
A flower which contains both stamen and pistil is called as:
A. Bisexual flower
B. Unisexual flower
C. Unique flower
D. None of the above
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: Stamen (filament and an anther) is the male part and the pistil (stigma, style, and the ovary) is the female part of a flower.
Step by step answer:
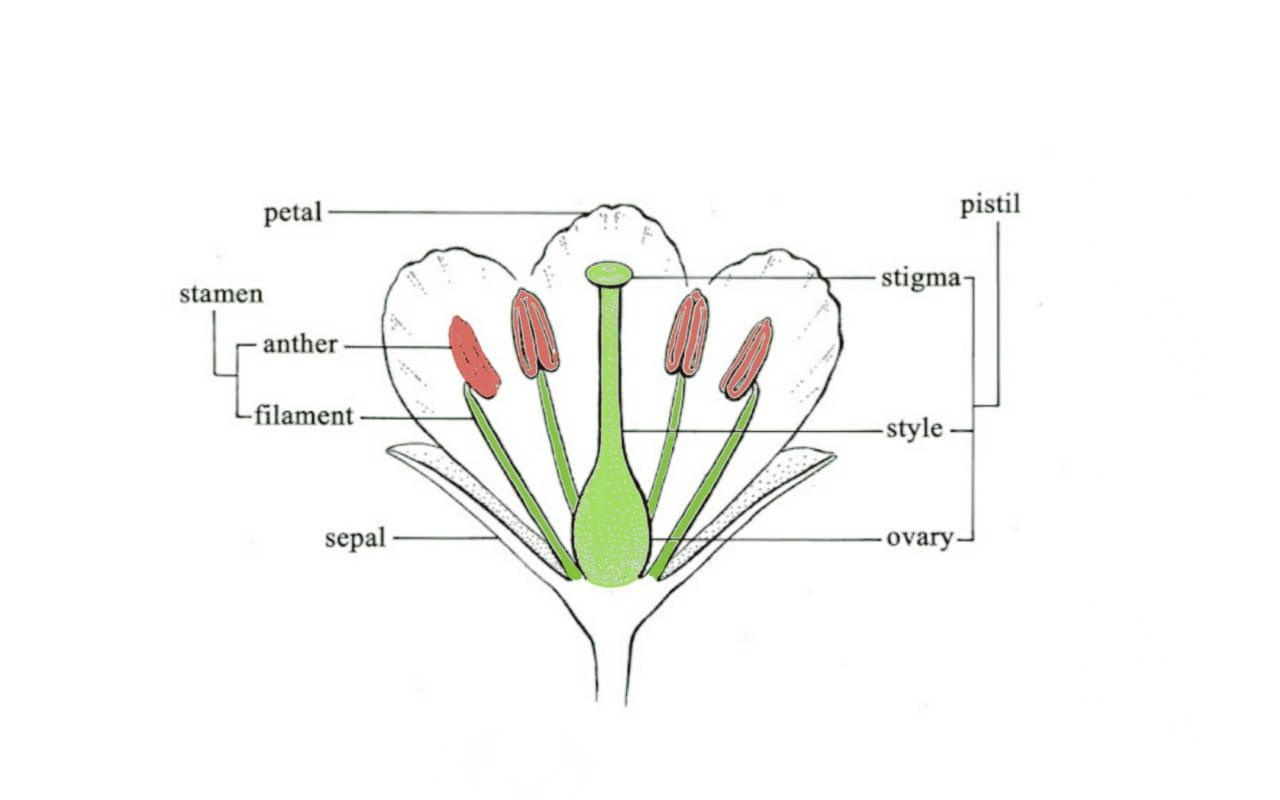
Bisexual flowers contain both the pistil and the stamen
The pistil is the female reproductive part of a flower. It consists of a stigma, style, and the ovary containing the ovules. The stigma is the sticky receptive part which anchors the pollen that falls on it (complex interaction occur only when both the stigma and the pollen are of the same species, this results in the formation/ germination of a pollen tube for the male gamete to traverse the style and reach the ovules in the ovary). The style is a long stalk connecting the stigma and the ovary. The ovary is the basal enlarged part of the pistil. It contains numerous ovules that are arranged in a specific sequence/ order that is unique to a species. The ovules contain the female gametes
The stamen is the male reproductive part of a flower. It consists of a filament and an anther that has the pollen grains. The filament is a long and thin stalk connecting the anther to the flower (it is thin and elastic to facilitate pollen grain release in the case of air vectors). The anther is an enlarged part that produces and houses the pollen grains. The pollen grains are small and sticky cells that contain the male gametes
A unisexual flower contains either the male or the female reproductive parts in the flower but not both
Note: Lily, rose, sunflower, mango, etc. are bisexual flowers while papaya, snake guard, bitter guard, cucumber, and watermelon flowers are unisexual flowers.
Step by step answer:

Bisexual flowers contain both the pistil and the stamen
The pistil is the female reproductive part of a flower. It consists of a stigma, style, and the ovary containing the ovules. The stigma is the sticky receptive part which anchors the pollen that falls on it (complex interaction occur only when both the stigma and the pollen are of the same species, this results in the formation/ germination of a pollen tube for the male gamete to traverse the style and reach the ovules in the ovary). The style is a long stalk connecting the stigma and the ovary. The ovary is the basal enlarged part of the pistil. It contains numerous ovules that are arranged in a specific sequence/ order that is unique to a species. The ovules contain the female gametes
The stamen is the male reproductive part of a flower. It consists of a filament and an anther that has the pollen grains. The filament is a long and thin stalk connecting the anther to the flower (it is thin and elastic to facilitate pollen grain release in the case of air vectors). The anther is an enlarged part that produces and houses the pollen grains. The pollen grains are small and sticky cells that contain the male gametes
A unisexual flower contains either the male or the female reproductive parts in the flower but not both
Note: Lily, rose, sunflower, mango, etc. are bisexual flowers while papaya, snake guard, bitter guard, cucumber, and watermelon flowers are unisexual flowers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




