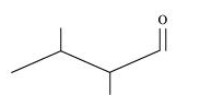
Isopropyl alcohol, ${\text{2,3 }} - {\text{ Dimethylbutanal, Heptan }} - {\text{ 4 }} - {\text{ one}}$
Ans: The bond line formulas for the given compounds are shown below.
Isopropyl Alcohol:
${\text{2,3 }} - {\text{ Dimethylbutanal}}$
${\text{Heptan }} - {\text{ 4 }} - {\text{ one}}$
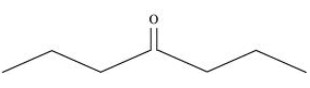
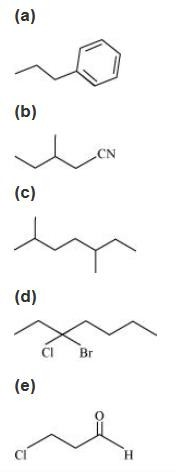
4. Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds:
(f) ${\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CHC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH}}$
Ans: (a)

In this structure, the longest chain of carbon contains 3 carbon atoms and one phenyl group is present. So, the IUPAC name is 1-phenyl propane.
(b)

In this structure, the longest chain of carbon contains four carbon atoms. Also, one methyl and one cyanide groups are attached with carbon-2 and carbon-1 respectively. So, the IUPAC name is 2-methyl-1-cyanobutane.
(c)

In this structure, the longest chain of carbon contains 7 carbon atoms and 2 methyl are positioned at carbon-2 and carbon-5. So, the IUPAC name of the compound is 2, 5-dimethyl heptane.
(d)

In this structure, the longest chain of carbon contains 7 carbon atoms. Also, 1 chloro and 1 bromo groups are present at carbon-3. So, the IUPAC name of the compound is 3-bromo-3-chloroheptane.
(e)

In this structure, the longest chain of carbon contains 3 carbon atoms. Also, 1 aldehyde and 1 chloro functional groups are present at carbon-1 and carbon-3 respectively. So, the IUPAC name of the compound is 3-chloropropanal.
(f)

In this structure, the longest chain of carbon contains 2 carbon atoms. Also, 1 alcohol and 2 chloro functional groups are present at carbon-1 and carbon-2 respectively. So, the IUPAC name of the compound is 2,2-dichloro-1-ethanol.
5. Which of the following represents the correct IUPAC name for the compounds concerned?
${\text{2,2 }} - {\text{ Dimethylpentane or 2}} - {\text{Dimethylpentane}}$
${\text{2,4,7 }} - {\text{ Trimethyloctane or 2,5,7 }} - {\text{ Trimethyloctane}}$
${\text{2 }} - {\text{ Chloro }} - {\text{ 4 }} - {\text{ methylpentane or 4 }} - {\text{ Chloro }} - {\text{ 2 }} - {\text{ methylpentane}}$
${\text{But }} - {\text{ 3 }} - {\text{ yn }} - {\text{ 1 }} - {\text{ ol or But }} - {\text{ 4 }} - {\text{ ol }} - {\text{ 1 }} - {\text{ yne}}$
Ans:
In the IUPAC nomenclature, the prefix Di- denotes that the parent chain has two identical substituent groups. As there are two methyl groups in the C–2 of the parent chain of the given chemical compound, the correct IPUAC name is ${\text{2,2 }} - {\text{ Dimethylpentane}}{\text{.}}$
The locant number 2, 4, 7 is less than the locant number 2, 5, 7. As a result, the given compound's IUPAC nomenclature is ${\text{2,4,7 }} - {\text{ Trimethyloctane}}$
If the functional groups are present at the parent chain's equivalent position, the lower number is assigned to the one that appears first in the name in alphabetical order. As a result, the proper IUPAC nomenclature for the given compound is ${\text{2 }} - {\text{ Chloro }} - {\text{ 4 }} - {\text{ methylpentane}}{\text{.}}$
The given molecule contains two functional groups: alcoholic and alkyne. The alcoholic group is the principal functional group. As a result, the parent chain will be terminated with ol. The alkyne group can be found in the parent chain's C–3. As a result, ${\text{But }} - {\text{ 3 }} - {\text{ yn }} - {\text{ 1 }} - {\text{ ol}}$ is the correct IUPAC nomenclature for the given compound.
6. Draw formulas for the first five members of each homologous series beginning with the following compounds.
$\left( {\text{a}} \right){\text{ H -- COOH }}$
$ \left( {\text{b}} \right){\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ }} $
$ \left( {\text{c}} \right){\text{ H -- CH = C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}} $
Ans: The following are the first 5 members of each homologous series, starting with the given compounds:
$ {\left( {\text{a}} \right){\text{ H -- COOH: Methanoic acid}}} $
$ {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ -- COOH : Ethanoic acid}}} $
$ {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ -- C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ -- COOH : Propanoic acid}}} $
$ {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ -- C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ -- C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ -- COOH : Butanoic acid}}} $
$ {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ -- C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ -- C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ -- C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ -- COOH : Pentanoic acid}}} $
${{\text{}}\left( {\text{b}} \right){\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ : Propanone}}} $ ${{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ : Butanone}}} $
${{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ : Pentan - 2 - one}}} $ ${{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ : Hexan - 2 - one}}} $
${{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ : Heptan - 2 - one}}} $
${\left( {\text{c}} \right){\text{ H -- CH = C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ : Ethene}}}$
$ {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ -- CH = C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ : Propene}}} $
$ {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ -- C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ -- CH = C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ : 1 - Butene}}} $
$ {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ -- C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ -- C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ -- CH = C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ : 1 - Pentene}}} $
$ {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ -- C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ -- C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ -- C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ -- CH = C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ : 1 - Hexene}}} $
7. Give condensed and bond line structural formulas and identify the functional group(s) present, if any, for:
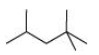
${\left( {\text{a}} \right){\text{ }}2,2,4{\text{ }} - {\text{ Trimethylpentane}}} $
${\left( {\text{b}} \right){\text{ }}2{\text{ }} - {\text{ Hydroxy }} - {\text{ }}1,2,3{\text{ }} - {\text{ propanetricarboxylic acid}}} $
$ \left( {\text{c}} \right){\text{ Hexanedial}} $
Ans:
$2,2,4{\text{ }} - {\text{ Trimethylpentane}}$
Condensed formula: ${\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)_{\text{2}}}{\text{CHC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C }}{\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)_{\text{3}}}$
Bond Line Formula:
$2{\text{ }} - {\text{ Hydroxy }} - {\text{ }}1,2,3{\text{ }} - {\text{ propanetricarboxylic acid}}$
Condensed Formula: $\left( {{\text{COOH}}} \right){\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}\left( {{\text{OH}}} \right)\left( {{\text{COOH}}} \right){\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\left( {{\text{COOH}}} \right)$
Bond Line Formula:
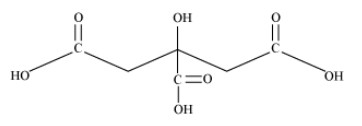
In the given compound, the functional groups present are carboxylic acid $\left( { - {\text{COOH}}} \right)$ and alcoholic group $\left( { - {\text{OH}}} \right).$
Hexanedial
Condensed Formula: $\left( {{\text{CHO}}} \right){\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)_{\text{4}}}\left( {{\text{CHO}}} \right)$
Bond Line Formula:
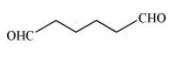
In the given compound, the functional group present is aldehyde $\left( { - {\text{CHO}}} \right).$
8. Identify the functional groups in the following compounds.
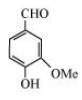
(a)
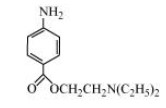
(b)
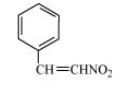
(c)
Ans:
In the given compound, aldehyde $\left( {--{\text{CHO}}} \right),$ hydroxyl $\left( {--{\text{OH}}} \right)$ and methoxy $\left( {--{\text{OMe}}} \right)$ functional groups are present.
