
Which of the following shows optical activity?
A.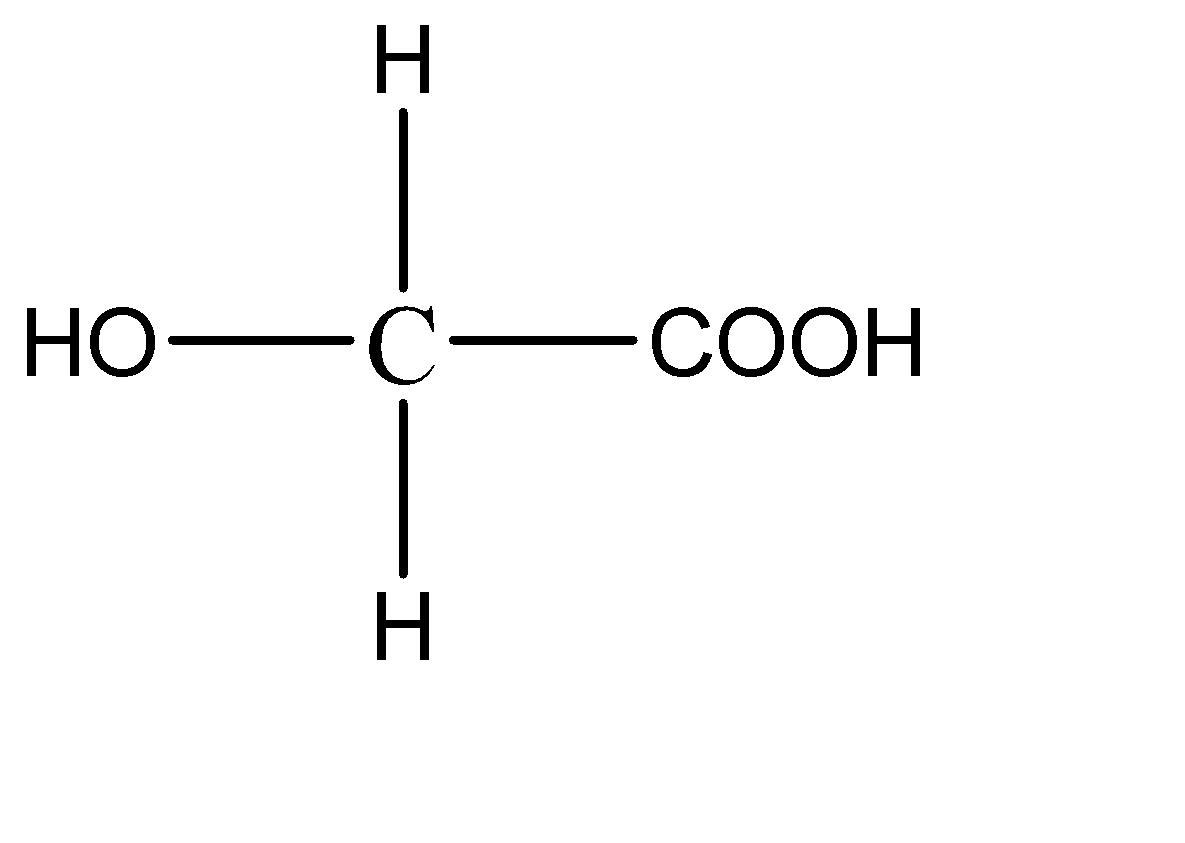
B.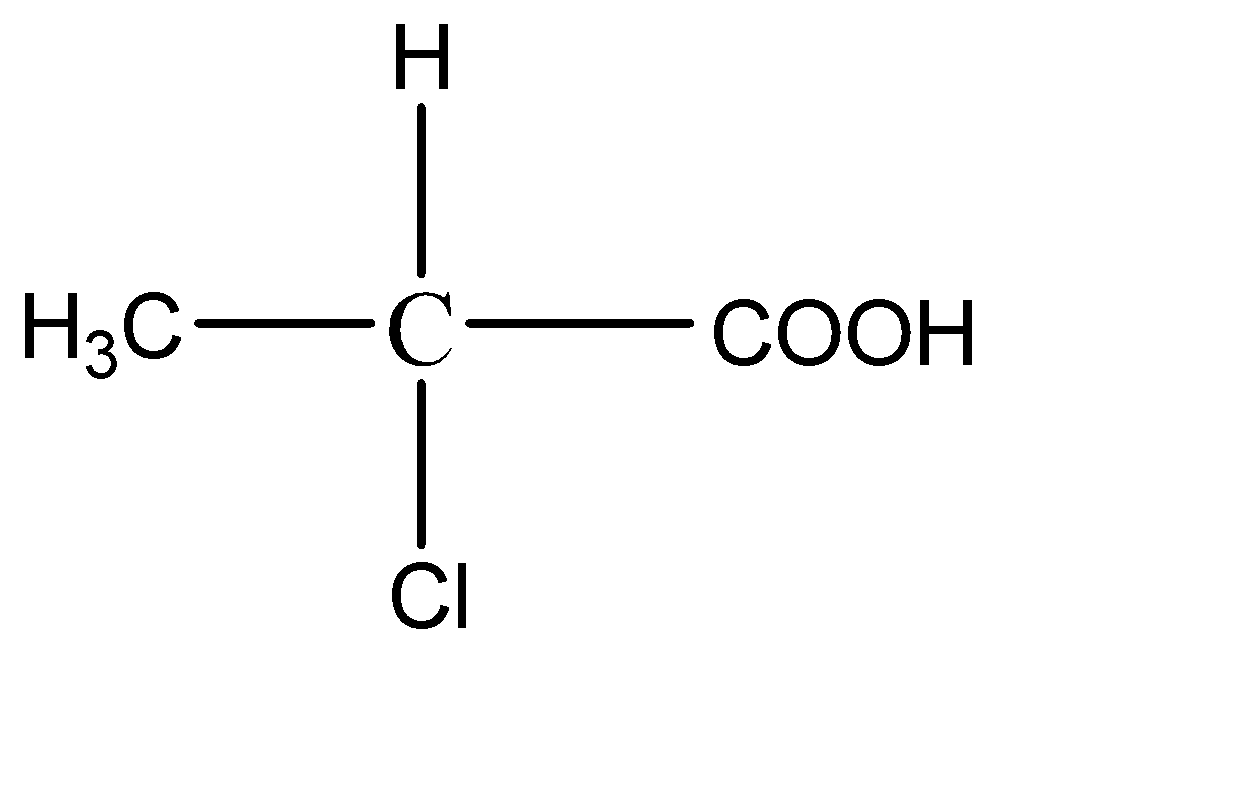
C.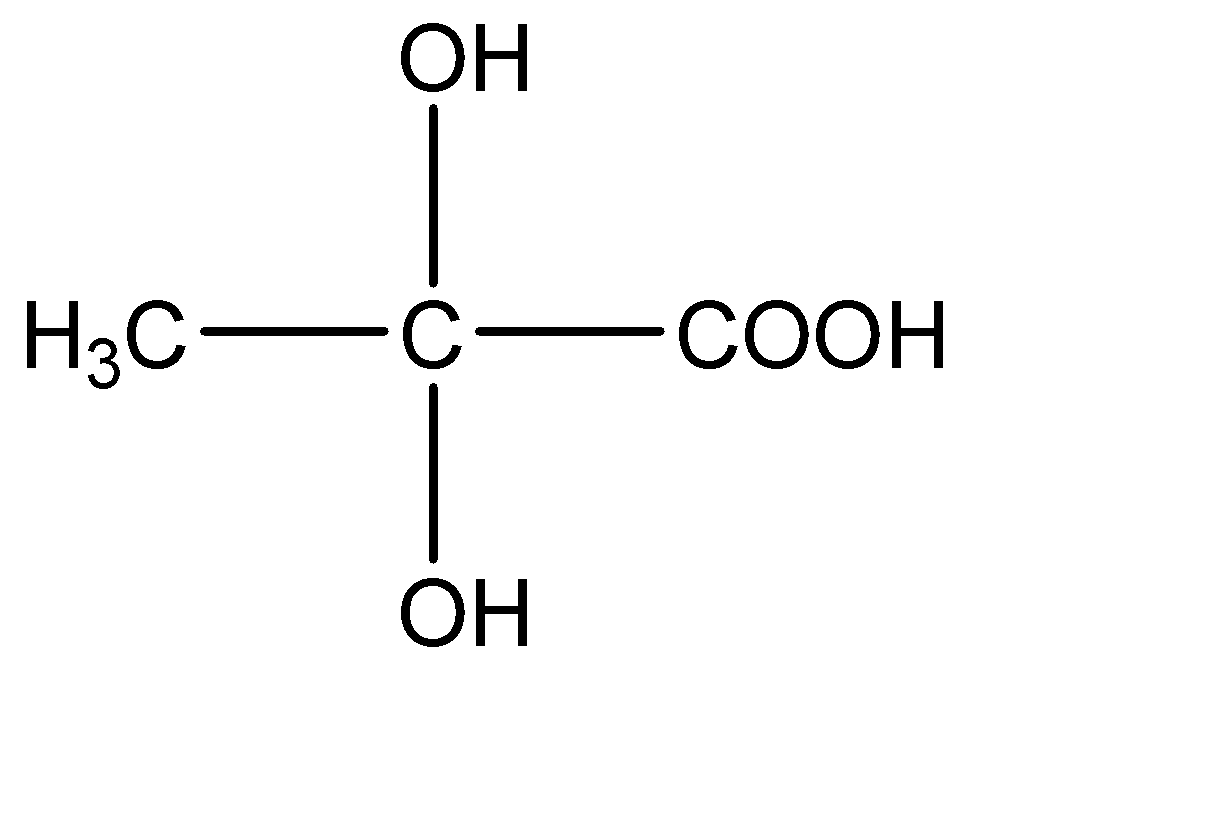
