
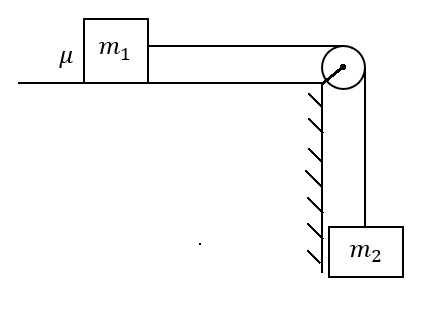
A block of mass \[{m_1}\] is resting on a rough horizontal plane, the coefficient of the kinetic friction between the block and the surface is \[\mu \]. If \[{m_1}\] is connected to another mass \[{m_2}\] with the help of string and pulley as shown in the figure, then the common acceleration when the system is released from the rest will be
A. \[\dfrac{{{m_2}g}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}}\]
B. \[\dfrac{{{m_2}g}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}}\]
C. \[\dfrac{{\mu \left( {{m_2} + {m_1}} \right)}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}}g\]
D. \[\left[ {\dfrac{{{m_2} - \mu {m_1}}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}}} \right]g\]

Answer
583.5k+ views
Hint: Apply Newton’s second law of motion to both the masses and rearrange the equations you got to determine the effective acceleration of the system.
Complete step by step answer:
Draw a free body diagram to denote the forces acting on the above system as follows,
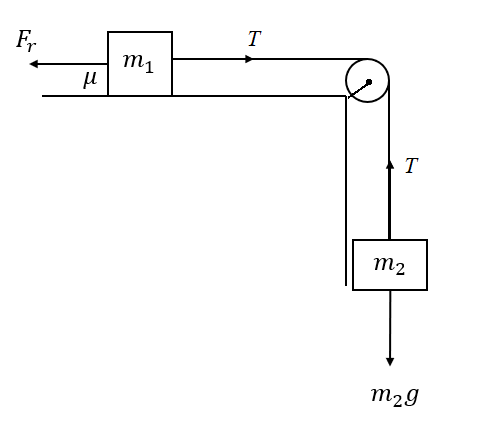
In the above free body diagram, \[{F_r}\] is the frictional force acting on the mass \[{m_1}\], T is the tension in the string, and \[{m_2}g\] is the weight of \[{m_2}\].
Apply Newton’s second law of motion on the mass \[{m_1}\] as follows,
\[{F_{net}} = {m_1}a\]
\[ \Rightarrow T - {F_r} = {m_1}a\] …… (1)
We know that the frictional force acting on the mass \[{m_1}\] is given by the equation,
\[{F_r} = \mu {m_1}g\]
Therefore, equation (1) becomes,
\[ \Rightarrow T - \mu {m_1}g = {m_1}a\] …… (2)
Apply Newton’s second law of motion on the mass \[{m_2}\] as follows,
\[T - {m_2}g = {m_2}\left( { - a} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow T - {m_2}g = - {m_2}a\] …… (3)
Here, the negative sign of the acceleration implies that the mass is accelerated in the downward direction.
Subtract equation (2) from equation (3).
\[T - {m_2}g - \left( {T - \mu {m_1}g} \right) = - {m_2}a - {m_1}a\]
\[ \Rightarrow {m_2}g - \mu {m_1}g = \left( {{m_1} + {m_2}} \right)a\]
\[\therefore a = \dfrac{{\left( {{m_2} - \mu {m_1}} \right)}}{{\left( {{m_1} + {m_2}} \right)}}g\]
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
Always specify the direction of the forces and the direction of the acceleration of the body. In this problem, the direction of the mass \[{m_1}\] is towards right and hence taken positive while the direction of the acceleration of the mass \[{m_2}\] is downwards, hence taken as negative.
Complete step by step answer:
Draw a free body diagram to denote the forces acting on the above system as follows,

In the above free body diagram, \[{F_r}\] is the frictional force acting on the mass \[{m_1}\], T is the tension in the string, and \[{m_2}g\] is the weight of \[{m_2}\].
Apply Newton’s second law of motion on the mass \[{m_1}\] as follows,
\[{F_{net}} = {m_1}a\]
\[ \Rightarrow T - {F_r} = {m_1}a\] …… (1)
We know that the frictional force acting on the mass \[{m_1}\] is given by the equation,
\[{F_r} = \mu {m_1}g\]
Therefore, equation (1) becomes,
\[ \Rightarrow T - \mu {m_1}g = {m_1}a\] …… (2)
Apply Newton’s second law of motion on the mass \[{m_2}\] as follows,
\[T - {m_2}g = {m_2}\left( { - a} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow T - {m_2}g = - {m_2}a\] …… (3)
Here, the negative sign of the acceleration implies that the mass is accelerated in the downward direction.
Subtract equation (2) from equation (3).
\[T - {m_2}g - \left( {T - \mu {m_1}g} \right) = - {m_2}a - {m_1}a\]
\[ \Rightarrow {m_2}g - \mu {m_1}g = \left( {{m_1} + {m_2}} \right)a\]
\[\therefore a = \dfrac{{\left( {{m_2} - \mu {m_1}} \right)}}{{\left( {{m_1} + {m_2}} \right)}}g\]
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
Always specify the direction of the forces and the direction of the acceleration of the body. In this problem, the direction of the mass \[{m_1}\] is towards right and hence taken positive while the direction of the acceleration of the mass \[{m_2}\] is downwards, hence taken as negative.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




