
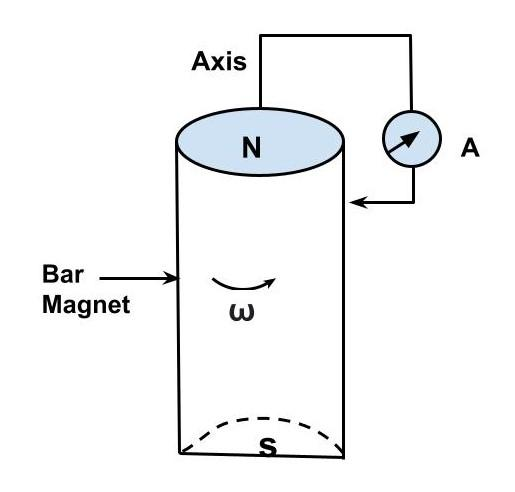
A cylindrical bar magnet is rotated about its axis as shown in the figure. A wire is connected from the axis and is made to touch the cylindrical surface through a contact. Then
A. A direct current flows in the ammeter A
B. No current flows through the ammeter A
C. An alternating sinusoidal current flows through the ammeter A with a time period $T = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega }$
D. A time varying non-sinusoidal current flows through the ammeter A

Answer
495k+ views
Hint: In order to answer the question, we need to know on which concept of electromagnetic induction on which it is based. Electromagnetic induction is the creation of emf in a wire or coil when the magnetic flux linking the coil changes.
Complete answer:
This problem makes use of the electromagnetic induction phenomenon. Induced emf occurs when the number of magnetic lines of force (magnetic flux) travelling through a circuit changes (or when a moving conductor cuts the magnetic flux). Only as long as there is a shift or cutting of flux does the induced emf remain.
When a cylindrical bar magnet is spun about its axis, there is no change in the circuit's flux, hence no emf is generated and no current flows through the ammeter A.
The correct option is: (B) No current flows through the ammeter A
Note:
It's worth mentioning that, according to Faraday's law, whenever the magnetic flux associated with a coil changes, an emf is induced in the coil. The emf persists as long as the magnetic flux changes. However, there is no movement of a bar magnet in this case, either forward or backward, or up and down.
Complete answer:
This problem makes use of the electromagnetic induction phenomenon. Induced emf occurs when the number of magnetic lines of force (magnetic flux) travelling through a circuit changes (or when a moving conductor cuts the magnetic flux). Only as long as there is a shift or cutting of flux does the induced emf remain.
When a cylindrical bar magnet is spun about its axis, there is no change in the circuit's flux, hence no emf is generated and no current flows through the ammeter A.
The correct option is: (B) No current flows through the ammeter A
Note:
It's worth mentioning that, according to Faraday's law, whenever the magnetic flux associated with a coil changes, an emf is induced in the coil. The emf persists as long as the magnetic flux changes. However, there is no movement of a bar magnet in this case, either forward or backward, or up and down.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




