
A pulley is attached to the ceiling of a lift moving upwards. Two particles are attached to the two ends of a massless string passing over the smooth pulley. The masses of the particles are in the ratio $2:1$. If the acceleration of the particles is $\dfrac{g}{2}$ w.r.t. lift, then the acceleration of the lift will be.
A. g
B. $\dfrac{g}{2}$
C. $\dfrac{g}{3}$
D. $\dfrac{g}{4}$
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: Concept of relative motion and the effect of acceleration of lift on the acceleration of the two masses is to be used. Then, it can be solved.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us consider that the acceleration of lift is as shown in figure.
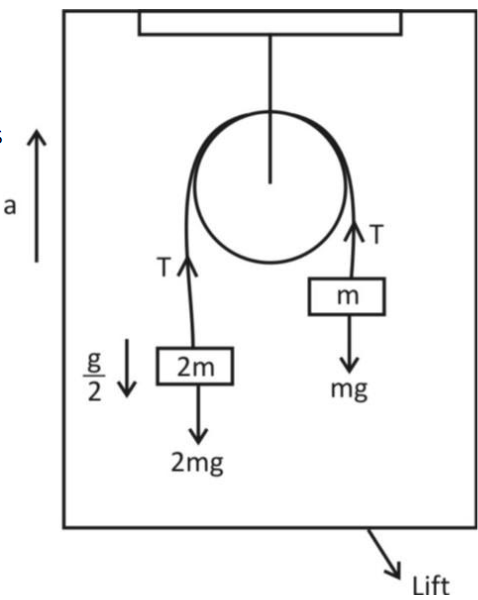
The mass $2$m being heavy, moves downward while mass m being small will move upward in an atwood machine.
Then, from figure we have acceleration of bigger mass (i.e. $2$m)$ = a - \dfrac{g}{2}$
Acceleration of smaller mass (i.e.m) $ = a + \dfrac{g}{2}$
There will develop a tension, T in the string as shown in figure. So, the equation form mass $2$m is,
$T - 2mg = 2m\left( {a - \dfrac{g}{2}} \right)$… (i)
And for mass, m is
$T - mg = m\left( {a + \dfrac{g}{2}} \right)$… (ii)
Subtracting equation (ii) from equation (i), we get
$T - 2mg - \left( {T - mg)} \right) = 2m\left( {a - \dfrac{g}{2}} \right) - m\left( {a + \dfrac{g}{2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow T - 2 mg - T + mg = 2ma - \dfrac{{2mg}}{2} - ma - \dfrac{{mg}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow - mg = ma - \dfrac{{3mg}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow ma = \dfrac{{3mg}}{2} - mg$
$ \Rightarrow ma = \dfrac{{3mg - 2mg}}{2} \Rightarrow ma = \dfrac{{mg}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow a = \dfrac{g}{2}$
Hence, the acceleration of the lift will be $\dfrac{g}{2}$.
Note:
Here, as in the case of mass $2$m, both the acceleration a and $\dfrac{g}{2}$ are in the opposite direction.
So, net acceleration of $2m = a - \dfrac{g}{2}$
While in case of mass m, thay are in the same direction.
So, acceleration of small mass $ = a + \dfrac{g}{2}$.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us consider that the acceleration of lift is as shown in figure.

The mass $2$m being heavy, moves downward while mass m being small will move upward in an atwood machine.
Then, from figure we have acceleration of bigger mass (i.e. $2$m)$ = a - \dfrac{g}{2}$
Acceleration of smaller mass (i.e.m) $ = a + \dfrac{g}{2}$
There will develop a tension, T in the string as shown in figure. So, the equation form mass $2$m is,
$T - 2mg = 2m\left( {a - \dfrac{g}{2}} \right)$… (i)
And for mass, m is
$T - mg = m\left( {a + \dfrac{g}{2}} \right)$… (ii)
Subtracting equation (ii) from equation (i), we get
$T - 2mg - \left( {T - mg)} \right) = 2m\left( {a - \dfrac{g}{2}} \right) - m\left( {a + \dfrac{g}{2}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow T - 2 mg - T + mg = 2ma - \dfrac{{2mg}}{2} - ma - \dfrac{{mg}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow - mg = ma - \dfrac{{3mg}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow ma = \dfrac{{3mg}}{2} - mg$
$ \Rightarrow ma = \dfrac{{3mg - 2mg}}{2} \Rightarrow ma = \dfrac{{mg}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow a = \dfrac{g}{2}$
Hence, the acceleration of the lift will be $\dfrac{g}{2}$.
Note:
Here, as in the case of mass $2$m, both the acceleration a and $\dfrac{g}{2}$ are in the opposite direction.
So, net acceleration of $2m = a - \dfrac{g}{2}$
While in case of mass m, thay are in the same direction.
So, acceleration of small mass $ = a + \dfrac{g}{2}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




