
2, 3 dimethyl but-2-ene when reacted with bromine forms a compound which upon heating with alcoholic $ \text{KOH} $ produces the following major product:
(A)
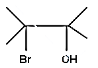
(B)
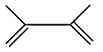
(C)
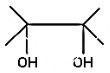
(D)
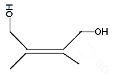




Answer
548.4k+ views
Hint: The addition of alcoholic $ \text{KOH} $ to an alkyl halide followed by heating the substance leads to the formation of an alkene and this takes place through an elimination reaction. The hydroxyl atom of the alcohol acts as a string base that helps in the extraction of a beta hydrogen atom from the alkyl halide.
Complete Stepwise Solution:
The reaction of 2, 2 dimethyl but-2-ene with bromine can be given as follows:
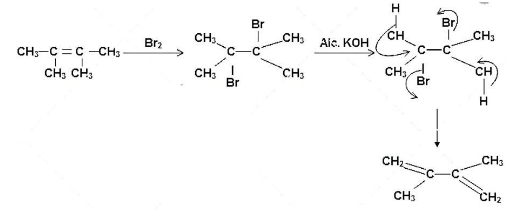
In the first step, the bromine molecule adds onto the carbon atoms of the double bond to form 2,3 – dibromo, 2,3-dimethyl butane. The addition of the alcoholic potassium hydroxide solution follows next that results in the formation of the 2,3-dimethyl but-1, 3- dinene. This is from the attack of the hydroxyl group of alcoholic potassium hydroxide that attacks the beta-hydrogen atoms with respect to the bromine atoms and two beta-elimination reactions take place in the molecule leading to the formation of the diene.
Hence, the compound formed when 2, 3 dimethyl but-2-ene reacts with bromine forms a compound which upon heating with alcoholic $ \text{KOH} $ is 2,3-dimethyl but-1, 3- dinene, option B.
Note:
The bromination of the alkenes or the alkynes is a non-stereoselective reaction as the bromine molecule being non-polar, it adds onto the alkene or the alkyne non-selectively. Potassium hydroxide when dissolved in water and that aqueous solution is added to any alkene or alkyne then it behaves as a strong base that adds to the double bond and forms the alcohol from the alkene and alkynes.
Complete Stepwise Solution:
The reaction of 2, 2 dimethyl but-2-ene with bromine can be given as follows:

In the first step, the bromine molecule adds onto the carbon atoms of the double bond to form 2,3 – dibromo, 2,3-dimethyl butane. The addition of the alcoholic potassium hydroxide solution follows next that results in the formation of the 2,3-dimethyl but-1, 3- dinene. This is from the attack of the hydroxyl group of alcoholic potassium hydroxide that attacks the beta-hydrogen atoms with respect to the bromine atoms and two beta-elimination reactions take place in the molecule leading to the formation of the diene.
Hence, the compound formed when 2, 3 dimethyl but-2-ene reacts with bromine forms a compound which upon heating with alcoholic $ \text{KOH} $ is 2,3-dimethyl but-1, 3- dinene, option B.
Note:
The bromination of the alkenes or the alkynes is a non-stereoselective reaction as the bromine molecule being non-polar, it adds onto the alkene or the alkyne non-selectively. Potassium hydroxide when dissolved in water and that aqueous solution is added to any alkene or alkyne then it behaves as a strong base that adds to the double bond and forms the alcohol from the alkene and alkynes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