In the given compound, amino $\left( {--{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}} \right),$ ketone $\left( {{\text{C }} = {\text{ O}}} \right),$ diethylamine $\left( {{\text{N}}{{\left( {{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}} \right)}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$ functional groups are present.
In the given compound, nitro group $\left( { - {\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$ and ${\text{C }} = {\text{ C}}$ double bond are present.
9. Which of the two: ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{NC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O --}}$ or ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O --}}$ is expected to be more stable and why?
Ans: The nitro group is an electron-withdrawing group. As a result, it exhibits the -I effect. This group reduces the compound's negative charge by attracting electrons towards it and stabilizing it. The ethyl group, on the other hand, is an electron-releasing group. As a result, the ethyl group exhibits the +I effect. This raises the compound's negative charge, making it unstable. As a result, ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{NC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O --}}$ is projected to be more stable than ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O --}}{\text{.}}$
10. Explain why alkyl groups act as electron donors when attached to a $\pi $ system.
Ans: When an alkyl group is linked to a $\pi $ system, the process of hyperconjugation causes it to act as an electron-donor group. Let us use propene as an example to better comprehend this topic.

The sigma electrons of an alkyl group's C-H bond are delocalised during hyperconjugation. This group is directly connected to an unsaturated system's atom. The delocalisation happens as a result of a partial overlap of a $s{p^3}$ sigma bond orbital with an empty p orbital of the pi bond of a nearby carbon atom's bond.

11. Draw the resonance structures for the following compounds. Show the electron shift using curved-arrow notation.
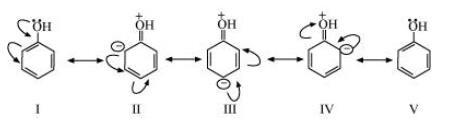
$\left( {\text{a}} \right){\text{ }}{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{OH }} $
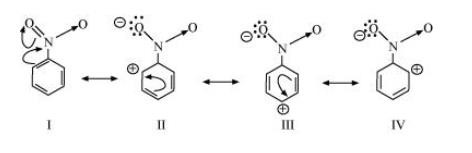
$ \left( {\text{b}} \right){\text{ }}{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ }}$
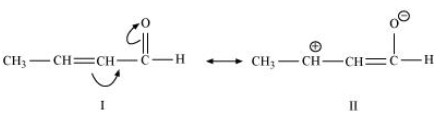
$ \left( {\text{c}} \right){\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH = CHCHO }} $
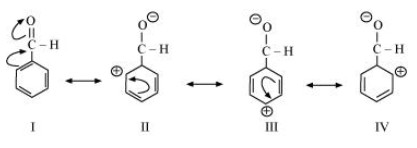
$ \left( {\text{d}} \right){\text{ }}{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{ -- CHO }} $
$ \left( {\text{e}} \right){\text{ }}{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{ -- }}\mathop {\text{C}}\limits^ + {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ }} $
$ \left( {\text{f}} \right){\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH = CH}}\mathop {\text{C}}\limits^ + {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}} $
Ans:
The resonating structures for ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{OH}}$ are shown below.
The resonating structures for ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ are shown below.
The resonating structures for ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH = CHCHO}}$ are shown below.
The resonating structures of ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{ -- CHO}}$ are shown below.
The resonating structures of ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{ -- }}\mathop {\text{C}}\limits^ + {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$ are shown below.
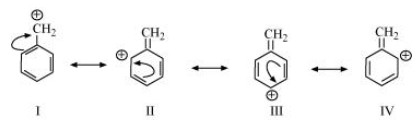
The resonating structures of ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH = CH}}\mathop {\text{C}}\limits^ + {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$ are shown below.
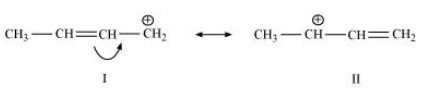
12. What are electrophiles and nucleophiles? Explain with examples.
Ans: An electrophile is a reagent that removes a pair of electrons. In other words, an electrophile $\left( {{{\text{E}}^ + }} \right)$ is a reagent that seeks electrons. Electrophiles are electron-deficient and receiver of an electron pair.
Electrophiles include carbocations and $\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}^ + } \right)$ neutral compounds with functional groups such as the carbonyl group.
A reagent that produces an electron pair is known as a nucleophile. A nucleus-seeking reagent is referred to as a nucleophile (Nu:).
For instance, ${\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - },{\text{ N}}{{\text{C}}^ - },$ carbanions $\left( {{{\text{R}}_3}{{\text{C}}^ - }} \right),$ and so on.
Because of the presence of a lone pair, neutral molecules such as water and ammonia also serve as nucleophiles.
13. Identify the reagents shown in bold in the following equations as nucleophiles or electrophiles:
$\left( {\text{a}} \right){\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COOH + }}{\mathbf{O}}{{\mathbf{H}}^{\mathbf{ - }}}{\text{ }} \to {\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CO}}{{\text{O}}^ - }{\text{ + }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}} $
$ \left( {\text{b}} \right){\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ + }}{\mathbf{C}}{{\mathbf{N}}^{\mathbf{ - }}}{\text{ }} \to {\text{ }}{\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}\left( {{\text{CN}}} \right)\left( {{\text{OH}}} \right) $
$ \left( {\text{c}} \right){\text{ }}{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{ + }}{\mathbf{C}}{{\mathbf{H}}_{\mathbf{3}}}\mathop {\mathbf{C}}\limits^{\mathbf{ + }} {\mathbf{O }} \to {\text{ }}{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{COC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} $
Ans: Electrophiles are entities that are electron-deficient and can accept an electron pair. Nucleophiles, on the other hand, are electron-rich entities that can transfer their electrons.
In this equation, ${\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }$ serves as a nucleophile because it is an electron-rich species.
In this equation, ${\text{C}}{{\text{N}}^ - }$serves as a nucleophile because it is an electron-rich species.
In this equation, ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\mathop {\text{C}}\limits^{\text{ + }} {\text{O}}$ serves as an electrophile because it is an electron-deficient species.
