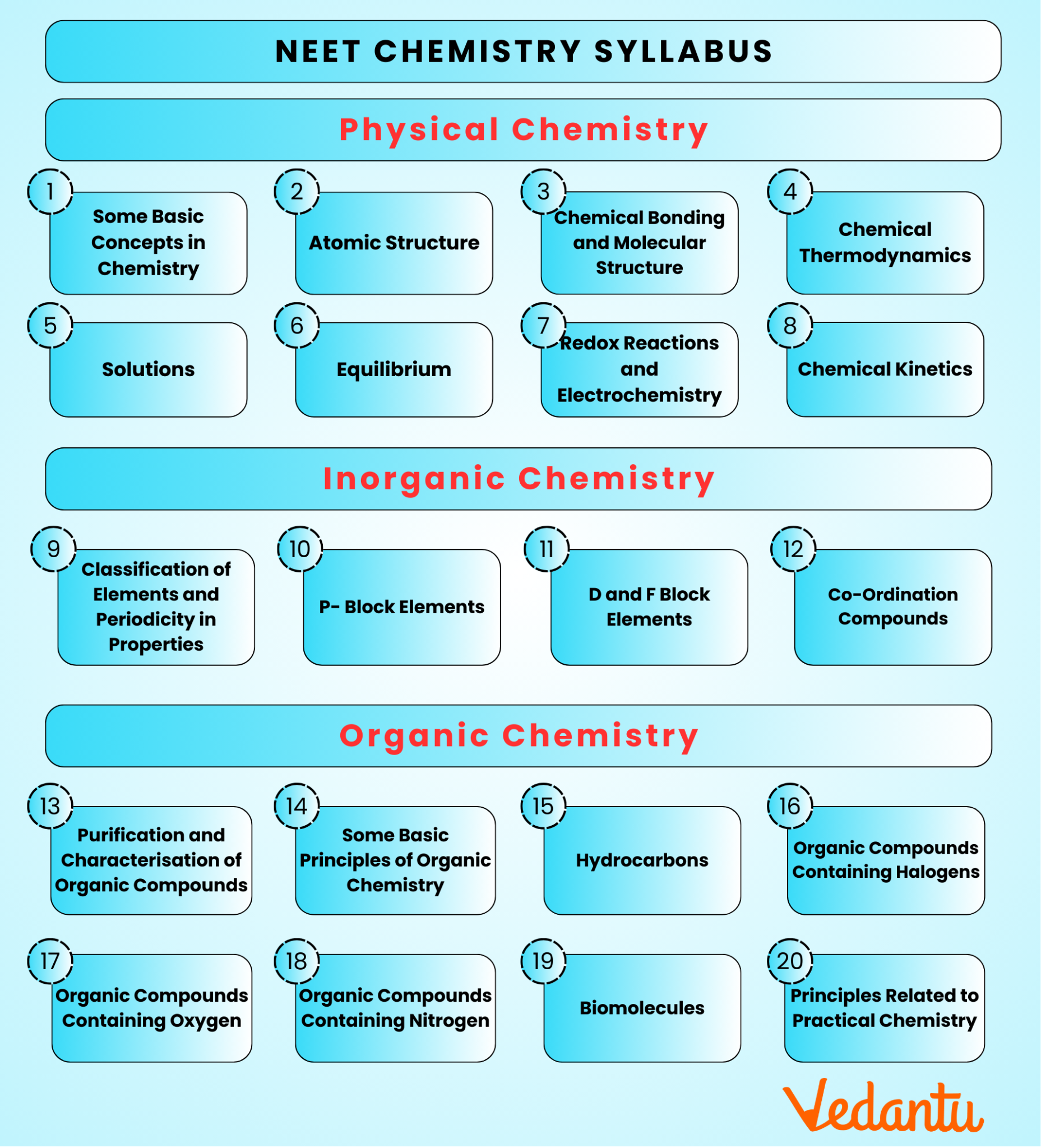
NEET 2026 Chemistry Syllabus – Complete Topic-wise Breakdown
FAQs on NEET 2026 Chemistry Syllabus: Check Detailed Topics and Subtopics
1. What is the NEET Chemistry Syllabus 2026?
The NEET Chemistry Syllabus 2026 is divided into three main sections: Physical Chemistry, Organic Chemistry, and Inorganic Chemistry. It includes topics from both Class 11 and Class 12, covering subjects like atomic structure, chemical bonding, thermodynamics, organic compounds, and coordination chemistry.
2. What is the Chemistry Syllabus for NEET 2026?
The Chemistry syllabus for NEET 2026 includes topics from Class 11 such as Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry, Structure of Atom, Thermodynamics, and States of Matter, and Class 12 topics like Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids, Coordination Compounds, and Surface Chemistry.
3. What are the Important Topics in NEET 2026 Chemistry Syllabus?
Important topics for NEET 2026 Chemistry include:
Physical Chemistry: Mole Concept, Chemical Kinetics, Thermodynamics, and Atomic Structure.
Organic Chemistry: Alcohols, Ethers, Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, and Organic Compounds.
Inorganic Chemistry: Coordination Compounds, Chemical Bonding, and p-block elements.
4. Is There Any Deleted Syllabus in NEET 2026 Chemistry?
The NEET deleted syllabus 2026 chemistry removes certain chapters as per the National Medical Commission (NMC) guidelines. Topics like Environmental Chemistry, Biomolecules, and some parts of p-block elements may be excluded or reduced for NEET 2026, depending on official notifications.
5. How is the NEET 2026 Chemistry Syllabus Reduced?
The Chemistry reduced syllabus for NEET 2026 has some modifications as part of the effort to streamline the curriculum. Certain chapters and topics have been cut down or excluded based on the official guidelines, so candidates should refer to the most recent syllabus published by the National Testing Agency (NTA).
