
A ray of light is normally incident on one face of an equilateral glass prism. What is the angle of incidence on the other face of the prism?
(A) \[{0{^\circ }}\]
(B) \[{30{^\circ }}\]
(C) \[{45{^\circ }}\]
(D) \[{90{^\circ }}\]
Answer
581.7k+ views
Hint:First of all, we will draw the diagram, which will show that the light ray enters at the right angle in the first face. Then we will use the angle sum property of a triangle, from where we can find the third angle, when we know the two angles of a triangle.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given problem, we are supplied with the following data:
A ray of light ray hits the face of the prism in a direction perpendicular to the plane.
Also given that the prism is an equilateral prism. We are asked to find the angle of incidence of the other face.To begin with, we will draw the diagram of the prism to have a better understanding.
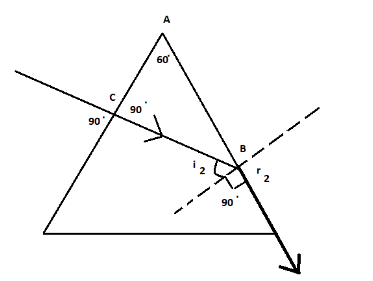
From the diagram, we can say that the incident ray is normal to the plane. Hence, there is no phenomenon of refraction on this face because the incident ray hit this face in perpendicular direction, so we can write:
Angle of incidence on this face is \[{i_1} = {0{^\circ }}\] .
Angle of refraction on this face \[{r_1} = {0{^\circ }}\] .
Now, from the diagram, we need to find the angle \[ABC\] .
From the triangle \[ABC\], it is quite obvious that angle \[ACB\] is \[{90{^\circ }}\]. Since, the prism was an equilateral prism, so angle \[BAC\] is \[{60{^\circ }}\] .
So, by the angle sum property, which states that the sum of all the angles of a triangle is always \[{180{^\circ }}\] .
Now, we carry out the manipulations, which is given below:
$
\angle ABC + \angle BAC + \angle ACB = {180{^\circ }} \\
\Rightarrow\angle ABC + {60{^\circ }} + {90{^\circ }} = {180{^\circ }} \\
\Rightarrow\angle ABC = {180{^\circ }} - {60{^\circ }} - {90{^\circ }} \\
\therefore\angle ABC = {30{^\circ }} \\
$
Hence, the angle of incidence on the other face of the prism \[{30{^\circ }}\]. Thus, the correct option is B.
Note: It is important to note that you have seen that the light ray enters the prism at right angle, so it is quite obvious that the light ray had not suffered refraction. The light ray is undeviating in nature. So, remember that in this case, the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction on this face are both zero.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given problem, we are supplied with the following data:
A ray of light ray hits the face of the prism in a direction perpendicular to the plane.
Also given that the prism is an equilateral prism. We are asked to find the angle of incidence of the other face.To begin with, we will draw the diagram of the prism to have a better understanding.

From the diagram, we can say that the incident ray is normal to the plane. Hence, there is no phenomenon of refraction on this face because the incident ray hit this face in perpendicular direction, so we can write:
Angle of incidence on this face is \[{i_1} = {0{^\circ }}\] .
Angle of refraction on this face \[{r_1} = {0{^\circ }}\] .
Now, from the diagram, we need to find the angle \[ABC\] .
From the triangle \[ABC\], it is quite obvious that angle \[ACB\] is \[{90{^\circ }}\]. Since, the prism was an equilateral prism, so angle \[BAC\] is \[{60{^\circ }}\] .
So, by the angle sum property, which states that the sum of all the angles of a triangle is always \[{180{^\circ }}\] .
Now, we carry out the manipulations, which is given below:
$
\angle ABC + \angle BAC + \angle ACB = {180{^\circ }} \\
\Rightarrow\angle ABC + {60{^\circ }} + {90{^\circ }} = {180{^\circ }} \\
\Rightarrow\angle ABC = {180{^\circ }} - {60{^\circ }} - {90{^\circ }} \\
\therefore\angle ABC = {30{^\circ }} \\
$
Hence, the angle of incidence on the other face of the prism \[{30{^\circ }}\]. Thus, the correct option is B.
Note: It is important to note that you have seen that the light ray enters the prism at right angle, so it is quite obvious that the light ray had not suffered refraction. The light ray is undeviating in nature. So, remember that in this case, the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction on this face are both zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