14. Classify the following reactions in one of the reaction types studied in this unit.
$\left( {\text{a}} \right){\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Br + H}}{{\text{S}}^{\text{ - }}}{\text{ }} \to {\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{HS + B}}{{\text{r}}^{\text{ - }}} $
$ \left( {\text{b}} \right){\text{ }}{\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)_{\text{2}}}{\text{C = C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + HCl }} \to {\text{ }}{\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)_{\text{2}}}{\text{ClC - C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$
$ \left( {\text{c}} \right){\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{Br + H}}{{\text{O}}^{\text{ - }}}{\mathbf{ }} \to {\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ = C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O + B}}{{\text{r}}^{\text{ - }}} $
$ \left( {\text{d}} \right){\text{ }}{\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)_{\text{3}}}{\text{C - C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH + HBr}}{\mathbf{ }} \to {\text{ }}{\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)_{\text{2}}}{\text{CBrC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O }}$
Ans:
The given reaction is a type of a substitution reaction because the bromine group in bromoethane is substituted by thionyl group.
The given reaction is a type of an addition reaction because two reactant molecules react to produce a single product.
The given reaction is a type of an elimination reaction because hydrogen and bromine are eliminated by bromoethane in order to produce ethene.
Substitution takes place in this reaction, followed by atom and atom group rearrangement.
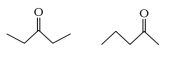
15. What is the relationship between the members of the following pairs of structures? Are they structural or geometrical isomers or resonance contributors?
(a)
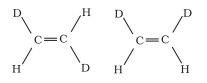
(b)
(c)
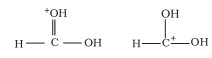
Ans:
Compounds with the same chemical formula but different structures are referred to as structural isomers. The mentioned compounds have the same molecular formula, but the position of the functional group differs (ketone group).
The ketone group is at C-3 of the parent chain (hexane chain) in structure I, and at C-2 of the parent chain in structure II (hexane chain). As a result, the given pair of compounds are structural isomers.
Geometrical isomers are compounds that have the same chemical formula, composition, and series of covalent bonds but have different relative positions of their atoms in space.
The relative positions of Deuterium (D) and hydrogen (H) in space differ in structures I and II. As a result, the given pairs are geometrical isomers.
The structures shown are either canonical or contributing structures. They are fictitious and do not represent any actual molecule. As a result, the given pair represents resonance structures known as resonance isomers.
16. For the following bond cleavages, use curved-arrows to show the electron flow and classify each as homolysis or heterolysis. Identify reactive intermediate produced as free radical, carbocation and carbanion.

Ans:
The bond cleavage can be illustrated using curved arrows to show the electron flow of the given reaction as

As one of the shared pairs in a covalent bond travels with the connected atom, it is an example of homolytic cleavage. A free radical is produced as a reaction intermediate.
The bond cleavage can be illustrated using curved arrows to show the electron flow of the given reaction as

It is an example of heterolytic cleavage because the bond breaks in such a way that the shared pair of electrons stay with the carbon of propanone. The reactive intermediate created is carbanion.
The bond cleavage can be illustrated using curved arrows to show the electron flow of the given reaction as

It is an example of heterolytic cleavage because the bond breaks in such a way that the bromine ion retains the shared pair of electrons. A carbocation is produced as a reaction intermediate.
The bond cleavage can be illustrated using curved arrows to show the electron flow of the given reaction as

The bond breaks in such a way that the shared pair of electrons stays with one of the fragments, resulting in a heterolytic cleavage. A carbocation is created as an intermediate.
17. Explain the terms Inductive and Electromeric effects. Which electron displacement effect explains the following correct orders of acidity of the carboxylic acids?
$ {\left( {\text{a}} \right){\text{ C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CCOOH > C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CHCOOH > ClC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOH}}} $
$\left( {\text{b}} \right){\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOH > }}{\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)_{\text{2}}}{\text{CHCOOH > }}{\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{\text{.COOH}}$
Ans: Inductive effect: It refers to the permanent shift of sigma electrons along a saturated chain whenever an electron withdrawing or electron donating group is present. The inductive effect could be either a $ + {\text{ }}I$ effect or $ - {\text{ }}I$ effect. When an atom or group attracts electrons more strongly than hydrogen, it is said to have the $ - {\text{ }}I$ effect. Example,
${\text{F}} - \leftarrow {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}} - \leftarrow {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}} - \leftarrow {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}} - \leftarrow {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$
When an atom or set of atoms attracts electrons less strongly than hydrogen, this is referred to as the $ + {\text{ }}I$ effect. For instance, ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} - \to {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}} - \to {\text{Cl}}$
Electromeric effect: In the presence of an attacking agent, it involves the complete transfer of the shared pair of pi electrons to either of the two atoms joined by multiple bonds. For example,

Electrometric effects might be $ + {\text{ }}E$ or $ - {\text{ }}E.$ The $ + {\text{ }}E$ effect occurs when electrons are transferred to the assaulting reagent. Whereas when electrons are moved away from the attacking reagent, this is referred to as the $ - {\text{ }}E$ effect.
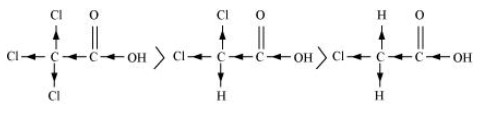
$\left( {\text{a}} \right){\text{ C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CCOOH > C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CHCOOH > ClC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOH}}$
On the basis of the inductive effect $\left( { - {\text{ }}I} \right)$, the order of acidity can be explained. The $ - {\text{ }}I$ effect increases as the number of chlorine atoms increases. The acid strength increases in proportion to the increase in $ - {\text{ }}I$ effect.
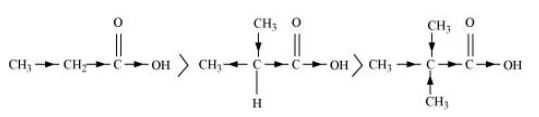
$\left( {\text{b}} \right){\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOH > }}{\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)_{\text{2}}}{\text{CHCOOH > }}{\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{\text{.COOH}}$
The inductive effect ($ + {\text{ }}I$ effect) can be used to explain the order of acidity. The $ + {\text{ }}I$ effect increases in proportion to the quantity of alkyl groups. The acid strength increases in proportion to the increase in $ + {\text{ }}I$ effect.
18. Give a brief description of the principles of the following techniques taking an example in each case. (a) Crystallisation (b) Distillation (c) Chromatography
Ans:
Crystallisation: It is one of the most widely used methods for purifying solid chemical molecules.
Principle: The differential in the solubilities of the compound and the impurities in a solvent. The impure substance dissolves in the solvent, which is only sparingly soluble at ambient temperature but completely soluble at higher temperatures. The solution is concentrated until it is virtually saturated. When the solution is cooled, the pure compound crystallises and is extracted by filtration.
Pure aspirin, for example, is created by recrystallising crude aspirin. 2 - 4 g of crude aspirin is dissolved in approximately 20 mL of ethyl alcohol. To ensure complete decomposition, the solution is heated.
Distillation: This approach is used to separate volatile liquids from nonvolatile contaminants or a mixture of those liquids with a large enough difference in boiling points.
Principle: It works on the principle that liquids with different boiling points vapourize at different temperatures. The vapours are then cooled, and the liquids that form are separated.
For example: Distillation can be used to separate a combination of chloroform and aniline. The mixture is placed in a condenser-equipped round bottom flask. After that, it is heated. Because chloroform is more volatile, it vaporizes first and enters the condenser. The vapours condense in the condenser, and chloroform trickles down. Aniline is left in the round bottom flask.
Chromatography: It is one of the most effective technologies for organic chemical separation and purification.
