
What is a Chromosome? draw a labeled diagram of the structure of the Eukaryotic Chromosome.
Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint:Chromosomes are structures in the form of an x and packed within the nucleus of the cell in condensation. In the chromosome is included the genetic material of the cell. The chromosomes pass the genetic data from the parent to the infant.
Complete answer:The chromosomes are normally a structure like a thread which is packed very densely inside the cell nucleus and heavily enveloped. The chromosome consists of the cell's DNA and a protein unit called histone. The individual's thread is spun around the histone protein unit. The chromosome has a central point, called the centromere, which divides the chromosome into two sections, top, and bottom. It is like X in the form of a chromosome. The top of the chromosome is called the P-arm and the bottom of the Q arm. The p arm's length is shorter than that of the q arm. We have mentioned that the chromosome has a protein that is coiled into the DNA so that it can coil properly. DNA visualization is a complex and microscope-based operation. It cannot be seen.
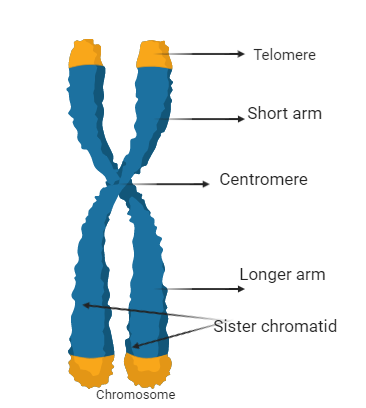
The condensed structure of the DNA in the chromosome is arranged in compact form with H1, H2A, H2b, H3, and H4 histone proteins. This is the structure that can be seen during the cell division metaphase. The long DNA in the eukaryotes can be packaged into the nucleus of the cell via this condensed packaging.
The p-arm and the q-arm are two weapons known. The kinetochore forms for the association of the spindle fibers during cell division. There is a restriction called the centromere. The centromere’s location describes the chromosome type as metacentric, submetacentric, acrocentric, and telocentric. At the end of the arm is a telomere which is in extremely compact areas such as the centromere. There are high heterochromatin condensation and less chromatin condensation in areas. To observe the chromosome, you must first dissect the DNA, but then you can only see the chromosome.
Note: Remember, the genetic material in the chromosome is doubled in the process of sexual gametogenesis and then sent to the gametes so that genetic integrity among parents and offspring are retained when the fusion occurs or the cell grows. The genetic material is replicated using the mitosis process.
Complete answer:The chromosomes are normally a structure like a thread which is packed very densely inside the cell nucleus and heavily enveloped. The chromosome consists of the cell's DNA and a protein unit called histone. The individual's thread is spun around the histone protein unit. The chromosome has a central point, called the centromere, which divides the chromosome into two sections, top, and bottom. It is like X in the form of a chromosome. The top of the chromosome is called the P-arm and the bottom of the Q arm. The p arm's length is shorter than that of the q arm. We have mentioned that the chromosome has a protein that is coiled into the DNA so that it can coil properly. DNA visualization is a complex and microscope-based operation. It cannot be seen.

The condensed structure of the DNA in the chromosome is arranged in compact form with H1, H2A, H2b, H3, and H4 histone proteins. This is the structure that can be seen during the cell division metaphase. The long DNA in the eukaryotes can be packaged into the nucleus of the cell via this condensed packaging.
The p-arm and the q-arm are two weapons known. The kinetochore forms for the association of the spindle fibers during cell division. There is a restriction called the centromere. The centromere’s location describes the chromosome type as metacentric, submetacentric, acrocentric, and telocentric. At the end of the arm is a telomere which is in extremely compact areas such as the centromere. There are high heterochromatin condensation and less chromatin condensation in areas. To observe the chromosome, you must first dissect the DNA, but then you can only see the chromosome.
Note: Remember, the genetic material in the chromosome is doubled in the process of sexual gametogenesis and then sent to the gametes so that genetic integrity among parents and offspring are retained when the fusion occurs or the cell grows. The genetic material is replicated using the mitosis process.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




