
When a monosaccharide forms a cyclic hemiacetal, the carbon atom that contained the carbonyl group is identified as the ________ carbon atom because-
a.) D, the carbonyl group is drawn to the right
b.) L, the carbonyl group is drawn to the left
c.) Acetal, it forms bond to an -OR and an -OR’
d.) Anomeric, its substituents can assume an $\beta $ or $\alpha $ position
Answer
601.2k+ views
Hint: When two cyclic forms of a carbohydrate differ in configuration only at hemiacetal carbons, they are said to be anomers. Thus, anomers are cyclic sources of hemiacetal carbon epimeric carbohydrate that is called anomeric carbon (C-1 of aldose).
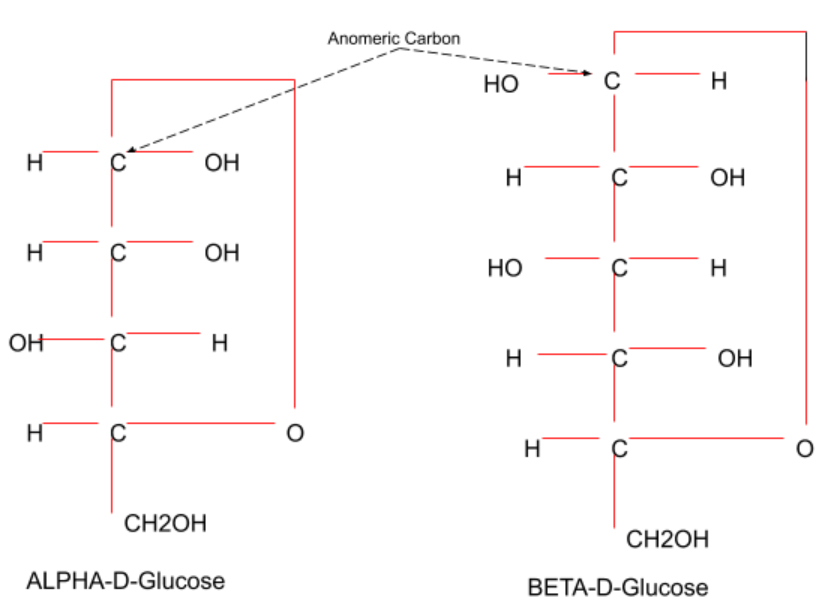
Complete step-by-step answer:
An anomer is a type of geometric variance contained in carbohydrate molecules in some atoms. The epimer is a separate stereo isomer in a single stereo genic core. An anomer is an epimer with a cyclic saccharide hemiacetal/hemiketal carbon, an anomeric carbon. Anomeric carbon is the Carbon in the open-chain carbohydrate molecule shape originating in the Carbonyl Carbon compound (ketone or aldehyde functional group). Anomerization is the transformation of anomer into an anomer. Like for stereoisomeric materials, different anomers have varying physical properties, melting points, and unique rotations.
Anomerization is the transfer cycle of anomers. Anomerization is termed mutarotation for sugar reduction which is readily solved which is catalyzed by acid and base. Usually this reversible phase contributes to an anomeric mixture in which the two anomers finally stabilize. The interaction between the two anomers is sugar sensitive. For example, a solution can gradually shift towards a mixture of approximately 64% β-D-glucopyranoside and 36% α-D-glucopyranoside irrespective of the configuration of the starting D-glucose. The physical movement of the mixture varies as the ratio increases; this phenomenon is called mutarotation.
Hence, we can say that option D is the correct option.
Note: In comparison to analogous carbonyl compounds, acetals are formed from and soluble into aldehydes or ketones and have the same state of oxidation at the middle of the carbons. The central carbon atom is saturated and has tetrahedral structure and is linked with four bonds.

Complete step-by-step answer:
An anomer is a type of geometric variance contained in carbohydrate molecules in some atoms. The epimer is a separate stereo isomer in a single stereo genic core. An anomer is an epimer with a cyclic saccharide hemiacetal/hemiketal carbon, an anomeric carbon. Anomeric carbon is the Carbon in the open-chain carbohydrate molecule shape originating in the Carbonyl Carbon compound (ketone or aldehyde functional group). Anomerization is the transformation of anomer into an anomer. Like for stereoisomeric materials, different anomers have varying physical properties, melting points, and unique rotations.
Anomerization is the transfer cycle of anomers. Anomerization is termed mutarotation for sugar reduction which is readily solved which is catalyzed by acid and base. Usually this reversible phase contributes to an anomeric mixture in which the two anomers finally stabilize. The interaction between the two anomers is sugar sensitive. For example, a solution can gradually shift towards a mixture of approximately 64% β-D-glucopyranoside and 36% α-D-glucopyranoside irrespective of the configuration of the starting D-glucose. The physical movement of the mixture varies as the ratio increases; this phenomenon is called mutarotation.
Hence, we can say that option D is the correct option.
Note: In comparison to analogous carbonyl compounds, acetals are formed from and soluble into aldehydes or ketones and have the same state of oxidation at the middle of the carbons. The central carbon atom is saturated and has tetrahedral structure and is linked with four bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




