
a) Explain Rosenmund reduction with equation.
b) How does propanone (\[C{{H}_{3}}CO{{H}_{3}}\]) react with hydrazine? Give an equation.
c) Name an oxidising agent used in the Etard's reaction.
Answer
600.6k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, we should know that Rosenmund reduction is a reaction where acid chlorides are converted into aldehydes. In the second part we should know that hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula\[{{N}_{2}}{{H}_{4}}\]. And in the third part we should know that Étard reaction is a chemical reaction that involves the direct oxidation of an aromatic bound methyl group to an aldehyde.
Step by step answer:
We will answer this solution in parts.
Rosenmund reduction: We should know that Rosenmund reduction is a reaction where acid chlorides are converted into aldehydes. We use hydrogen gas, palladium and barium sulfate. The example that we should know of this reduction is of acyl chlorides forming aldehydes. This reaction is shown below:

We should know that in the above equation, the high reactivity of hydrogen gas makes it readily initiate a substitution in the acyl chloride, forming HCl and the required aldehyde.
Now, we will discuss the second part of the question. We should know that propanone is a ketone. And from this we can say that ketones can be converted to a hydrazine derivative by reaction with hydrazine. Let us react with propanone with hydrazine.

We should note that, these hydrazones that are produced, they can be further converted to the corresponding alkane by reaction with base and heat. These two steps can be combined into one reaction called the Wolff-Kishner Reduction which represents a general method for converting aldehydes and ketones into alkanes.
Now, we should understand the Etard reaction. We should know that Etard reaction is used to oxidise aromatic methyl groups. Now we will know about some details of etard reaction, we should know that in the start we have a methyl group that is bound to an aromatic ring. We react this with chromyl chloride. This reaction oxidises the above compound to carboxylic acid. So, as asked in the question, the oxidising agent that is used in Etard reaction is chromyl chloride.
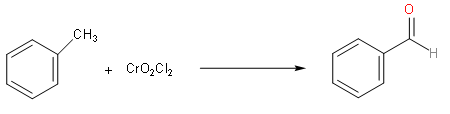
So, we correctly answer all the parts of the above question.
Note:
We should note that the Rosenmund reaction is a hydrogenation process where molecular hydrogen reacts with the acyl chloride in the presence of catalyst, palladium, on barium sulfate. We use barium sulfate because it reduces the activity of the palladium due to its low surface area, thereby preventing overreduction.
We should note that hydrazine is highly toxic and dangerously unstable unless we should place it in solution. So, we should be careful.
Step by step answer:
We will answer this solution in parts.
Rosenmund reduction: We should know that Rosenmund reduction is a reaction where acid chlorides are converted into aldehydes. We use hydrogen gas, palladium and barium sulfate. The example that we should know of this reduction is of acyl chlorides forming aldehydes. This reaction is shown below:

We should know that in the above equation, the high reactivity of hydrogen gas makes it readily initiate a substitution in the acyl chloride, forming HCl and the required aldehyde.
Now, we will discuss the second part of the question. We should know that propanone is a ketone. And from this we can say that ketones can be converted to a hydrazine derivative by reaction with hydrazine. Let us react with propanone with hydrazine.

We should note that, these hydrazones that are produced, they can be further converted to the corresponding alkane by reaction with base and heat. These two steps can be combined into one reaction called the Wolff-Kishner Reduction which represents a general method for converting aldehydes and ketones into alkanes.
Now, we should understand the Etard reaction. We should know that Etard reaction is used to oxidise aromatic methyl groups. Now we will know about some details of etard reaction, we should know that in the start we have a methyl group that is bound to an aromatic ring. We react this with chromyl chloride. This reaction oxidises the above compound to carboxylic acid. So, as asked in the question, the oxidising agent that is used in Etard reaction is chromyl chloride.
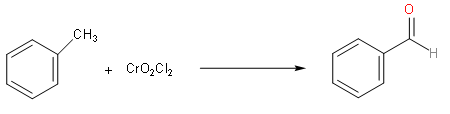
So, we correctly answer all the parts of the above question.
Note:
We should note that the Rosenmund reaction is a hydrogenation process where molecular hydrogen reacts with the acyl chloride in the presence of catalyst, palladium, on barium sulfate. We use barium sulfate because it reduces the activity of the palladium due to its low surface area, thereby preventing overreduction.
We should note that hydrazine is highly toxic and dangerously unstable unless we should place it in solution. So, we should be careful.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