D.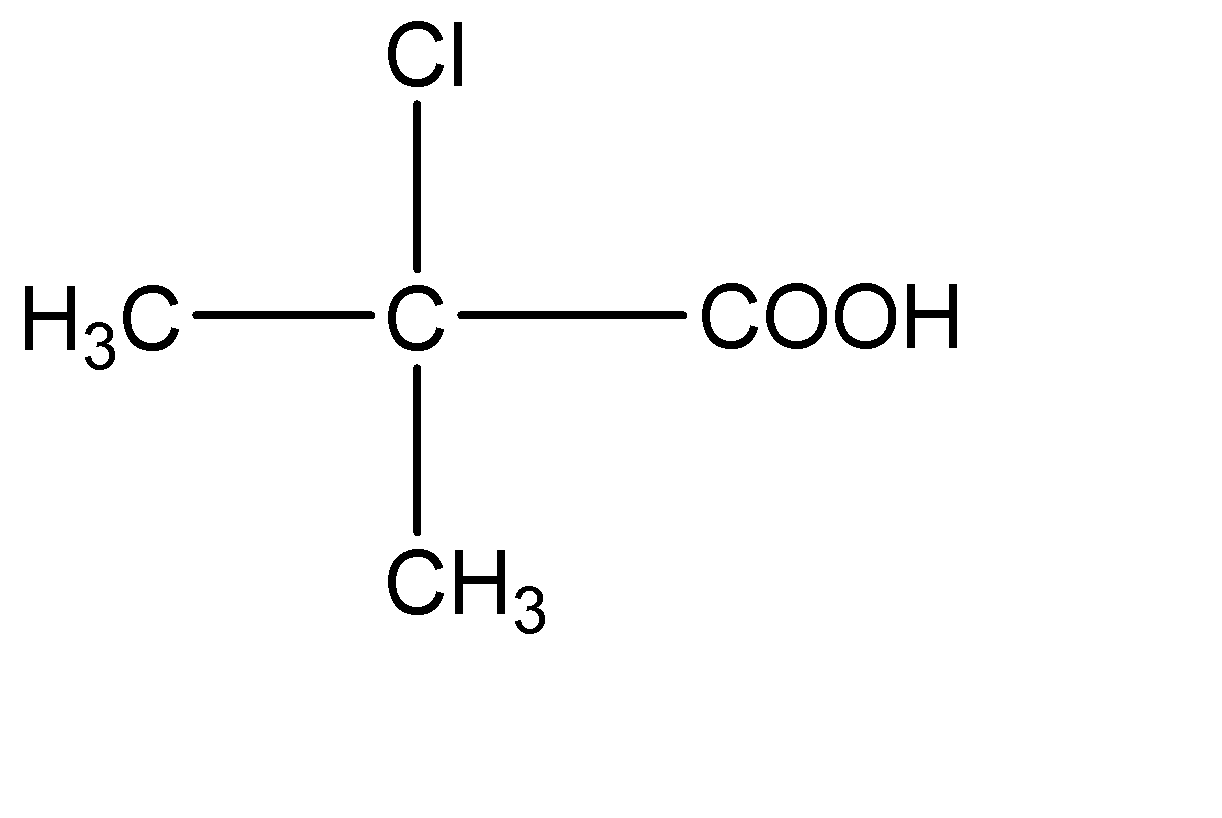
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Optical activity can be understood as a phenomenon where the chiral carbon atoms in the organic compound tend to rotate the polarized light in either a clockwise or a counter – clockwise direction.