Principle: The differential in movement of separate components of a mixture through the stationary phase under the influence of the mobile phase is the basis for the principle.
Example: Chromatography, can separate a combination of red and blue ink. On the chromatogram, a drop of the combination is inserted. The component of the ink that is less adsorbed on the chromatogram travels with the mobile phase, whereas the component that is more adsorbed remains stationary.
19. Describe the method, which can be used to separate two compounds with different solubilities in a solvent${\text{S}}{\text{.}}$
Ans: The process of fractional crystallisation is used to separate two compounds with varying solubilities in a solvent ${\text{S}}{\text{.}}$ The fractional crystallisation process is divided into four phases.
Solution’s Preparation: The powdered combination is placed in a flask, and the solvent is slowly and simultaneously added and agitated. The solvent is added until the solute is completely dissolved in it. This saturated solution is then boiled.
Solution’s Filtration: In a China dish, the hot saturated solution is filtered through filter paper.
Fractional Crystallisation: Allow the solution in a China dish to cool. To begin with, the less soluble molecule crystallizes, while the more soluble compound remains in solution. During the separation of these crystals from the liquor, the latter is concentrated once more. The hot solution is allowed to cool, resulting in the formation of crystals of the more soluble chemical.
Isolation and Drying: Filtration is used to separate the crystals from the mother liquor. The crystals are finally dried.
20. What is the difference between distillation, distillation under reduced pressure and steam distillation?
Ans: The differences between distillation, reduced pressure distillation, and steam distillation are shown below.
Distillation: It is used to purify chemicals that are related with non-volatile impurities or liquids that do not disintegrate when heated. In other words, distillation is used to separate volatile liquids from nonvolatile contaminants or a mixture of such liquids with significant boiling point difference. This process separates a mixture of fuel and kerosene.
Reduced Pressure Distillation: This procedure is used to purify a liquid that decomposes when heated. Under reduced pressure, the liquid will boil at a lower temperature than its boiling point and so will not decompose.
This Process is Used to Purify Glycerol. At a temperature of ${\text{593 K,}}$ it boils with decomposition. It boils at ${\text{453 K}}$ without breakdown at a lower pressure.
Steam Distillation: It is used to purify an organic molecule that is steam volatile and water immiscible. The compound is heated by passing steam, and the steam is condensed to water. After some time, the water-liquid mixture begins to boil and flows through the condenser. A separating funnel is then used to separate this condensed mixture of water and liquid.
A solution of water and aniline can be separated by this method.
21. Discuss the chemistry of Lassaigne’s test.
Ans: Lassaigne's Test: This test detects the presence of nitrogen, sulfur, halogens, and phosphorus in an organic compound. An organic compound has these elements in covalent form. By fusing the chemical with sodium metal, these are transformed into the ionic form.
$ {{\text{Na + C + N }} \to {\text{ NaCN}}} $
$ {{\text{Na + S + C + N }} \to {\text{ NaSCN}}} $
$ {{\text{2Na + S }} \to {\text{ N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}} $
$ {{\text{Na + X }} \to {\text{ NaX}}} $
The sodium cyanide, sulphide, and halide are removed from the fused material by boiling it in distilled water. Lassaigne's extract is the name given to the extract obtained in this manner. The presence of nitrogen, sulphur, halogens, and phosphorus is then determined in this Lassaigne's extract.
Chemistry of Nitrogen Test: The sodium fusion extract is heated with iron (II) sulphate and then acidified with sulphuric acid in the Lassaigne's test for nitrogen in an organic molecule. Sodium cyanide first interacts with iron (II) sulphate to generate sodium hexacyanoferrate in this method (II). The iron (II) is then oxidized by sulphuric acid to generate iron (III) hexacyanoferrate (II), which is Prussian blue. The reactions involved are shown below.
$ {{\text{6C}}{{\text{N}}^{{\text{ - }}}}{\text{ + F}}{{\text{e}}^{{\text{2 + }}}}{\text{}} \to {\text{ }}{{\left[ {{\text{Fe}}{{\left( {{\text{CN}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right]}^{{\text{4 - }}}}} $
$ {{\text{3}}{{\left[ {{\text{Fe}}{{\left( {{\text{CN}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right]}^{{\text{4 - }}}}{\text{ + 4F}}{{\text{e}}^{{\text{3 + }}}}{\text{}} \to {\text{ F}}{{\text{e}}_{\text{4}}}{{\left[ {{\text{Fe}}{{\left( {{\text{CN}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right]}_{\text{3}}}{\text{}}} $
Test for Sulphur:
$\left( {\text{i}} \right){\text{ Lassaignes's extract + Lead acetate}} \to {\text{ Black precipitate}}$
Chemistry of the test: The sodium fusion extract is acidified with acetic acid and then lead acetate is added to it in the Lassaigne's test for sulphur in an organic compound. The presence of sulphur in the combination is shown by the precipitation of lead sulphide, which is black in color.
${{\text{S}}^{{\text{2 - }}}}{\text{ + P}}{{\text{b}}^{{\text{2 + }}}}{\text{ }} \to {\text{ PbS}}$
$\left( {{\text{ii}}} \right){\text{ Lassaignes's extract + Sodium nitroprusside }} \to {\text{ Violet colour}}$
Chemistry of the Test: Sodium nitroprusside is used to treat the sodium fusion extract. The presence of sulphur in the compound is also indicated by the presence of violet color.
${{\text{S}}^{{\text{2 - }}}}{\text{ + [Fe}}{\left( {{\text{CN}}} \right)_{\text{5}}}{\text{NO}}{{\text{]}}^{{\text{2 - }}}}{\text{}} \to {\text{ [Fe}}{\left( {{\text{CN}}} \right)_{\text{5}}}{\text{NOS}}{{\text{]}}^{{\text{ - 4}}}}$
If both nitrogen and sulphur are present in an organic molecule, ${\text{NaSCN}}$ is formed instead of ${\text{NaCN}}{\text{.}}$
${\text{Na + C + N + S }} \to {\text{ NaSCN}}$
This ${\text{NaSCN}}$ (sodium thiocyanate) color is blood red. The absence of free cyanide ions prevents the formation of prussian color.
Test for Halogen: The sodium fusion extract is acidified with nitric acid and then treated with silver nitrate in the Lassaigne's test for halogens in an organic molecule. If the organic compound contains both nitrogen and sulphur, the Lassaigne's extract is heated to remove the nitrogen and sulphur, which would otherwise interfere with the halogen test.
22. Differentiate between the principle of estimation of nitrogen in an organic compound by (i) Dumas method and (ii) Kjeldahl’s method.
Ans: In the Dumas method, a specified amount of a nitrogen-containing organic molecule is burned strongly with an excess of copper oxide in a carbon dioxide atmosphere to yield free nitrogen as well as carbon dioxide and water.
The process can also yield traces of nitrogen oxides, which can be converted to dinitrogen by passing the gaseous mixture over a heated copper gauge. The dinitrogen generated is collected over a potassium hydroxide aqueous solution. At room temperature and atmospheric pressure, the volume of nitrogen generated is then measured.
Kjeldahl's method, on the other hand, involves heating a known quantity of a nitrogen-containing organic molecule with concentrated sulphuric acid. The compound's nitrogen is quantitatively transformed into ammonium sulphate. It is then distilled with a high concentration of sodium hydroxide. The ammonia produced by this method is injected into a known volume of ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{.}}$The chemical equations involved are shown below.
