
When a cross is made between a tall plant with yellow seeds (TtYy) and a tall plant with the green seed (Ttyy), what proportion of phenotype in the offspring could be expected to be
A. Tall and green
B. Dwarf and green
Answer
560.7k+ views
Hint: The scientist, Gregor Mendel performed dihybrid crosses on pea plants and discovered a fundamental law of genetics known as the Law of Independent Assortment. From his experiment, he observed that the pairs of traits in the parental generation sorted independently from one another, from one generation to the next. The dihybrid cross allows one to look at the pattern of inheritance of two different traits at the same time.
Complete answer: The main purpose of the dihybrid cross was to determine if any relationship existed between the different allelic pairs. Since the given phenotype of the TtYy parent, it’s quite clear that the tallness is dominant over the dwarfism and also the yellow seed is dominant over the green seeds. The genotype of the green and tall progeny will be TTyy and Ttyy, and that of the dwarf and the green progeny will be ttyy. The proportion of the tall and the green progeny is three and the proportion of the dwarf and the green progeny is one.
In a dihybrid cross, the parents carry different pairs of the alleles for each trait. One parent carries the homozygous dominant allele, while the other one carries the homozygous recessive allele. The offsprings produced after the crosses in the F1 generation are all heterozygous for the specific traits.
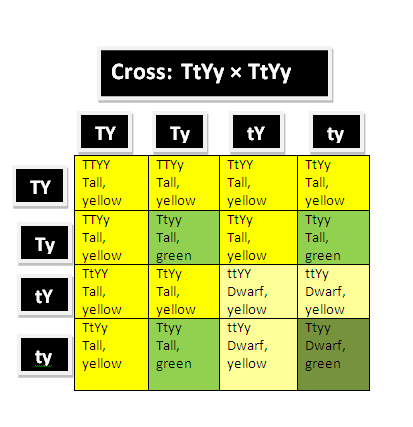
A. The proportion of tall and green plant is 3/16.
B. The proportion of Dwarf and green plant is 1/16.
Note: The dihybrid cross is a cross between the two different lines or the genes that differ in two observed traits. According to the statement of Mendel, between the alleles of both these loci, there is always a relationship of completely dominant - recessive traits.
Complete answer: The main purpose of the dihybrid cross was to determine if any relationship existed between the different allelic pairs. Since the given phenotype of the TtYy parent, it’s quite clear that the tallness is dominant over the dwarfism and also the yellow seed is dominant over the green seeds. The genotype of the green and tall progeny will be TTyy and Ttyy, and that of the dwarf and the green progeny will be ttyy. The proportion of the tall and the green progeny is three and the proportion of the dwarf and the green progeny is one.
In a dihybrid cross, the parents carry different pairs of the alleles for each trait. One parent carries the homozygous dominant allele, while the other one carries the homozygous recessive allele. The offsprings produced after the crosses in the F1 generation are all heterozygous for the specific traits.

A. The proportion of tall and green plant is 3/16.
B. The proportion of Dwarf and green plant is 1/16.
Note: The dihybrid cross is a cross between the two different lines or the genes that differ in two observed traits. According to the statement of Mendel, between the alleles of both these loci, there is always a relationship of completely dominant - recessive traits.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




