
What is a geostationary stationary satellite? State the uses of satellites.
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: A satellite is an object that revolves around a larger object in a particular orbit. There can be two types of satellites: Natural satellites, such as the moon orbiting the Earth, or Artificial satellites, such as geostationary satellites. When rockets launch artificial satellites, they put them into orbit in space, where gravity keeps the satellite in its required orbit.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A geostationary satellite is the one that revolves in geosynchronous orbit, or geostationary orbit, with an orbital period equal to the Earth's rotation period. It returns to its same position in the space after each sidereal day. A geostationary satellite has a geostationary orbit – a circular geosynchronous orbit which is situated directly above the Earth's equator.
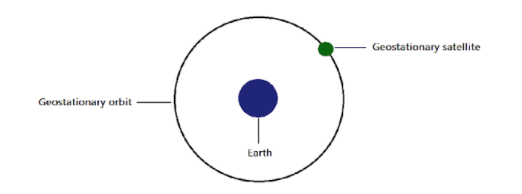
Geostationary satellites have the unique property of remaining permanently fixed at the same position in the sky as viewed from any particular location on Earth. It means that the ground-based antennas do not require tracking them, but can remain fixed in one direction.
Advantages of Geostationary satellites:
- They get high temporal resolution data.
- The tracking of the geostationary satellite by its earth stations is simplified.
- The satellite always remains in the same position.
The applications of artificial satellites are:
- They are used for communication purposes.
- They carry instruments or passengers to perform experiments in space.
- They are used for the Weather Forecasting System.
- They are used in GPS (Global Positioning System).
- They are used for military purposes including photography and communications.
Note:Gravitational force is important to keep the satellites in their respective geostationary orbits. Gravity, combined with the satellite's momentum from its launch into space causes the satellite to go into its orbit above the Earth, instead of falling back down to the ground.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A geostationary satellite is the one that revolves in geosynchronous orbit, or geostationary orbit, with an orbital period equal to the Earth's rotation period. It returns to its same position in the space after each sidereal day. A geostationary satellite has a geostationary orbit – a circular geosynchronous orbit which is situated directly above the Earth's equator.

Geostationary satellites have the unique property of remaining permanently fixed at the same position in the sky as viewed from any particular location on Earth. It means that the ground-based antennas do not require tracking them, but can remain fixed in one direction.
Advantages of Geostationary satellites:
- They get high temporal resolution data.
- The tracking of the geostationary satellite by its earth stations is simplified.
- The satellite always remains in the same position.
The applications of artificial satellites are:
- They are used for communication purposes.
- They carry instruments or passengers to perform experiments in space.
- They are used for the Weather Forecasting System.
- They are used in GPS (Global Positioning System).
- They are used for military purposes including photography and communications.
Note:Gravitational force is important to keep the satellites in their respective geostationary orbits. Gravity, combined with the satellite's momentum from its launch into space causes the satellite to go into its orbit above the Earth, instead of falling back down to the ground.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




