
a) Explain a monohybrid cross seed coat color as a trait Pisum sativum. Work out the cross upto F2 generation.
b) State the laws of inheritance that can be divided from such a cross.
c) How is the phenotypic ratio of F2 generation different in a dihybrid cross.
Answer
572.7k+ views
Hint:Monohybrid cross is a cross in which the only trait is taken into consideration. A Dihybrid cross is a cross in which two traits are taken into consideration.
Complete step by step answer: Observable characteristics of an organism, which are genetically controlled, are called the phenotype. The genetic constitution of an organism is called its genotype. This is related to Mendel’s experiments, understanding which we can answer these questions easily.
a) Mendel took pure varieties of a pea plant with contrasting characters.
For instance, if a pea plant with a yellow seed coat is crossed with a pea plant having a germ seed coat, then in the F1 generation all plants produce yellow seeds.
In the next season, Mendel sowed seeds obtained in the F1 generation and self-pollinated them. He found that those seeds produce varieties of yellow and green coated seeds in the ratio of \[3:1\]. He called these plants F2 generation.
Monohybrid cross
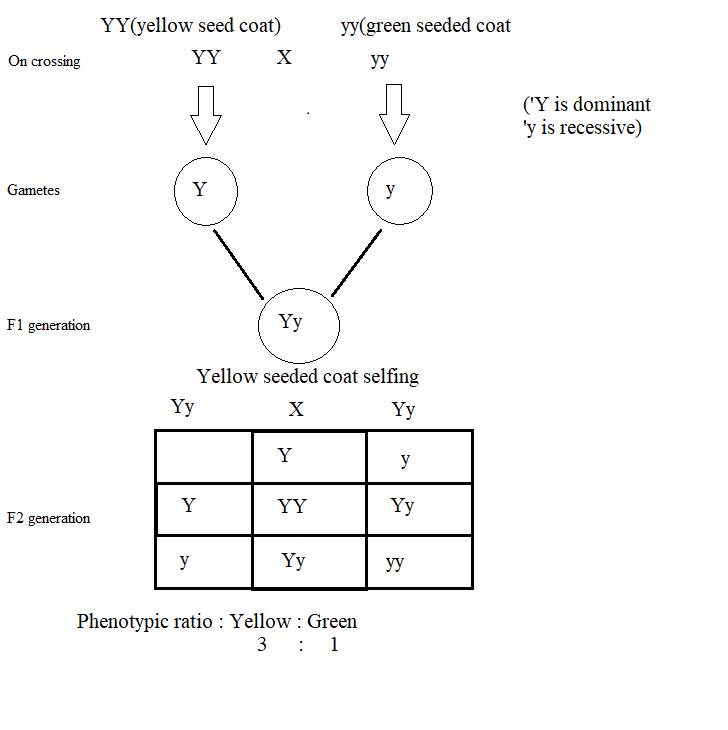
b) Two laws can be derived from such a cross,
Law of Dominance: According to this law, characters are controlled by discrete units called factors, which occur in pairs with one member of the pair dominating over the other in a dissimilar pair. It explains the expression of only one of the parental characters in the F1 generation and the expression or appearance of both in the F2 generation.
In the given cross, the allele for yellow seeds is dominant over the allele that produces green seeds. In F1 generation all offspring showed the yellow color of seed (dominant character) and expression of both yellow and green in the F2 generation.
Law of segregation: This law states that the two alleles of a pair segregate or separate during gamete formation such that a gamete receives only one of the \[2\] factors. In homozygous parents, all gametes produced are similar, while in heterozygous parents, two kinds of gametes are produced in equal proportions. The alleles for yellow and green seeds in the F1 generation segregate and the gamete either contains yellow allele or green allele giving rise to different combinations in the F2 generation. Thus, showing that the gamete receives only one of the two factors.
c) Phenotypic ratio of the F2 generation in a monohybrid cross is \[3:1\], whereas, in a dihybrid cross, it is \[9:3:3:1\].
Note:Mendel in his experiments not only crossed the plant taking the seed coat color as a trait but also worked on other pairs of contrasting traits like stem height, flower color, flower position, pod shape, pod color, seed shape, and seed color.
Complete step by step answer: Observable characteristics of an organism, which are genetically controlled, are called the phenotype. The genetic constitution of an organism is called its genotype. This is related to Mendel’s experiments, understanding which we can answer these questions easily.
a) Mendel took pure varieties of a pea plant with contrasting characters.
For instance, if a pea plant with a yellow seed coat is crossed with a pea plant having a germ seed coat, then in the F1 generation all plants produce yellow seeds.
In the next season, Mendel sowed seeds obtained in the F1 generation and self-pollinated them. He found that those seeds produce varieties of yellow and green coated seeds in the ratio of \[3:1\]. He called these plants F2 generation.
Monohybrid cross

b) Two laws can be derived from such a cross,
Law of Dominance: According to this law, characters are controlled by discrete units called factors, which occur in pairs with one member of the pair dominating over the other in a dissimilar pair. It explains the expression of only one of the parental characters in the F1 generation and the expression or appearance of both in the F2 generation.
In the given cross, the allele for yellow seeds is dominant over the allele that produces green seeds. In F1 generation all offspring showed the yellow color of seed (dominant character) and expression of both yellow and green in the F2 generation.
Law of segregation: This law states that the two alleles of a pair segregate or separate during gamete formation such that a gamete receives only one of the \[2\] factors. In homozygous parents, all gametes produced are similar, while in heterozygous parents, two kinds of gametes are produced in equal proportions. The alleles for yellow and green seeds in the F1 generation segregate and the gamete either contains yellow allele or green allele giving rise to different combinations in the F2 generation. Thus, showing that the gamete receives only one of the two factors.
c) Phenotypic ratio of the F2 generation in a monohybrid cross is \[3:1\], whereas, in a dihybrid cross, it is \[9:3:3:1\].
Note:Mendel in his experiments not only crossed the plant taking the seed coat color as a trait but also worked on other pairs of contrasting traits like stem height, flower color, flower position, pod shape, pod color, seed shape, and seed color.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