Complete Step-by-Step Answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us discuss some important basic concepts.
In an organic compound, a chiral carbon is the carbon atom which has four different atoms or molecules attached to it. It is important that all the four bonds formed by the carbon atom have different atoms or molecules for it to be called a chiral carbon. Chiral carbons are also responsible for a phenomenon known as optical activity. On the other hand, achiral carbons can be understood as the carbon atoms which have at least two bonded atoms or molecules to be the same. Achiral carbon atoms do not show optical activity.
Hence for finding the compound which shows optical activity from the given options, we must find the compound which has a chiral carbon.
1.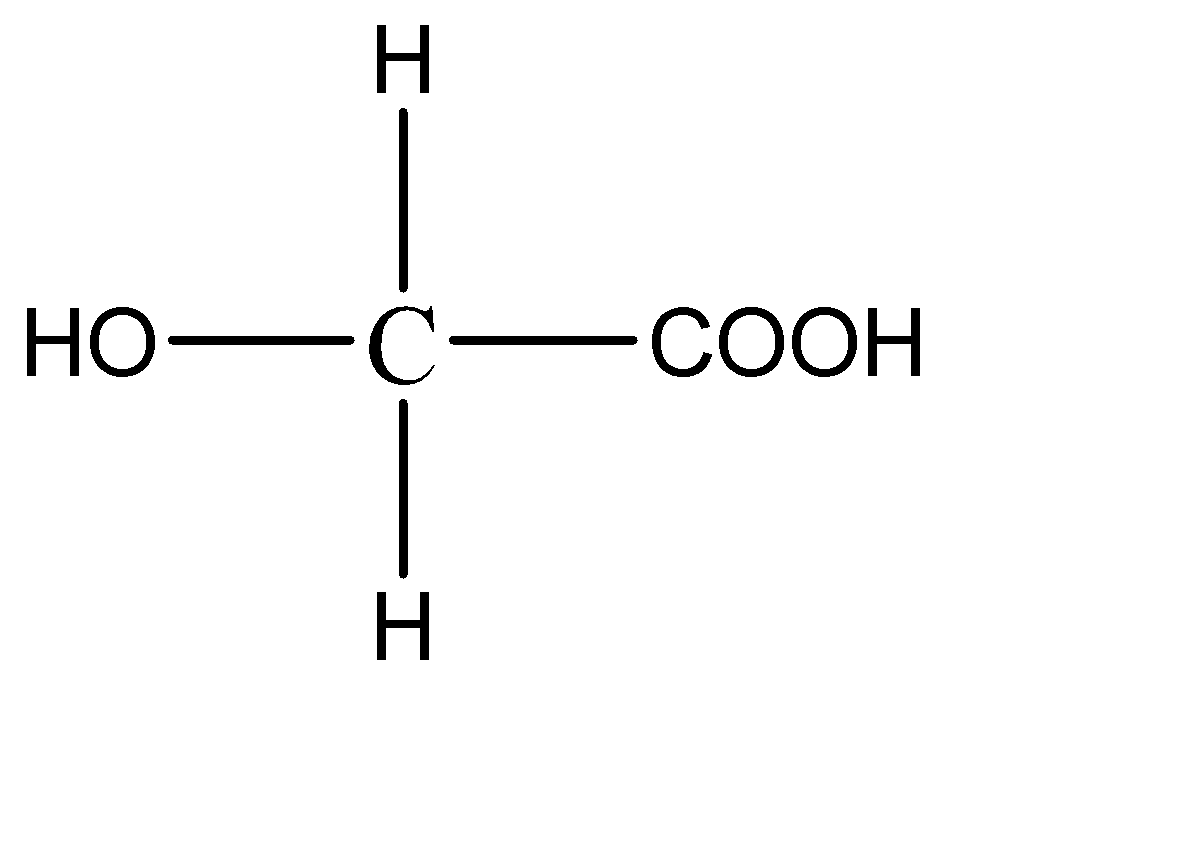
This compound has 2 hydrogen atoms on the central carbon atom. Hence this compound does not have a chiral carbon.