Volumetric analysis (titration against a standard alkali) is used to measure the quantity of acid that is left unused, and the amount of ammonia produced can be calculated. As a result, the percentage of nitrogen in the compound can be calculated. This approach is inapplicable to compounds with nitrogen in a ring structure, and it is also inapplicable to compounds with nitro and azo groups.
23. Discuss the principle of estimation of halogens, sulphur and phosphorus present in an organic compound.
Ans: Estimation of Halogens: The Carius method is used to calculate halogens. In this approach, a known amount of organic chemical is heated with fuming nitric acid in the presence of silver nitrate in a Carius tube, which is placed in a furnace. The carbon and hydrogen in the compound are oxidized to generate ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ and }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O,}}$ respectively, while the halogen in the compound is transformed into the form of ${\text{AgX}}$ . After that, the ${\text{AgX}}$ is filtered, washed, dried, and weighed.
Estimation of Sulphur: In this approach, a known amount of organic substance is heated in a hard glass tube called the Carius tube with either fuming nitric acid or sodium peroxide. The compound's sulphur is oxidized to generate sulphuric acid. The precipitation of barium sulphate occurs when an excess of barium chloride is added to it. After that, the precipitate is filtered, washed, dried, and weighed.
Estimation of Phosphorus: A known amount of organic substance is heated with fuming nitric acid in this procedure. The compound's phosphorus is oxidized to generate phosphoric acid. Phosphorus can be precipitated as ammonium phosphomolybdate by adding ammonia and ammonium molybdate to the solution. Phosphorus can also be measured by precipitating it as ${\text{MgN}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{P}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ and then on igniting it yeild ${\text{M}}{{\text{g}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{P}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}}{\text{.}}$
24. Explain the principle of paper chromatography.
Ans: Paper chromatography employs the use of chromatography paper. This paper includes trapped water, which behaves as the stationary phase. The solution of the mixture is spotted on the base of this chromatography paper. The paper strip is then hung in a suitable solvent, which serves as the mobile phase. By capillary action, this solvent moves up the chromatography paper and flows over the spot during the procedure. Different component spots travel to different heights with mobile phase. The resulting paper is known as a chromatogram.
25. Why is nitric acid added to sodium extract before adding silver nitrate for testing halogens?
Ans: The Lassaigne's extract is first heated with weak nitric acid before being tested for the presence of halogens. This is done to convert ${\text{NaCN to HCN and N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S to }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}$ and then expel these gases. If there is any nitrogen or sulphur present in the form of ${\text{NaCN or N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S,}}$ it is eliminated. The chemical equations involved are shown below.
$ {\text{N}}{{\text{a}}}{\text{CN + HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ }}$ $\to {\text{ }}{{\text{H}}}{\text{CN + NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}} $
$ {\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S + 2HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ }} \to {\text{ }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S + 2NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}} $
26. Explain the reason for the fusion of an organic compound with metallic sodium for testing nitrogen, sulphur and halogens.
Ans: Organic chemicals are covalently bonded to nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. They must first be changed to ionic form in order to be detected. This is accomplished by combining the organic chemical with sodium metal. This is known as the "Lassaigne's test." The chemical equations used in the test are as follows:
${{\text{Na + C + N }} \to {\text{ NaCN}}} $
$ {{\text{Na + S + C + N }} \to {\text{ NaSCN}}} $
$ {{\text{2Na + S }} \to {\text{ N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}} $
$ {{\text{Na + X }} \to {\text{ NaX}}} $
Here, X is halogen like chlorine, bromine, iodine.
Organic compounds contain carbon, nitrogen, sulfur, and halogen.
27. Name a suitable technique of separation of the components from a mixture of calcium sulphate and camphor.
Ans: A combination of camphor and calcium sulphate is separated by sublimation. The sublimable chemical converts from solid to vapour without going through the liquid state throughout this procedure. Camphor is a sublimable molecule, whereas calcium sulphate is a non-sublimable solid. As a result, when heated, camphor will sublime while calcium sulphate will remain.
28. Explain, why an organic liquid vaporises at a temperature below its boiling point in its steam distillation?
Ans: In the process of steam distillation, the organic liquid begins to boil when the total of the organic liquid’s vapour pressure $\left( {{p_1}} \right)$ and the water’s vapour pressure $\left( {{p_2}} \right)$ equals atmospheric pressure $\left( p \right),{\text{ i}}{\text{.e}}.{\text{ }}p{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}{p_1}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{p_2}.$ Therefore,
${p_1}{\text{ < }}{p_2}$
Hence, organic liquid will vapourize at a lower temperature than its boiling point.
29. Will ${\text{CC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{4}}}$ give white precipitate of ${\text{AgCl}}$ on heating it with silver nitrate? Give reason for your answer.
Ans: When ${\text{CC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{4}}}$ heated with silver nitrate, it does not produce the white precipitate of ${\text{AgCl}}{\text{.}}$ This is because the chlorine atoms in ${\text{CC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{4}}}$ are covalently connected to carbon. It must be present in ionic form in order to obtain the precipitate, which requires preparing the Lassaigne's extract of ${\text{CC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{4}}}.$
30. Why is a solution of potassium hydroxide used to absorb carbon dioxide evolved during the estimation of carbon present in an organic compound?
Ans: Carbon dioxide is an acidic substance, whereas potassium hydroxide is a strong basic. As a result, when carbon dioxide combines with potassium hydroxide, potassium carbonate and water are formed.
${\text{2KOH + C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{}} \to {\text{}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$
As a result, the mass of the ${\text{KOH}}$containing U-tube increases. This rise represents the amount of ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ created. The proportion of carbon in the organic compound can be determined based on its mass.
31. Why is it necessary to use acetic acid and not sulphuric acid for acidification of sodium extract for testing sulphur by lead acetate test?
Ans: Due to the common ion effect, the addition of sulphuric acid would precipitate lead sulphate, but the addition of acetic acid would assure complete precipitation of sulphur in the form of lead sulphate. As a result, acetic acid must be used to acidify sodium extract before testing for sulphur using the lead acetate test.
32. An organic compound contains $69{\text{ }}\% $ carbon and $4.8{\text{ }}\% $ hydrogen, the remainder being oxygen. Calculate the masses of carbon dioxide and water produced when ${\text{0}}{\text{.20 g}}$of this substance is subjected to complete combustion.
Ans: The percentage of carbon in organic compound is $69{\text{ }}\% .$
It means ${\text{100 g}}$ of organic compound contains ${\text{69 g}}$ of carbon. So, the mass of carbon contained in ${\text{0}}{\text{.20 g}}$ of organic compound is calculated as
$ {\text{Mass of C = }}\dfrac{{69{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}0.20}}{{100}}{\text{ }} $
$= {\text{ }}0.138{\text{ g of C}} $
The molecular mass of carbon dioxide is ${\text{44 g}}/{\text{mol}}{\text{.}}$ Therefore, ${\text{12 g}}$of carbon is contained in ${\text{44 g}}$ of ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}.$
Therefore, the mass of ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ contained in ${\text{0}}{\text{.138 g}}$ of carbon is calculated as
$ {\text{Mass of C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{44{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}0.138}}{{12}}{\text{ }} $
$ = {\text{ }}0.506{\text{ g}} $
Thus, 0.506 g of CO2 will be produced on complete combustion of 0.2 g of organic compound.
