
Which is the major product obtained by hydrolysis of compounds formed by reaction between formaldehyde and ethyl magnesium bromide?
A. Ethanol
B. Propan-2-ol
C. Propan-1-ol
D. 2-Methyl-propan-2-ol
Answer
524.9k+ views
Hint: To answer the hydrolysis product, first of all we should find the product from the reaction between formaldehyde and ethyl magnesium bromide and then we will do the hydrolysis of that product.
Complete step by step solution:
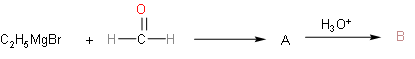
So, the above reaction explains the question. We have to find final product B after hydrolysis from A. So, first of all we'll know about Grignard reagent. In this reaction the Grignard reagent that is present is ethyl magnesium bromide. Ethyl magnesium bromide will dissociate into ethyl with negative charge and magnesium bromide with positive charge. In the formaldehyde molecule, oxygen atoms will have negative charge, so magnesium bromide will attack on oxygen part and negative part will get attached to the carbon atom in formaldehyde.
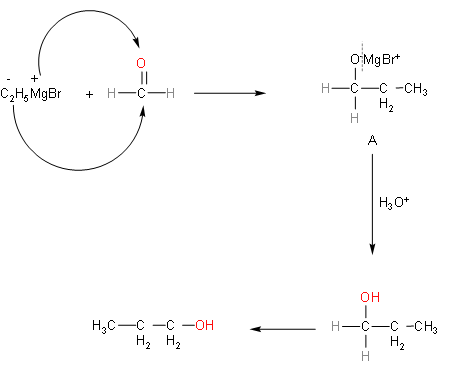
So, from the reaction we can say that A was the intermediate product and was unstable. In the second step, hydrolysis of Product-A gives us propane-1-ol.
So, the correct answer is option C.
Note:We will now know the reason for using magnesium in Grignard reagent. The reaction to the formation of Grignard reagents requires the use of magnesium ribbon. All magnesium is covered with a passivation film of magnesium oxide, which prevents reactions to organic halide. The application of Grignard preformed reagent is also used as an initiator.
We should note that formaldehyde is a colourless, strong-smelling gas used in making building materials and many household products. It is best known for its preservative and anti-bacterial properties.
Complete step by step solution:
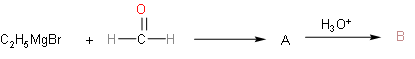
So, the above reaction explains the question. We have to find final product B after hydrolysis from A. So, first of all we'll know about Grignard reagent. In this reaction the Grignard reagent that is present is ethyl magnesium bromide. Ethyl magnesium bromide will dissociate into ethyl with negative charge and magnesium bromide with positive charge. In the formaldehyde molecule, oxygen atoms will have negative charge, so magnesium bromide will attack on oxygen part and negative part will get attached to the carbon atom in formaldehyde.

So, from the reaction we can say that A was the intermediate product and was unstable. In the second step, hydrolysis of Product-A gives us propane-1-ol.
So, the correct answer is option C.
Note:We will now know the reason for using magnesium in Grignard reagent. The reaction to the formation of Grignard reagents requires the use of magnesium ribbon. All magnesium is covered with a passivation film of magnesium oxide, which prevents reactions to organic halide. The application of Grignard preformed reagent is also used as an initiator.
We should note that formaldehyde is a colourless, strong-smelling gas used in making building materials and many household products. It is best known for its preservative and anti-bacterial properties.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

AssertionIn electrolytic refining of metal impure metal class 12 chemistry JEE_Main

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Solutions Hindi Medium (2025-26)

CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Set 1 56/2/1 2025: Question Paper, Answers & Analysis

CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Set 3 2025 with Answers

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses




