




Polygenic Inheritance- Understanding Its Definition, Examples in Humans and Plants
Polygenic inheritance explains how multiple genes work together to determine a single trait, leading to continuous variation in characteristics such as height, skin Colour, or weight. This topic is a key part of NEET Biology, helping students understand the complexity behind traits influenced by many genes. This page clarifies these concepts so learners can see how various genetic factors combine to produce the differences observed in populations. By understanding polygenic inheritance, you gain insights into the genetic basis of continuous variation, an essential component of modern biology and medical research.
Polygenic Inheritance Definition
Polygenic inheritance, also known as multiple gene or multiple factor inheritance, refers to a form of quantitative inheritance where two or more independent genes collectively influence a single trait. Each gene adds a small effect to the overall phenotype, resulting in a range of continuous variation (e.g., skin Colour, height, and weight).
Traits of Polygenic Inheritance
Look at the table below. It shows how different Genes control a single Trait for a Human Being.
Key Characteristics of Polygenic Inheritance
Polygenes- Each gene involved exerts a minor effect on the phenotype, and detecting the impact of a single gene can be challenging.
Additive Effect- Multiple genes produce an equal, cumulative influence on a trait, with no single gene dominating.
No Epistasis- There is no masking effect between genes at different loci; contributing alleles are called “active,” while non-contributing alleles are “null.”
No Dominance or Linkage- Polygenic traits depend on the combined effect of multiple alleles, rather than a simple dominant-recessive relationship.
Continuous Variation- Phenotypes show a broad range of forms, making it difficult to predict the exact outcome.
Difference from Multiple Alleles- In multiple alleles (e.g., ABO blood group), three or more alleles exist at the same locus, although each individual only carries two. Polygenic traits, however, involve multiple genes at different loci.
Complex Prediction- Because many genes interact, statistical methods are often used to estimate how a trait distributes in a population.
Examples of Polygenic Inheritance
Polygenic traits appear in many organisms, including humans, where they influence a wide array of characteristics and disease risks. Common examples include-
Skin Colour
Hair Colour
Eye Colour
Height
Blood Pressure
Risk for Certain Diseases
Resistance to Specific Infections
Polygenic Inheritance in Humans- Skin Pigmentation
A notable example of polygenic inheritance is human skin pigmentation. Research shows that around 60 different loci can contribute to this trait. To illustrate, imagine three distinct unlinked loci, each with two alleles (A/a, B/b, and C/c). Capital letters (A, B, C) represent alleles for darker skin, and lowercase letters (a, b, c) represent lighter skin. The more uppercase alleles are present, the darker the skin tone becomes.
Parental Genotypes- AABBCC (dark skin) × aabbcc (light skin)
F₁ Generation- All offspring are AaBbCc (intermediate skin Colour)
F₂ Generation (AaBbCc × AaBbCc)- Results in a range of skin tones from very dark to very light. The ratio of these phenotypes is 1-6-15-20-15-6-1.
These small, additive genetic effects illustrate how polygenic inheritance produces continuous variation in traits, making them more complex to study than single-gene (Mendelian) inheritance.
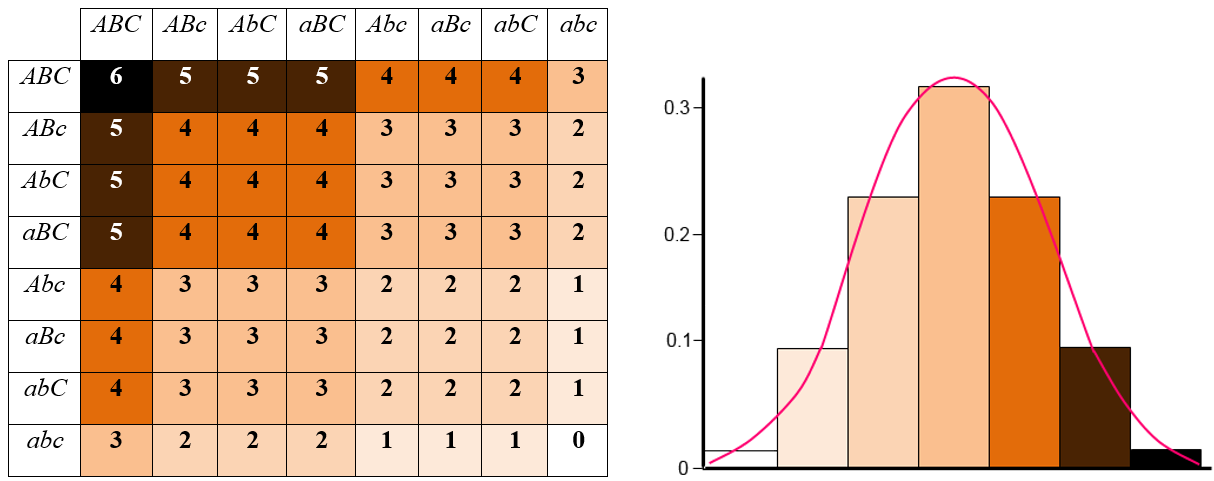
Punnett Square and Continuous Variation in F₂ Generation
When examining polygenic traits, a Punnett square can illustrate the continuous range of phenotypes in the F₂ generation. This progression can span from lighter variants to darker ones, showcasing how multiple genes contribute to a broad spectrum of traits.
Examples of Polygenic Inheritance in Humans
Height
About 400 genes influence human height.
Environmental factors such as nutrition and health also play a big role.
Eye Colour
Determined by multiple genes (at least 9 recognised eye Colours).
Two main genes and 14 additional genes affect the trait, and many of these are located on the X chromosome.
A varying number of alleles contributes to different eye colours.
Polygenic Inheritance in Plants
Plants exhibit polygenic traits in characteristics such as stem Colour and shape, pollen attributes, flower Colour, yield, oil content, seed size, and time to maturity or flowering.
Kernel Colour in Wheat
Three independent allele pairs influence kernel Colour.
A cross between dark red (AABBCC) and white (aabbcc) kernels yields F₁ offspring with intermediate red kernels (AaBbCc).
Crossing two F₁ plants produces F₂ offspring in varying shades of red to white in a ratio of 63 red (with multiple intensities) to 1 white.
Corolla Length in Tobacco
Around five genes affect corolla length.
Polygenic inheritance here leads to a wide range of lengths, reflecting how multiple genes can drive continuous variation.
Environmental Influence on Polygenic Inheritance
Genotype and Phenotype Range- The genetic makeup (genotype) sets the possible range for a trait, but environmental conditions determine the actual expression (phenotype) within those limits.
Norm of Reaction- This term describes how broadly a phenotype can vary for a given genotype under different environmental conditions. It can be narrow or broad depending on the trait.
Examples of Environmental Impact-
Identical twins raised separately can show differences in traits like height or intelligence due to distinct environments.
Human traits such as intelligence, depression, height, skin Colour, and schizophrenia can be influenced by lifestyle, climate, and other external factors.
Diet and overall health strongly affect height.
Hydrangea flower Colour changes with soil aluminum levels.
Himalayan rabbit fur, Colour patterns vary based on temperature.
In essence, both genes and environment interact to shape the continuous variations observed in polygenic traits, making it a cornerstone concept in understanding how complex characteristics develop in both plants and animals.
Essential Study Materials for NEET UG Success
FAQs on Polygenic Inheritance- Definition, Examples in Plants and Humans for NEET
1. What is Polygenic Inheritance?
Polygenic inheritance involves multiple genes contributing to a single trait. Each gene adds a small effect, leading to continuous variation, such as height or skin Colour in humans.
2. How is Polygenic Inheritance Different from Multiple Alleles?
In multiple alleles, three or more forms of a gene exist at the same locus, but each individual only carries two of those alleles (e.g., ABO blood groups). In polygenic inheritance, multiple genes at different loci collectively influence one trait.
3. Why Does Polygenic Inheritance Result in Continuous Variation?
Because multiple genes each make a small contribution, their combined effects produce a wide spectrum of possible phenotypes. This gradual range is called continuous variation.
4. What are Some Common Examples of Polygenic Inheritance in Humans?
Traits such as height, skin Colour, eye Colour, hair Colour, and even certain disease risks (like blood pressure or mental health conditions) often involve polygenic inheritance.
5. Does the Environment Affect Polygenic Traits?
Yes. Environmental factors—such as nutrition, climate, and overall health—can influence how genes are expressed. This interaction can modify the final phenotype within the range set by an individual’s genotype.
6. Can You Provide an Example of Polygenic Inheritance in Plants?
In wheat, kernel Colour is controlled by three pairs of alleles. Crossing dark red kernels with white kernels can yield various shades of red in the F₂ generation, illustrating continuous variation.
7. What is the Norm of Reaction?
The norm of reaction refers to the range of possible phenotypes a genotype can produce under different environmental conditions. Some genotypes have narrow ranges, while others have broad ones.
8. Why is Polygenic Inheritance Hard to Predict?
Multiple genes and environmental influences create complex interactions, making it difficult to accurately forecast the exact phenotype. Statistical methods are often used to study and predict these patterns in populations.
9. How Many Genes are Involved in Determining Human Height?
Research suggests that around 400 genes contribute to human height. These genes, along with environmental factors like diet and health, influence an individual’s final stature.
10. Is Eye Colour Purely Genetic or Also Influenced by the Environment?
Eye colour is primarily determined by multiple genes (with at least two main genes and numerous others involved). Environmental factors don’t typically alter eye colour as drastically as they do height or skin pigmentation, but minor influences can occur.























