Complete Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 5 - Learn with Expert Guidance
NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit Of Life (2025-26)
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit Of Life (2025-26)
1. Why is the cell called the fundamental unit in Class 9 Science Chapter 5?
In Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life, the cell is called the fundamental unit because all living organisms are made up of cells, and all life processes occur within cells.
2. Which chapter introduces cells in Ch 5 Science Class 9?
Cells are introduced in Ch 5 Science Class 9, titled The Fundamental Unit of Life, which is part of the Class 9 Science NCERT syllabus.
3. What types of cell-related questions are asked from Class 9 Science Chapter 5?
Class 9 Science Chapter 5 question answer includes definition-based questions, difference-based questions, short explanations, and diagram-based questions related to cell organelles in The Fundamental Unit of Life.
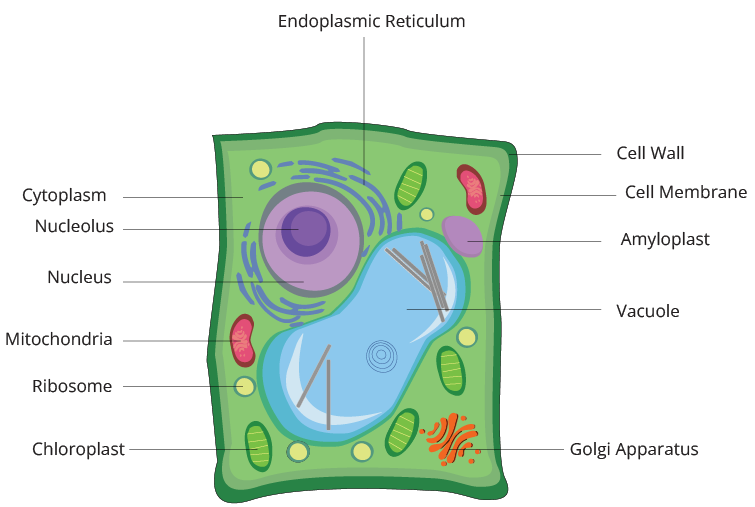
4. How are plant cells and animal cells explained in The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9?
In The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 Science Chapter 5, plant cells and animal cells are explained by comparing their structures, such as the presence of a cell wall and chloroplasts in plant cells.
5. What role do cell organelles play in Class 9 Science Chapter 5?
Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life explains how cell organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, and ribosomes perform specific functions essential for the survival of cells.
6. From where are Class 9 Science Chapter 5 questions and answers prepared?
Class 9 Science Chapter 5 questions and answers are prepared strictly from the NCERT textbook and explained in detail in NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 5.
7. Why do students look for The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 questions and answers PDF?
Students prefer The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 questions and answers PDF because it provides organised explanations of Class 9 Science Chapter 5 that are easy to access and follow.
8. How does NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 5 explain microscopic structures?
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 5 explain microscopic structures using simple language and stepwise descriptions, helping Class 9 Science students understand concepts from The Fundamental Unit of Life clearly.
9. What is the academic importance of The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 Science?
The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 Science Chapter 5 is academically important because it forms the base for future Biology chapters in higher classes and strengthens core concepts in Class 9 Science.
10. How are diagrams addressed in Class 9 Science Chapter 5 question answer?
In Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life, diagram-based questions focus on labeling and explaining cell parts, which are clearly covered in NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 5.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video