
A small charged particle of mass $m$ and charge $q$ is suspended by an insulated thread in front of a very large conducting charged sheet of the uniform surface density of charge $\sigma $. The angle made by the thread with the vertical in equilibrium?
A) ${\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{\sigma q}}{{2{\varepsilon _0}mg}}} \right)$
B) ${\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{\sigma }{{q{\varepsilon _0}mg}}} \right)$
C) ${\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{q}{{2\sigma {\varepsilon _0}mg}}} \right)$
D) Zero

Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: In this problem, first write the expression for the electric field intensity due to the uniformly charged sheet and then draw the free body of the small charged particle to obtain the force equilibrium equation.
Complete step by step answer:
In this question, A small charged particle of mass $m$ and charge $q$ is suspended by an insulated thread in front of a very large conducting charged sheet of the uniform surface density of charge $\sigma $. We need to calculate the angle made by the thread with the vertical in equilibrium.
Let us assume, the velocity of the boat in the still water is $u$ the velocity of the river stream is $v$, and the distance between the two spots is $d$.
The electric field intensity acts due to the uniformly charged sheet is given as
$E = \dfrac{\sigma }{{2{\varepsilon _0}}}$
Here, $E$ is the electric field intensity act by sheet, $\sigma $ is the surface charge density of the plate.
The resolution of the angle made by the thread is shown in the below diagram.
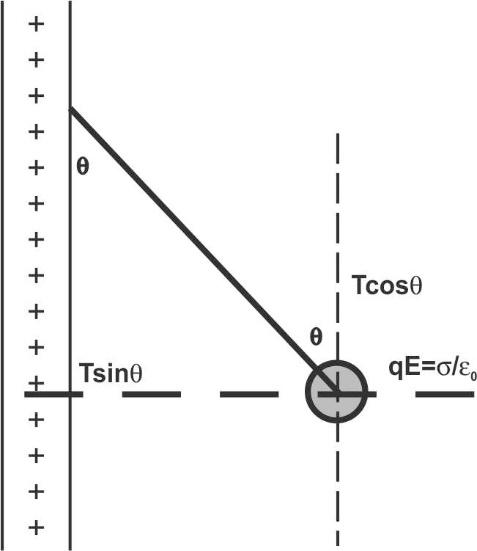
The upward force is the product of \[{\text{T}}\] and \[\cos \theta \] as from the figure is ${\text{T}}\cos \theta $.
The downward force is the product of the mass of the small charged particle $m$ and the gravitational acceleration $g$ from the figure is $mg$.
In equilibrium, the upward force is equal to the downward force.
${\text{T}}\cos \theta = mg$ ….. (1)
The forward force is the product of \[{\text{T}}\] and \[\sin \theta \] as from the figure is ${\text{T}}\sin \theta $.
The backward force is the product of charge of the small particle $q$ and electric field intensity act due to the uniformly charged sheet.
${F_b} = qE $
$\Rightarrow F_b = q\left( {\dfrac{\sigma }{{2{\varepsilon _0}}}} \right)$
$ F_b = \dfrac{{q\sigma }}{{2{\varepsilon _0}}} $
In equilibrium, the forward force is equal to the backward force.
${\text{T}}\sin \theta = \dfrac{{q\sigma }}{{2{\varepsilon _0}}}$ …….….. (2)
As we know the formula for $\tan \theta $.
$\Rightarrow \tan \theta = \dfrac{{\sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }}$
Divide the equation (2) by equation (1)
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{T}}\sin \theta }}{{{\text{T}}\cos \theta }} = \dfrac{{q\sigma }}{{2{\varepsilon _0}mg}} $
$\Rightarrow \theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{{q\sigma }}{{2{\varepsilon _0}mg}}$
$\therefore$ The angle made by the thread with the vertical in equilibrium is \[\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{{q\sigma }}{{2{\varepsilon _0}mg}}\]. Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:
Make sure that for the equilibrium condition, the upward force is equal to the downward force and the forward force is equal to the backward force. Be careful about the sign convention of the force.
Complete step by step answer:
In this question, A small charged particle of mass $m$ and charge $q$ is suspended by an insulated thread in front of a very large conducting charged sheet of the uniform surface density of charge $\sigma $. We need to calculate the angle made by the thread with the vertical in equilibrium.
Let us assume, the velocity of the boat in the still water is $u$ the velocity of the river stream is $v$, and the distance between the two spots is $d$.
The electric field intensity acts due to the uniformly charged sheet is given as
$E = \dfrac{\sigma }{{2{\varepsilon _0}}}$
Here, $E$ is the electric field intensity act by sheet, $\sigma $ is the surface charge density of the plate.
The resolution of the angle made by the thread is shown in the below diagram.

The upward force is the product of \[{\text{T}}\] and \[\cos \theta \] as from the figure is ${\text{T}}\cos \theta $.
The downward force is the product of the mass of the small charged particle $m$ and the gravitational acceleration $g$ from the figure is $mg$.
In equilibrium, the upward force is equal to the downward force.
${\text{T}}\cos \theta = mg$ ….. (1)
The forward force is the product of \[{\text{T}}\] and \[\sin \theta \] as from the figure is ${\text{T}}\sin \theta $.
The backward force is the product of charge of the small particle $q$ and electric field intensity act due to the uniformly charged sheet.
${F_b} = qE $
$\Rightarrow F_b = q\left( {\dfrac{\sigma }{{2{\varepsilon _0}}}} \right)$
$ F_b = \dfrac{{q\sigma }}{{2{\varepsilon _0}}} $
In equilibrium, the forward force is equal to the backward force.
${\text{T}}\sin \theta = \dfrac{{q\sigma }}{{2{\varepsilon _0}}}$ …….….. (2)
As we know the formula for $\tan \theta $.
$\Rightarrow \tan \theta = \dfrac{{\sin \theta }}{{\cos \theta }}$
Divide the equation (2) by equation (1)
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{T}}\sin \theta }}{{{\text{T}}\cos \theta }} = \dfrac{{q\sigma }}{{2{\varepsilon _0}mg}} $
$\Rightarrow \theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{{q\sigma }}{{2{\varepsilon _0}mg}}$
$\therefore$ The angle made by the thread with the vertical in equilibrium is \[\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\dfrac{{q\sigma }}{{2{\varepsilon _0}mg}}\]. Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:
Make sure that for the equilibrium condition, the upward force is equal to the downward force and the forward force is equal to the backward force. Be careful about the sign convention of the force.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