The percentage of hydrogen in organic compound is $4.8{\text{ % }}{\text{.}}$ It means ${\text{100 g}}$ of organic compound contains ${\text{4}}{\text{.8 g}}$ of hydrogen.
Therefore, the mass of hydrogen contained in ${\text{0}}{\text{.20 g}}$ of organic compound is calculated as
$ {\text{Mass of H = }}\dfrac{{4.8{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}0.20}}{{100}}{\text{ }} $
$ = {\text{ }}0.0096{\text{ g of H}} $
It is known that the molecular mass of water is ${\text{18 g}}/{\text{mol}}{\text{.}}$
Thus, ${\text{2 g}}$ of hydrogen is contained in ${\text{18 g}}$ of water. Therefore, the mass of water contained in ${\text{0}}{\text{.0096 g}}$ of hydrogen is calculated as
${\text{Mass of }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O = }}\dfrac{{18{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}0.0096}}{2}{\text{ }}$
$ = {\text{ }}0.0864{\text{ g}} $
33. A sample of ${\text{0}}{\text{.50 g}}$ of an organic compound was treated according to Kjeldahl’s method. The ammonia evolved was absorbed in ${\text{50 ml of 0}}{\text{.5 M }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{.}}$ The residual acid required ${\text{60 mL of 0}}{\text{.5 M}}$ solution of ${\text{NaOH}}$ for neutralisation. Find the percentage composition of nitrogen in the compound.
Ans: Given: The total mass of organic compound is ${\text{0}}{\text{.50 g}}{\text{.}}$
${\text{60 mL of 0}}{\text{.5 M}}$ solution of ${\text{NaOH}}$ was required for neutralisation by residual acid.
$ {\text{60 mL of 0}}{\text{.5 M NaOH solution = }}\dfrac{{60}}{2}{\text{ mL of 0}}{\text{.5M }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{}} $
$ {\text{ }}\dfrac{{60}}{2}{\text{ mL of 0}}{\text{.5M }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{ = 30 mL of 0}}{\text{.5 M }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}} $
Therefore, acid consumed in absorption of evolved ammonia is calculated as
${\text{ = }}\left( {{\text{50 - 30}}} \right){\text{ mL }} $
$ {\text{ = 20 mL}} $
Again, ${\text{20 mL of 0}}{\text{.5 M }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{ = 40 mL of 0}}{\text{.5 M N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$
Also, since ${\text{1000 mL of 1 M N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$contains ${\text{14 g}}$ of nitrogen, the mass of nitrogen in ${\text{40 mL of 0}}{\text{.5 M N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ is calculated as
${\text{Mass of N = }}\dfrac{{14{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}40{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}0.5}}{{1000}}{\text{ }} $
$ = {\text{ }}0.28{\text{ g}} $
Therefore, the percentage of nitrogen in ${\text{0}}{\text{.50 g}}$ of organic compound is calculated as
${\text{Percentage of nitrogen = }}\dfrac{{0.28}}{{0.5}}{\text{ }} \times {\text{ 100% }} $
$ {\text{ = 56 % }}$
34. ${\text{0}}{\text{.3780 g}}$ of an organic chloro compound gave ${\text{0}}{\text{.5740 g}}$ of silver chloride in Carius estimation. Calculate the percentage of chlorine present in the compound.
Ans: Given: The mass of organic compound is ${\text{0}}{\text{.3780 g}}$ and the mass of silver chloride formed is ${\text{0}}{\text{.5740 g}}{\text{.}}$
The molar mass of ${\text{AgCl}}$ is $143.32{\text{ g}}/{\text{mol}}$ and the molar mass of chlorine is $35.5{\text{ g}}/{\text{mol}}{\text{.}}$
One mole of silver chloride contains one mole of chlorine. So, the mass of chlorine in ${\text{0}}{\text{.5740 g}}$ of silver chloride is calculated as
$ {\text{Mass of AgCl = }}\dfrac{{{\text{35}}{\text{.5 }} \times {\text{ 0}}{\text{.5740}}}}{{143.32}}{\text{ }}$
$ {\text{ = 0}}{\text{.1421 g}}$
Thus, the percentage of chlorine is calculated as
${\text{Percentage of chlorine = }}\dfrac{{0.1421}}{{0.3780}}{\text{ }} \times {\text{ 100% }}$
${\text{ = 37}}{\text{.59 % }} $
Hence, the percentage of chlorine is ${\text{37}}{\text{.59 % }}{\text{.}}$
35. In the estimation of sulphur by Carius method, $0.468{\text{ g}}$ of an organic sulphur compound afforded ${\text{0}}{\text{.668 g}}$ of barium sulphate. Find out the percentage of sulphur in the given compound.
Ans: Given: The total mass of organic compound is $0.468{\text{ g}}$ and the mass of barium sulphate formed is ${\text{0}}{\text{.668 g}}{\text{.}}$
The molar mass of ${\text{BaS}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ is $233{\text{ g}}/{\text{mol}}$ and the molar mass of sulphur is $32{\text{ g}}/{\text{mol}}{\text{.}}$
So,
${\text{1 mol of BaS}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{ = 233 g of BaS}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{ }} $
$ {\text{ = 32 g of sulphur}} $
Thus,
$0.668{\text{ g of BaS}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{{\text{32 }} \times {\text{ 0}}{\text{.668}}}}{{233}}{\text{ g of sulphur}} $
$ {\text{ = 0}}{\text{.0917 g of sulphur}}$
Therefore, the percentage of sulphur is calculated as
${\text{Percentage of sulphur = }}\dfrac{{0.0917}}{{0.468}}{\text{ }} \times {\text{ 100% }} $
$ {\text{ = 19}}{\text{.59 % }} $
Hence, the percentage of sulphur is ${\text{19}}{\text{.59 % }}{\text{.}}$
36. In the organic compound ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ = CH -- C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ -- C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ -- C }} \equiv {\text{ CH,}}$the pair of hydridised orbitals involved in the formation of: ${\text{C2 -- C3}}$ bond is:
$\left( {\text{a}} \right){\text{ }}sp{\text{ }}--{\text{ }}s{p^2}{\text{ }} $
$\left( {\text{b}} \right){\text{ }}sp{\text{ }}--{\text{ }}s{p^3}{\text{ }} $
$ \left( {\text{c}} \right){\text{ }}s{p^2}{\text{ }}--{\text{ }}s{p^3}{\text{ }} $
$ \left( {\text{d}} \right){\text{ }}s{p^3}{\text{ }}--{\text{ }}s{p^3} $
Ans: The given organic compound is shown below.
$\mathop {\text{C}}\limits^1 {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ = }}\mathop {\text{C}}\limits^2 {\text{H -- }}\mathop {\text{C}}\limits^3 {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ -- }}\mathop {\text{C}}\limits^4 {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ -- }}\mathop {\text{C}}\limits^5 {\text{ }} \equiv {\text{ }}\mathop {\text{C}}\limits^6 {\text{H}}$
The hybridization of carbon atoms numbered as 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 are $sp,{\text{ }}sp,{\text{ }}s{p^3}{\text{ }},{\text{ }}s{p^3}{\text{ }},{\text{ }}s{p^2}{\text{ }},{\text{ and }}s{p^2}$ respectively. Therefore, the pair of hybridized orbitals involved in the formation of ${\text{C2 -- C3}}$ bond is $sp{\text{ }}--{\text{ }}s{p^3}.$
37. In the Lassaigne’s test for nitrogen in an organic compound, the Prussian blue colour is obtained due to the formation of:
$ \left( {\text{a}} \right){\text{ N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{4}}}\left[ {{\text{Fe}}{{\left( {{\text{CN}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right]{\text{ }} $
$\left( {\text{b}} \right){\text{ F}}{{\text{e}}_{\text{4}}}{\left[ {{\text{Fe}}{{\left( {{\text{CN}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right]_{\text{3}}}{\text{ }} $
$ \left( {\text{c}} \right){\text{ F}}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}\left[ {{\text{Fe}}{{\left( {{\text{CN}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right]{\text{ }} $
$\left( {\text{d}} \right){\text{ F}}{{\text{e}}_{\text{3}}}{\left[ {{\text{Fe}}{{\left( {{\text{CN}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right]_{\text{4}}} $
Ans: The sodium fusion extract is heated with iron (II) sulphate and then acidified with sulphuric acid in the Lassaigne's test for nitrogen in an organic molecule. Sodium cyanide initially interacts with iron (II) sulphate to generate sodium hexacyanoferrate (II). The iron (II) is then oxidized by sulphuric acid to generate iron (III) hexacyanoferrate (II), which is Prussian blue. The chemical reactions involved are shown below.
$6{\text{C}}{{\text{N}}^ - }{\text{ }} + {\text{ F}}{{\text{e}}^{2 + }}{\text{ }} \to {\left[ {{\text{Fe}}{{\left( {{\text{CN}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right]^{4 - }} $
$3{\left[ {{\text{Fe}}{{\left( {{\text{CN}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right]^{4 - }}{\text{ }} + {\text{ 4F}}{{\text{e}}^{3 + }}{\text{ }}\xrightarrow{{x.{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}}}{\text{ }}\mathop {{\text{F}}{{\text{e}}_4}{{\left[ {{\text{Fe}}{{\left( {{\text{CN}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right]}_3}.x{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}}\limits_{{\text{Prussian Blue}}} $
Therefore, the Prussian blue color is formed due to the formation of complex ${\text{F}}{{\text{e}}_4}{\left[ {{\text{Fe}}{{\left( {{\text{CN}}} \right)}_{\text{6}}}} \right]_3}.$
38. Which of the following carbocation is most stable?
$\left( {\text{a}} \right){\text{ }}{\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)_3}{\text{C}}{\text{.}}\mathop {\text{C}}\limits^{\text{ + }} {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}} $
$\left( {\text{b}} \right){\text{ }}{\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)_3}\mathop {\text{C}}\limits^{\text{ + }} $
$ \left( {\text{c}} \right){\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}\mathop {\text{C}}\limits^{\text{ + }} {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}} $
$\left( {\text{d}} \right){\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\mathop {\text{C}}\limits^ + {\text{HC}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} $
Ans: ${\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)_3}\mathop {\text{C}}\limits^{\text{ + }} $ is a tertiary carbocation. Because of the electron-releasing effect of three methyl groups, a tertiary carbocation is the most stable carbocation. Three methyl groups increase the + I effect, which stabilizes the positive charge on the carbocation. The stability of tertiary carbocations is also due to hyperconjugation and resonance energy.
39. The best and latest technique for isolation, purification and separation of organic compounds is:
Crystallization
Distillation
Sublimation
Chromatography
Ans: Chromatography is the most effective and up-to-date method of separating and purifying organic molecules. Initially, it was employed to separate a combination of colored substances.
40. The reaction: ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{I + KO}}{{\text{H}}_{\left( {aq} \right)}}{\text{ }} \to {\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH + KI}}$ is classified as:
Electrophilic substitution
Nucleophilic substitution
Elimination
Addition
Ans: The reaction is given as:
${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{I + KO}}{{\text{H}}_{\left( {{\text{aq}}} \right)}}{\text{ }} \to {\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{OH + KI}}$
It shows a nucleophilic substitution reaction. The hydroxyl group of potassium hydroxide with a lone pair serves as a nucleophile, substituting iodide ion in ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{I}}$ to produce ethanol.
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 Quick Overview of Topics
Chemistry class 11 Chapter 8 NCERT Solutions - Quick Overview of Detailed Structure of Topics and Subtopics Covered.
Topic | Subtopics |
Introduction to Organic Molecules | Definition of organic molecules, the distinction between organic and inorganic compounds |
Classification of Organic Compounds | Classification is based on functional groups, such as alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, alcohols, carboxylic acids, esters, etc. |
Isomerism | Structural isomerism, stereoisomerism, geometric isomerism, optical isomerism, examples and explanations |
Nomenclature of Organic Compounds | IUPAC nomenclature rules for naming organic compounds, naming alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, and other functional groups |
Introduction to Hydrocarbons | Definition of hydrocarbons, types of hydrocarbons (alkanes, alkenes, alkynes), properties and examples |
Structure and Bonding in Organic Molecules | Covalent bonding in organic molecules, hybridisation, sigma and pi bonds, structural formulas, molecular formulas |
Chemical Properties of Organic Compounds | Combustion, substitution, addition, and elimination reactions in organic compounds |
Some Basic Important Concepts for Organic Chemistry Class 11
Class 11 NCERT solutions help the students to go through the concepts easily. Here, find the Important concepts of Chapter 8 -Organic Chemistry -Some Basic Principles and Techniques to crack your exams.
Nomenclature:
IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) rules are used to name organic compounds systematically based on their structure and functional groups.
Prefixes, suffixes, and numbering systems are employed to denote substituents, parent chains, and functional groups.
Reactivity of Organic Compounds:
Organic compounds exhibit diverse reactivity patterns based on functional groups and structural features.
Common reactions include addition, elimination, substitution, oxidation, and reduction reactions.
Isomerism:
Isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements or spatial orientations.
Benefits of Referring to Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 8 -Organic Chemistry
The Vedantu’s Class 11 NCERT Solutions of Chapter 8 -Organic Chemistry, provided here in PDFs, offer various benefits, including:
Detailed explanations and step-by-step solutions for all topics in Organic Chemistry.
Solutions curated by experienced educators to ensure accuracy and clarity.
Solutions to a variety of problems to strengthen analytical and problem-solving abilities.
Step-by-step solutions for numerical problems and reaction mechanisms.
class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 NCERT solutions will give you insights about the General Introduction: methods of purification, qualitative and quantitative analysis, classification, and IUPAC nomenclature of organic compounds.
The section will give you crisp learnings on Electronic displacements in a covalent bond: inductive effect, electromeric effect, resonance, and hyperconjugation.
Important Study Materials for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 NCERT solutions
Students can access extra study materials on Organic Chemistry -Some Basic Principles and Techniques. These resources are available for download and offer additional support for your studies.