2.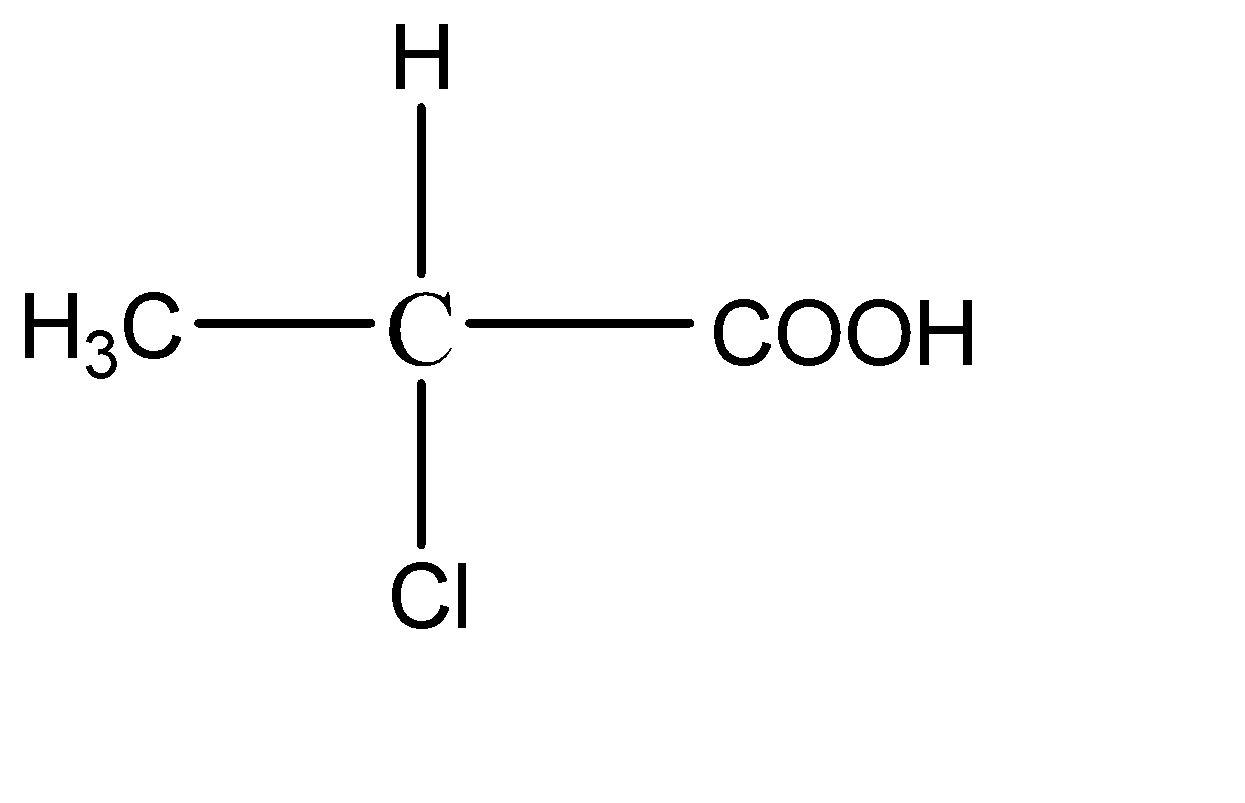
This compound has 4 different functional groups on all the bonds of the central carbon atom. Hence it has a chiral carbon.
