
A particle executing linear SHM. Its time period is equal to the smallest time interval in which a particle crosses a particular point. Its velocity may $\vec{V}$ be:
A. Zero
B. ${{V}_{\max }}$
C. $\dfrac{{{V}_{\max }}}{2}$
D. $\dfrac{{{V}_{\max }}}{\sqrt{2}}$
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: SHM is a sinusoidal periodic motion in other words it is a motion of repetition or oscillations. The time period is the total time taken by a particle to complete the required work done. The velocity of the motion is inversely proportional to the time period of the motion.
Complete step-by-step answer:
SHM is a special kind of periodic motion in which the restoring force on the moving body is directly proportional to the displacement magnitude of the object and acts towards the object’s equilibrium position.
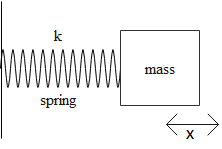
According to Hooke's law when a mass is attached to a spring whose one end is fixed at a point. For the linear motion, the force required by a body to extend or compress the spring by a certain distance is given by,
${{F}_{s}}=Kx$
Where,
K is the constant factor characteristic of the spring.
x is the displacement of the spring due to expansion or compression of the spring.
The waveform of SHM is sinusoidal and this is calculated by Hooke's law.
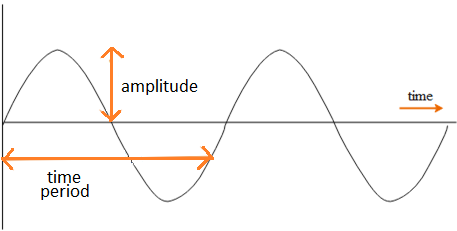
The time interval for an SHM is termed as the time period of the motion.
$T=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Where,
$f$ Is the frequency of the wave.
The velocity of the SHM is directly proportional to the frequency it will be inversely proportional to the time of the motion.
$v=\pm 2\pi f\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}}$
Where,
$A$ is the amplitude
$x$ is the displacement
So,
$\begin{align}
& v\propto f \\
& \Rightarrow T\propto \dfrac{1}{f}\propto \dfrac{1}{v} \\
& \Rightarrow T\propto \dfrac{1}{v} \\
\end{align}$
It is found that when the time interval will be the minimum interval of time required for the motion of the object from a certain point the velocity at that point will be the maximum velocity that can be attained by the object.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Ideally SHM is a constant type of motion. But due to the external opposite hindrances line frictional forces the motion is dissipative. This type of oscillation is known as damped oscillation. And motion with such oscillation is known as damped simple harmonic motion. In this, the energy of the oscillator dissipates continuously.
Complete step-by-step answer:
SHM is a special kind of periodic motion in which the restoring force on the moving body is directly proportional to the displacement magnitude of the object and acts towards the object’s equilibrium position.

According to Hooke's law when a mass is attached to a spring whose one end is fixed at a point. For the linear motion, the force required by a body to extend or compress the spring by a certain distance is given by,
${{F}_{s}}=Kx$
Where,
K is the constant factor characteristic of the spring.
x is the displacement of the spring due to expansion or compression of the spring.
The waveform of SHM is sinusoidal and this is calculated by Hooke's law.

The time interval for an SHM is termed as the time period of the motion.
$T=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Where,
$f$ Is the frequency of the wave.
The velocity of the SHM is directly proportional to the frequency it will be inversely proportional to the time of the motion.
$v=\pm 2\pi f\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}}$
Where,
$A$ is the amplitude
$x$ is the displacement
So,
$\begin{align}
& v\propto f \\
& \Rightarrow T\propto \dfrac{1}{f}\propto \dfrac{1}{v} \\
& \Rightarrow T\propto \dfrac{1}{v} \\
\end{align}$
It is found that when the time interval will be the minimum interval of time required for the motion of the object from a certain point the velocity at that point will be the maximum velocity that can be attained by the object.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Ideally SHM is a constant type of motion. But due to the external opposite hindrances line frictional forces the motion is dissipative. This type of oscillation is known as damped oscillation. And motion with such oscillation is known as damped simple harmonic motion. In this, the energy of the oscillator dissipates continuously.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