6. How Can I Prepare for the NEET Chemistry Syllabus 2026?
To prepare effectively for the NEET 2026 Chemistry syllabus, focus on understanding the basic concepts, practicing previous year question papers, and revising key formulas, chemical reactions, and equations. Regular mock tests and reference books can also help in achieving a high score.
7.What are the 79 chapters for NEET 2026?
The NEET 2026 syllabus consists of 79 chapters across Physics, Chemistry, and Biology.
6.Is NEET 2026 easy?
The difficulty level of NEET 2026 is expected to be moderate to difficult.
7.Can I crack NEET in 3 months?
Cracking NEET in 3 months is challenging but possible with a strategic study plan, focusing on high-yield topics, and consistent practice.
8.Which is the hardest chapter in NEET Chemistry?
The difficulty of chapters varies among students; however, topics like Thermodynamics and Organic Chemistry are often considered challenging.
9.How many hours should I study Chemistry for NEET?
It's recommended to dedicate 3-4 hours daily to Chemistry, balancing between Physical, Organic, and Inorganic sections.
10.Is Earthworm in NEET syllabus 2026?
Specific details about the inclusion of Earthworm in the NEET 2026 syllabus are not provided in the available sources.
11.Will NEET 2026 be conducted in two phases?
There is no official information suggesting that NEET 2026 will be conducted in two phases.
12.Is 10 years' paper enough for NEET?
Practicing the past 10 years' papers is beneficial, but supplementing with mock tests and current study materials is essential.
13.Can I score 700 in NEET in 100 days?
Achieving a score of 700 in 100 days requires an intensive, well-structured study plan, thorough understanding of concepts, and rigorous practice.
14.Is NEET 2026 syllabus reduced?
Yes, the NEET 2026 syllabus has been reduced, with certain topics removed or modified.
15. Is 590 a good score in NEET?
A score of 590 is considered good and may secure admission to reputable medical colleges, depending on that year's cutoffs.