3.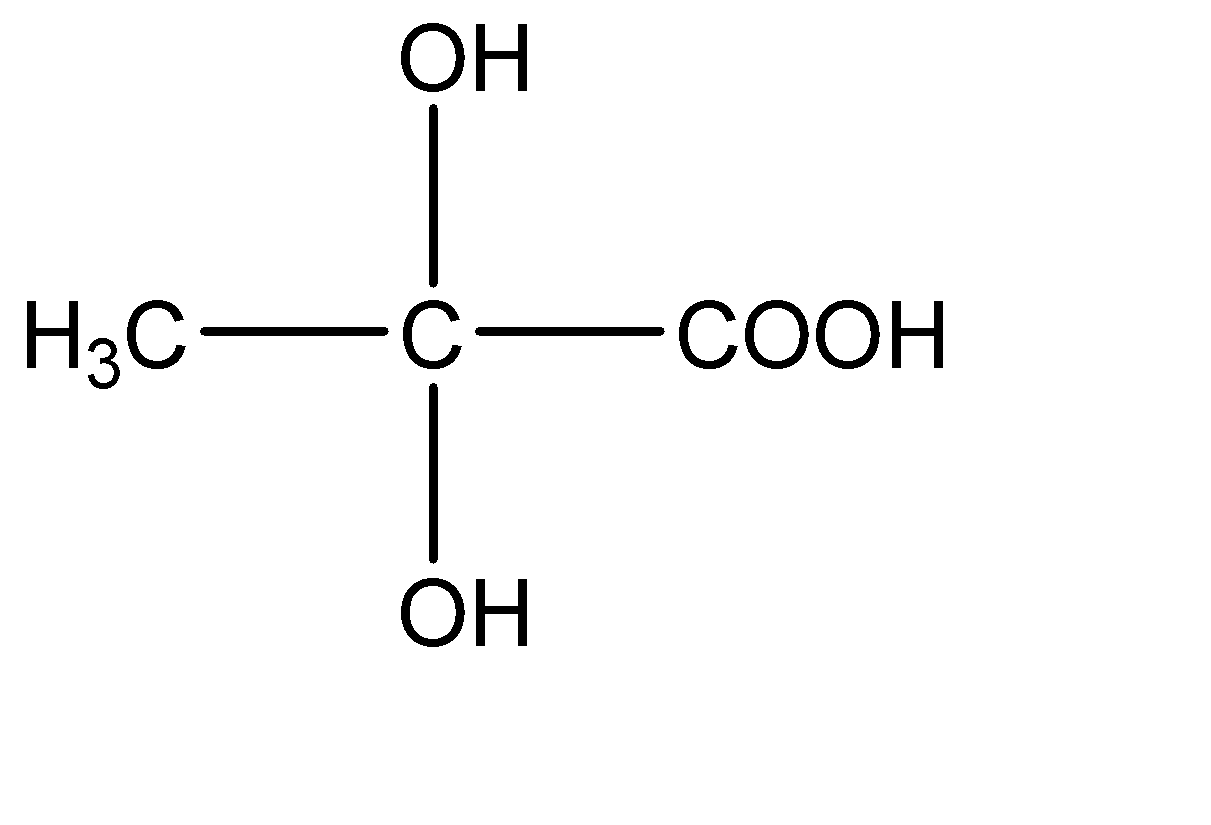
This compound has two -OH molecules on the central carbon atom. Hence this compound does not have a chiral carbon.
