
(a) Draw a labeled ray diagram showing the formation of a final image by a compound microscope at least distance of distinct vision.
(b) The total magnification produced by a compound microscope is 20. The magnification produced by the piece is 5. The microscope is focused on a certain object. The distance between the objective and eyepiece is observed to be 14cm. If the least distance of distinct vision is 20cm.Calculate the focal length of the objective and the eyepiece.
Answer
587.7k+ views
(a) Hint:
Here, we have to define a compound microscope and draw the formation of a final image by a compound microscope at least distance of distinct vision and draw the ray in a proper way and place the objective lens and the eyepiece of compound microscope at a fixed position.
Complete solution:
Firstly, we have to define the compound microscope. A compound microscope uses a lens close to the object being viewed to collect light (called the objective lens) which focuses a real image of the object inside the microscope. That image is then magnified by a second lens or group of lenses (called the eyepiece) that gives the viewer an enlarged inverted virtual image of the object. The use of a compound objective/eyepiece combination allows for much higher magnification. Compound microscope has a combination of lenses that enhances both magnifying powers as well as the resolving power.
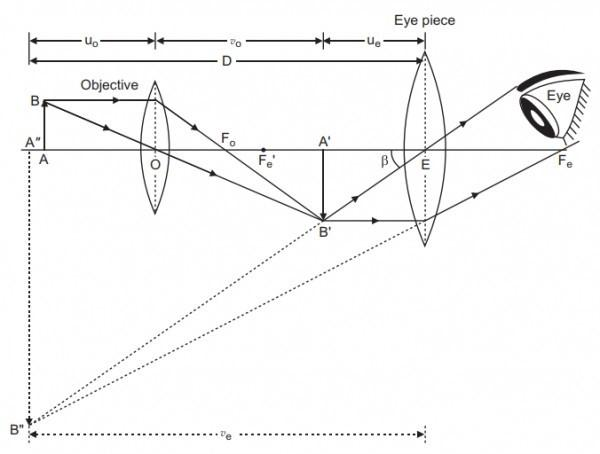
Note: Draw the ray diagram properly and be careful while drawing the rays of the objective and the eyepiece of a compound microscope.
(b) Hint: Here, we have to find the focal length of the objective and the eyepiece of a compound microscope and used the formula of total magnification $m = L {f_o} + D {f_e} = {m_o} {m_e} $ to obtain the value.
Complete solution:
For the least distance of clear vision, the total magnification is given by
$m = L {f_o} + D {f_e} = {m_o} {m_e} $
where,
$L$ is the separation between the eyepiece and the objective.
\[{f_0}\] is the focal length of the objective.
\[{f_e}\] is the focal length of the eyepiece.
\[D\] is the least distance for clear vision
Also, the given magnification for the eyepiece.
$m = L {f_o} + D {f_e} = {m_o} {m_e} $
${m_e} = 5$ $D = 20cm$ $m = 20$ $L = 14cm$
$m = {m_o} {m_e} $
${m_o} = \dfrac{m}{{{m_e}}} = \dfrac{{20}}{5} = 4$
$
20 = 14 \times 3.5 + 20 \times {f_e} \\
{f_e} = 5cm \\
$
Now, we have ${m_o} = L {f_o} $
${f_o} = \dfrac{{{m_o}}}{L} = \dfrac{{14}}{4} = 3.5cm$
Note: Remember the formula of total magnification $m = L {f_o} + D {f_e} = {m_o} {m_e} $ Be careful while putting the value in the formula and write the proper value at the exact time to obtain the value of \[{f_0}\].
Here, we have to define a compound microscope and draw the formation of a final image by a compound microscope at least distance of distinct vision and draw the ray in a proper way and place the objective lens and the eyepiece of compound microscope at a fixed position.
Complete solution:
Firstly, we have to define the compound microscope. A compound microscope uses a lens close to the object being viewed to collect light (called the objective lens) which focuses a real image of the object inside the microscope. That image is then magnified by a second lens or group of lenses (called the eyepiece) that gives the viewer an enlarged inverted virtual image of the object. The use of a compound objective/eyepiece combination allows for much higher magnification. Compound microscope has a combination of lenses that enhances both magnifying powers as well as the resolving power.

Note: Draw the ray diagram properly and be careful while drawing the rays of the objective and the eyepiece of a compound microscope.
(b) Hint: Here, we have to find the focal length of the objective and the eyepiece of a compound microscope and used the formula of total magnification $m = L {f_o} + D {f_e} = {m_o} {m_e} $ to obtain the value.
Complete solution:
For the least distance of clear vision, the total magnification is given by
$m = L {f_o} + D {f_e} = {m_o} {m_e} $
where,
$L$ is the separation between the eyepiece and the objective.
\[{f_0}\] is the focal length of the objective.
\[{f_e}\] is the focal length of the eyepiece.
\[D\] is the least distance for clear vision
Also, the given magnification for the eyepiece.
$m = L {f_o} + D {f_e} = {m_o} {m_e} $
${m_e} = 5$ $D = 20cm$ $m = 20$ $L = 14cm$
$m = {m_o} {m_e} $
${m_o} = \dfrac{m}{{{m_e}}} = \dfrac{{20}}{5} = 4$
$
20 = 14 \times 3.5 + 20 \times {f_e} \\
{f_e} = 5cm \\
$
Now, we have ${m_o} = L {f_o} $
${f_o} = \dfrac{{{m_o}}}{L} = \dfrac{{14}}{4} = 3.5cm$
Note: Remember the formula of total magnification $m = L {f_o} + D {f_e} = {m_o} {m_e} $ Be careful while putting the value in the formula and write the proper value at the exact time to obtain the value of \[{f_0}\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