S. No | Important Study Material Links for Chapter 8 Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and Techniques |
1. | Class 11 Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and Techniques Important Questions |
2. | Class 11 Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and Techniques Revision Notes |
3. | Class 11 Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles and Techniques NCERT Exemplar |
Conclusion
Class 11 chemistry chapter organic chemistry NCERT solutions provide a comprehensive and reliable resource for students studying this chapter. These solutions cover the essential concepts and topics related to organic chemistry, including nomenclature, isomerism, and reactions of alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes. By utilising these solutions, students can enhance their understanding, clarify their doubts, and improve their problem-solving skills. The step-by-step explanations and detailed answers offered in the NCERT Solutions ensure that students grasp the concepts effectively. Overall, the NCERT organic chemistry class 11 solutions are a valuable tool for students to excel in their exams and gain a strong foundation in organic chemistry.
NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry | Chapter-wise Links
Access Vedantu’s chapter-wise NCERT Chemistry Class 11 Solutions PDFs below for all other chapters.
S. No | Links for Chapter-wise NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | Chapter 3 - Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Solutions |
4 | Chapter 4 - Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Solutions |
5 | |
6 | |
7 | |
8 |
Related Important Links for Chemistry Class 11
S. No | Related Study Materials Links for Class 11 Chemistry |
1. | |
2. | |
3. | |
4. | |
5. | |
6. | |
7. | |
8. | CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Formulas |
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques (2025-26)
1. What are NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 and how do they help with CBSE exam preparation?
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 provide detailed, step-by-step explanations to all questions from Chapter 8—Organic Chemistry: Some Basic Principles and Techniques, as per the latest CBSE 2025–26 syllabus. They help students:
- Master CBSE-style answers and accepted nomenclature methods.
- Clarify concepts such as isomerism, bond fission, reaction mechanisms, and IUPAC rules.
- Develop accurate problem-solving steps, boosting exam confidence.
2. How should I approach solving isomerism and nomenclature questions in Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8?
Use the IUPAC naming conventions for organic compounds, carefully identifying parent chains, functional groups, and substituents. For isomerism:
- Structural isomerism: Same molecular formula, different atom arrangement.
- Stereoisomerism (geometrical & optical): Same connectivity, different spatial arrangement.
- Draw clear structures and apply the correct rules for each type.
3. What are the typical methods of separation and purification of organic compounds covered in Chapter 8 NCERT Solutions?
Key methods include:
- Crystallisation: Separates solids based on solubility differences.
- Distillation: Separates liquids with different boiling points.
- Steam distillation: Used for steam-volatile, water-immiscible compounds.
- Chromatography: Separates mixtures based on movement through a stationary phase.
4. Why is understanding electronic effects like inductive, resonance, and hyperconjugation crucial in organic chemistry?
Electronic effects explain reactivity and stability of organic molecules. For example:
- Inductive effect: Permanent shift of sigma electrons affects acidity/basicity.
- Resonance: Delocalises electrons, stabilising intermediates or molecules (e.g., benzene).
- Hyperconjugation: Increases carbocation stability via sigma bond electron delocalisation.
5. How do you distinguish between electrophiles and nucleophiles in NCERT Class 11 Chemistry solutions?
Electrophiles are electron-deficient species that accept electron pairs (e.g., H+, NO2+). Nucleophiles are electron-rich species that donate electron pairs (e.g., OH-, NH3, CN-). NCERT solutions provide examples and rules to identify both based on charge and structure.
6. How do NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 address qualitative and quantitative analysis of organic compounds?
NCERT Solutions explain:
- Lassaigne’s test: Detects elements like N, S, halogens by converting them to ionic form.
- Carius method: Quantifies halogens, S, and P by oxidising to measurable forms.
- Kjeldahl’s/Dumas methods: Estimate percentage of nitrogen.
7. What is the importance of reaction mechanism concepts such as homolytic and heterolytic fission in Chapter 8?
Homolytic fission splits a covalent bond evenly, forming two radicals, while heterolytic fission creates ions (carbocation and carbanion). NCERT Solutions explain these with diagrams and their application to different reaction types such as substitution, addition, and elimination, helping students classify and predict products confidently.
8. What are the FUQs (Frequently Unasked Questions) or advanced conceptual doubts students often have about Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8?
Some deeper or frequently unaddressed doubts include:
- How do resonance and hyperconjugation compete in stabilising carbocations? Resonance stabilises through delocalization over pi systems, while hyperconjugation uses adjacent sigma bonds; effectiveness depends on structure.
- What if a molecule contains multiple functional groups—how do you decide the parent chain naming in IUPAC? Priority order of functional groups is used, and the chain is numbered to give the lowest locants to the highest-priority group.
- Why does the presence of electron-withdrawing substituents increase acid strength in carboxylic acids? Electron-withdrawing groups stabilise the conjugate base, thus increasing acidity—a direct result of the inductive effect.
9. Are NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 sufficient for JEE/NEET level preparation?
For CBSE board exams, Chapter 8 NCERT Solutions are sufficient and cover all exam-relevant problems. For JEE and NEET preparation, they are essential as a base, but students are advised to practice extra problems (especially on reaction mechanisms, stereochemistry, and numerical analysis) from reference books and past year papers to aim for higher conceptual mastery.
10. What are some common mistakes students make in organic chemistry nomenclature and how can NCERT Solutions help avoid these?
Common mistakes include:
- Ignoring the longest continuous carbon chain.
- Incorrect locant assignment for functional groups and substituents.
- Mixing up prefixes and suffixes (e.g., methyl vs. methoxy).
11. Can you explain the principle behind paper chromatography as presented in NCERT Solutions for Chapter 8?
The principle of paper chromatography is that components of a mixture are separated based on their different affinities to a stationary phase (paper) and a mobile phase (solvent). Components that are less adsorbed travel further with the solvent, while those strongly adsorbed remain closer to the base line.
12. How does Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 NCERT Solutions explain the relevance of organic chemistry in real life and advanced studies?
NCERT Solutions highlight that organic chemistry forms the foundation for understanding biomolecules, pharmaceuticals, polymers, and everyday materials. The skills learned in naming, mechanism, and analysis prepare students for courses in medicine, biotechnology, and engineering, and for success in exams like NEET and JEE.
13. What strategies are suggested in NCERT Solutions for mastering problem-solving in organic chemistry Chapter 8?
Key strategies include:
- Drawing all structures out, including bond-line and condensed formulas.
- Practising stepwise mechanism writing for reactions.
- Identifying all relevant functional groups and assigning correct priorities in naming.
- Reviewing solved examples and attempting unsolved questions independently, then cross-checking with solutions.
14. Which foundational topics from Chapter 8 are frequently tested in CBSE board exams and competitive exams?
Topics frequently tested include:
- Isomerism (especially structural vs. stereoisomerism).
- IUPAC nomenclature rules for complex molecules.
- Bond fission and reaction mechanisms.
- Principles of purification and analytical techniques (chromatography, distillation).
- Qualitative/quantitative elemental analysis (Lassaigne's, Kjeldahl's methods).
15. How do NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 support conceptual understanding over rote memorization?
NCERT Solutions prioritize conceptual clarity by explaining the 'why' and 'how' behind reaction steps, importance of structure-property relationships, and methodical approaches to problem-solving. Stepwise solutions, clear diagrams, and reasoned answers encourage logical thinking, enabling students to tackle unfamiliar or higher-order questions effectively.

























