
(a) Explain the condensation polymer by an example.
(b) Give one example each of thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers.
(c) Give the names of monomers used for obtaining Buna-N.
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: (a) Condensation polymers are formed when a condensation reaction takes place between their individual monomeric units. Small compounds such as water, are eliminated as a by-product.
(b) Thermosetting polymers are infusible in nature. These cannot be reused. While thermoplastics are completely opposite to the former.
(c) The Buna-N is a copolymer, meaning it is formed from two different monomers. One of them is a four carbon compound and the other one is a nitrile.
Complete step by step solution:
(a)
It is known to you that condensation polymers are also known as step-growth polymers.
Condensation polymers are those polymers which are formed by the condensation of two or more than two monomers with the elimination of simple molecules like water, ammonia, hydrogen chloride, alcohol etc. In this type, the monomers generally have different bifunctional or trifunctional groups. For example- $\text{Nylon-6,6}$is obtained by the condensation of two monomers; hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid with the loss of water molecules. The overall reaction is as follows:
\[nN{{H}_{2}}{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{6}}N{{H}_{2}}+nCOOH{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{4}}COOH\xrightarrow{Polymerization}{{[-NH{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{6}}NHCO{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{4}}CO-]}_{n}}+n{{H}_{2}}O\]
(b)
- From the name only we can derive that thermoplastics are plastics that are somehow related to temperature, and you will see ahead, that is exactly the case. Keep in mind that they are made up of monomer units which are linear or slightly branched in their molecular structures and they have intermediate molecular force of attraction between them. For this reason, they are capable of softening when exposed to heat and harden again when cooled down. Some common examples are polythene, polystyrene, polyvinyls, etc. The structure of Polyvinyl chloride is as below:

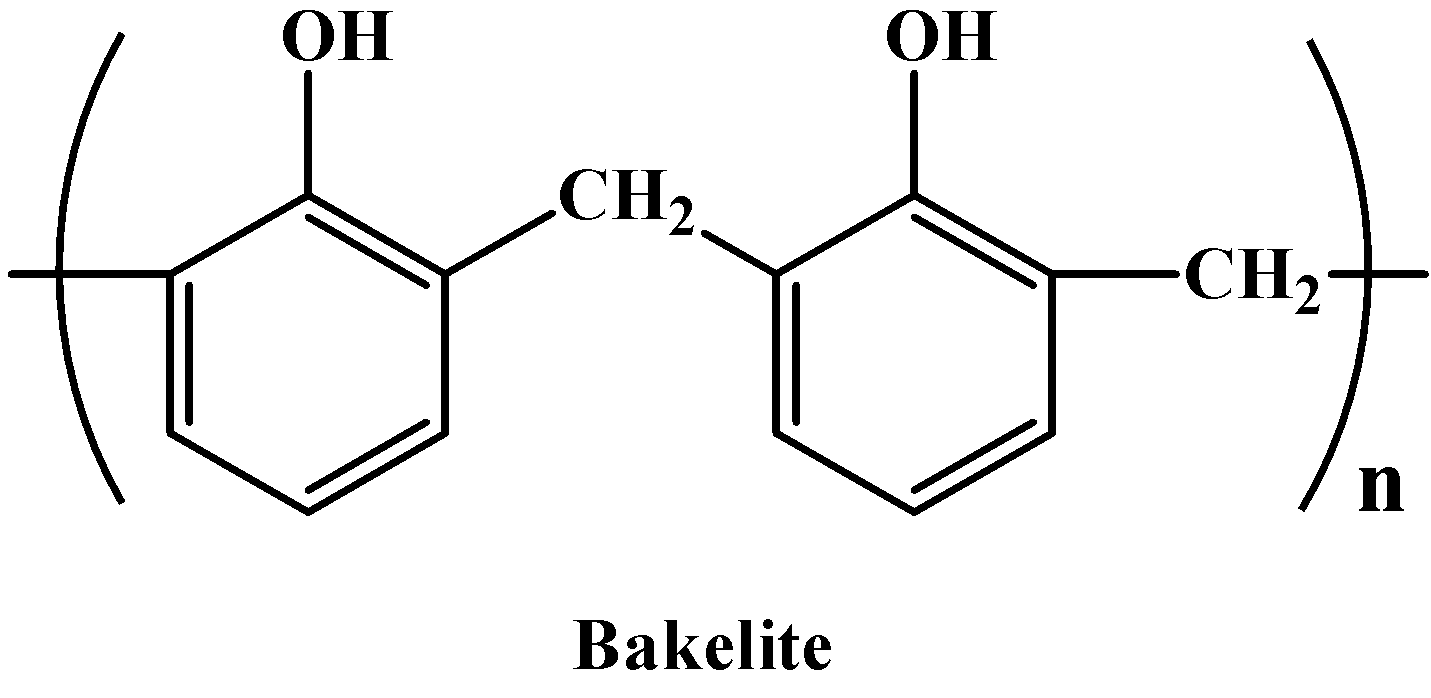
- Thermosetting plastics are, as mentioned in the hint, opposite to thermoplastics. By opposite we mean, they cannot be molded into different shapes when heated. Unlike the former, these have heavily branched chains and therefore have high intermolecular force of attraction between them. So they can only be used once. Some common examples are Bakelite, Urea-formaldehyde resins etc. the structure of Bakelite is given below:
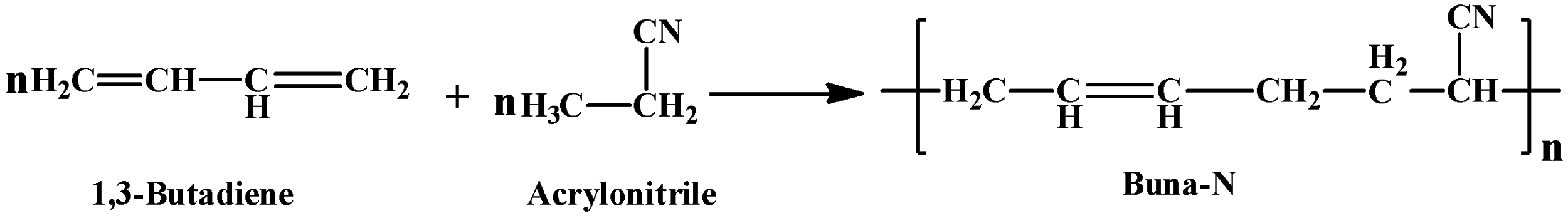
(c) Buna-N was one of the very first synthetic rubbers patented. As it contains a nitrile group ($\text{-CN}$) it is also known as nitrile rubber. As mentioned in the hint it is a copolymer of $\text{1,3-Butadiene}$ and acrylonitrile in the presence of a peroxide catalyst. It has many uses, some examples are as a lubricating oil and in organic solvents. The general formula of its synthesis reaction is as mentioned below:
Note:
- A condensation reaction is not the same as an elimination reaction. The elimination of simple molecules is not to be considered as an elimination reaction product.
- There are many different kinds of plastic other than the ones mentioned above. And there are also some which have properties intermediate to both thermoplastic and thermosetting plastic.
(b) Thermosetting polymers are infusible in nature. These cannot be reused. While thermoplastics are completely opposite to the former.
(c) The Buna-N is a copolymer, meaning it is formed from two different monomers. One of them is a four carbon compound and the other one is a nitrile.
Complete step by step solution:
(a)
It is known to you that condensation polymers are also known as step-growth polymers.
Condensation polymers are those polymers which are formed by the condensation of two or more than two monomers with the elimination of simple molecules like water, ammonia, hydrogen chloride, alcohol etc. In this type, the monomers generally have different bifunctional or trifunctional groups. For example- $\text{Nylon-6,6}$is obtained by the condensation of two monomers; hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid with the loss of water molecules. The overall reaction is as follows:
\[nN{{H}_{2}}{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{6}}N{{H}_{2}}+nCOOH{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{4}}COOH\xrightarrow{Polymerization}{{[-NH{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{6}}NHCO{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{4}}CO-]}_{n}}+n{{H}_{2}}O\]
(b)
- From the name only we can derive that thermoplastics are plastics that are somehow related to temperature, and you will see ahead, that is exactly the case. Keep in mind that they are made up of monomer units which are linear or slightly branched in their molecular structures and they have intermediate molecular force of attraction between them. For this reason, they are capable of softening when exposed to heat and harden again when cooled down. Some common examples are polythene, polystyrene, polyvinyls, etc. The structure of Polyvinyl chloride is as below:

- Thermosetting plastics are, as mentioned in the hint, opposite to thermoplastics. By opposite we mean, they cannot be molded into different shapes when heated. Unlike the former, these have heavily branched chains and therefore have high intermolecular force of attraction between them. So they can only be used once. Some common examples are Bakelite, Urea-formaldehyde resins etc. the structure of Bakelite is given below:

(c) Buna-N was one of the very first synthetic rubbers patented. As it contains a nitrile group ($\text{-CN}$) it is also known as nitrile rubber. As mentioned in the hint it is a copolymer of $\text{1,3-Butadiene}$ and acrylonitrile in the presence of a peroxide catalyst. It has many uses, some examples are as a lubricating oil and in organic solvents. The general formula of its synthesis reaction is as mentioned below:

Note:
- A condensation reaction is not the same as an elimination reaction. The elimination of simple molecules is not to be considered as an elimination reaction product.
- There are many different kinds of plastic other than the ones mentioned above. And there are also some which have properties intermediate to both thermoplastic and thermosetting plastic.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