4.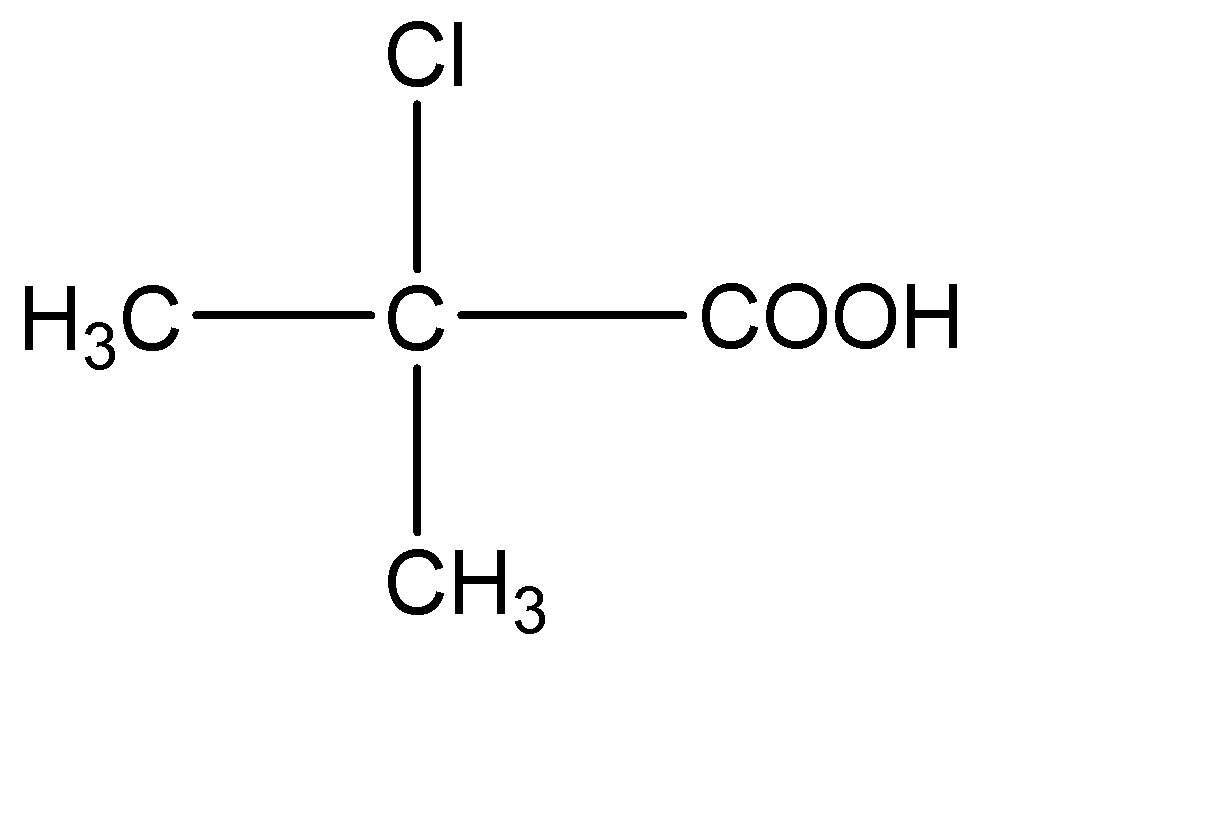
This compound has two - \[C{H_3}\] molecules on the central carbon atom. Hence this compound does not have a chiral carbon.
Hence, Option B is the correct option.
Note: In a solution if the total number of clockwise and counter – clockwise optical isomers is the same, then the solution is rendered optically inactive. This type of a mixture of optical isomers which is optically inactive is known as a racemic mixture.
Complete Step-by-Step Answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us discuss some important basic concepts.
In an organic compound, a chiral carbon is the carbon atom which has four different atoms or molecules attached to it. It is important that all the four bonds formed by the carbon atom have different atoms or molecules for it to be called a chiral carbon. Chiral carbons are also responsible for a phenomenon known as optical activity. On the other hand, achiral carbons can be understood as the carbon atoms which have at least two bonded atoms or molecules to be the same. Achiral carbon atoms do not show optical activity.
Hence for finding the compound which shows optical activity from the given options, we must find the compound which has a chiral carbon.
1.

This compound has 2 hydrogen atoms on the central carbon atom. Hence this compound does not have a chiral carbon.
2.

This compound has 4 different functional groups on all the bonds of the central carbon atom. Hence it has a chiral carbon.
3.

This compound has two -OH molecules on the central carbon atom. Hence this compound does not have a chiral carbon.
4.

This compound has two - \[C{H_3}\] molecules on the central carbon atom. Hence this compound does not have a chiral carbon.
Hence, Option B is the correct option.
Note: In a solution if the total number of clockwise and counter – clockwise optical isomers is the same, then the solution is rendered optically inactive. This type of a mixture of optical isomers which is optically inactive is known as a racemic mixture.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




