
A Bio convex lens of Focal length 15 cm is in Front of a plane mirror the distance between the lens and the mirror is 10cm. A small object is kept at a distance of 30 cm from the Lens. The final image is:
A. Virtual and at a distance of 16 cm from the mirror.
B. Real and at a distance of 16 cm from the mirror.
C. Virtual and at a distance of 20 cm from the mirror.
D. Real and at a distance of 20 cm from the mirror.
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint:Biconvex lens are simple lenses which consist of two convex surfaces in spherical form, generally having the same kind of curvature.
Complete step by step answer:
We get the image distance by using lens
Formula \[\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{15}-\dfrac{1}{30}\Rightarrow v=30\text{ cm}\]
\[v=30\text{ cm}\] in front of the Convex mirror, which means 20 cm behind the mirror. Assuming a mirror to reflect from both the sides, this image will act as a virtual object for the mirror and second image. \[{{I}_{2}}\] will be formed at 20 cm in front of the mirror.
1. Understanding the convention used while taking
\[+ve\] and \[-ve\]sign for Image and object distance, the direction along which ray of light is travel taken as \[+ve\]
2. Focal length:
For convex lens \[+ve\]
For concave lens \[-ve\]
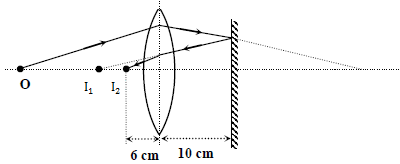
So, here the ray of light is coming from behind the mirror towards lens, for the second image \[{{I}_{2}}\] with respect to lens,
\[u=+10\text{ cm};f=15\text{ cm}\]
By using lens formula
\[\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{10}=\dfrac{1}{15}\]
\[\Rightarrow v=6\text{ cm}\]
So, this image is at a distance of \[10+6=16\text{ cm}\] in front of the mirror.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
In this we need to remember that we need to find the distance of the image from the mirror. So we need to add 10 to give a final answer.
Also real images are always inverted in nature. In this converging rays actually made a collection of focus points which we called a real image because generally an image is a collection of focus points in optics.
Complete step by step answer:
We get the image distance by using lens
Formula \[\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{15}-\dfrac{1}{30}\Rightarrow v=30\text{ cm}\]
\[v=30\text{ cm}\] in front of the Convex mirror, which means 20 cm behind the mirror. Assuming a mirror to reflect from both the sides, this image will act as a virtual object for the mirror and second image. \[{{I}_{2}}\] will be formed at 20 cm in front of the mirror.
1. Understanding the convention used while taking
\[+ve\] and \[-ve\]sign for Image and object distance, the direction along which ray of light is travel taken as \[+ve\]
2. Focal length:
For convex lens \[+ve\]
For concave lens \[-ve\]

So, here the ray of light is coming from behind the mirror towards lens, for the second image \[{{I}_{2}}\] with respect to lens,
\[u=+10\text{ cm};f=15\text{ cm}\]
By using lens formula
\[\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{10}=\dfrac{1}{15}\]
\[\Rightarrow v=6\text{ cm}\]
So, this image is at a distance of \[10+6=16\text{ cm}\] in front of the mirror.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
In this we need to remember that we need to find the distance of the image from the mirror. So we need to add 10 to give a final answer.
Also real images are always inverted in nature. In this converging rays actually made a collection of focus points which we called a real image because generally an image is a collection of focus points in optics.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




