
A catalyst increases the rate of reaction by……
A. Decreasing enthalpy
B. Decreasing internal energy
C. Decreasing activation energy
D. Increasing activation energy
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: A catalyst is a substance that can be added to a reaction to increase the react rate without – getting consumed in the process often only very small amounts of catalyst are required the concept of catalysis was invented by chemist E. Fulhame based on work in oxidation – reduction experiment. The term catalysis was used by Jons Jakob Berzelius in $1835$ to describe reactions that are accelerated by substances that remain unchanged after the reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
In general chemical reactions occur faster in the presence of a catalyst because the catalyst provides an alternative reaction pathway or mechanism with a lower activation energy than the non – catalysed mechanism. In catalysed mechanisms the catalyst usually reacts to form an intermediate which then regenerates the original catalyst in a process.
Catalysts work by providing a mechanism involving a different transition state and lower activation energy, consequently more molecules have the energy needed to reach the transition state. Hence, catalysts can enable reactions that would otherwise be blocked or slowed by a kinetic barrier. The catalyst may increase reaction rate or selectivity or enable the reaction at lower temperature. This effect can be illustrated with an energy profile diagram.
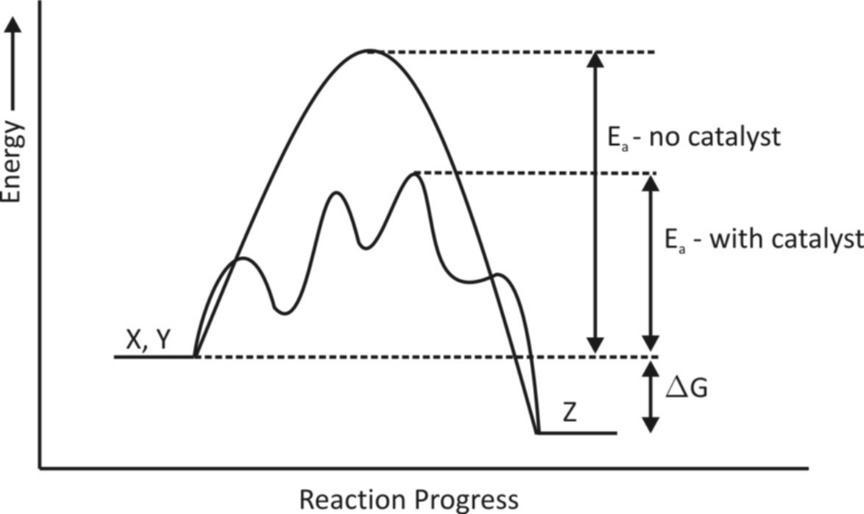
Generic potential energy diagram showing the effect of a catalyst in a hypothetical exothermic chemical reaction$X + Y\xrightarrow{{}}Z$.
The presence of the catalyst opens the different reaction pathway with a lower activation energy. The final result and the overall thermodynamic are the same.
The correct option is (C) – Decreasing activation energy.
Note:
The function of enzymes in the living system is to catalyse biochemical reactions. Enzymes are highly substrate specific and catalyse reaction by providing an alternate pathway of lower activation energy. A catalyst increases rate of reacting by decreasing activation energy and increasing the enthalpy change of the reaction
Complete step by step answer:
In general chemical reactions occur faster in the presence of a catalyst because the catalyst provides an alternative reaction pathway or mechanism with a lower activation energy than the non – catalysed mechanism. In catalysed mechanisms the catalyst usually reacts to form an intermediate which then regenerates the original catalyst in a process.
Catalysts work by providing a mechanism involving a different transition state and lower activation energy, consequently more molecules have the energy needed to reach the transition state. Hence, catalysts can enable reactions that would otherwise be blocked or slowed by a kinetic barrier. The catalyst may increase reaction rate or selectivity or enable the reaction at lower temperature. This effect can be illustrated with an energy profile diagram.

Generic potential energy diagram showing the effect of a catalyst in a hypothetical exothermic chemical reaction$X + Y\xrightarrow{{}}Z$.
The presence of the catalyst opens the different reaction pathway with a lower activation energy. The final result and the overall thermodynamic are the same.
The correct option is (C) – Decreasing activation energy.
Note:
The function of enzymes in the living system is to catalyse biochemical reactions. Enzymes are highly substrate specific and catalyse reaction by providing an alternate pathway of lower activation energy. A catalyst increases rate of reacting by decreasing activation energy and increasing the enthalpy change of the reaction
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




