
A spherical mirror and a thin spherical lens have each a focal length of $ - 15cm$. The mirror and lens are likely to be:
(A) Both concave
(B) Both convex
(C) The mirror is concave and lens is convex
(D) The mirror is convex and lens is concave
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint
As per the Cartesian sign convention used for optics, all distances are measured from the pole of the mirror or the optical centre of the lens. The direction of the incident light is taken as positive and all other rays in the same direction are taken positive too.
Complete step by step answer
In ray optics, directions are taken with respect to the incident ray and the pole of the mirror(P) (or optical centre in case of a lens). So if something lies, above the P it is positive, and vice versa. While for the horizontal sign convention, if the incident ray moves in the right direction, the left from the pole/ optical centre is taken as negative and vice versa.
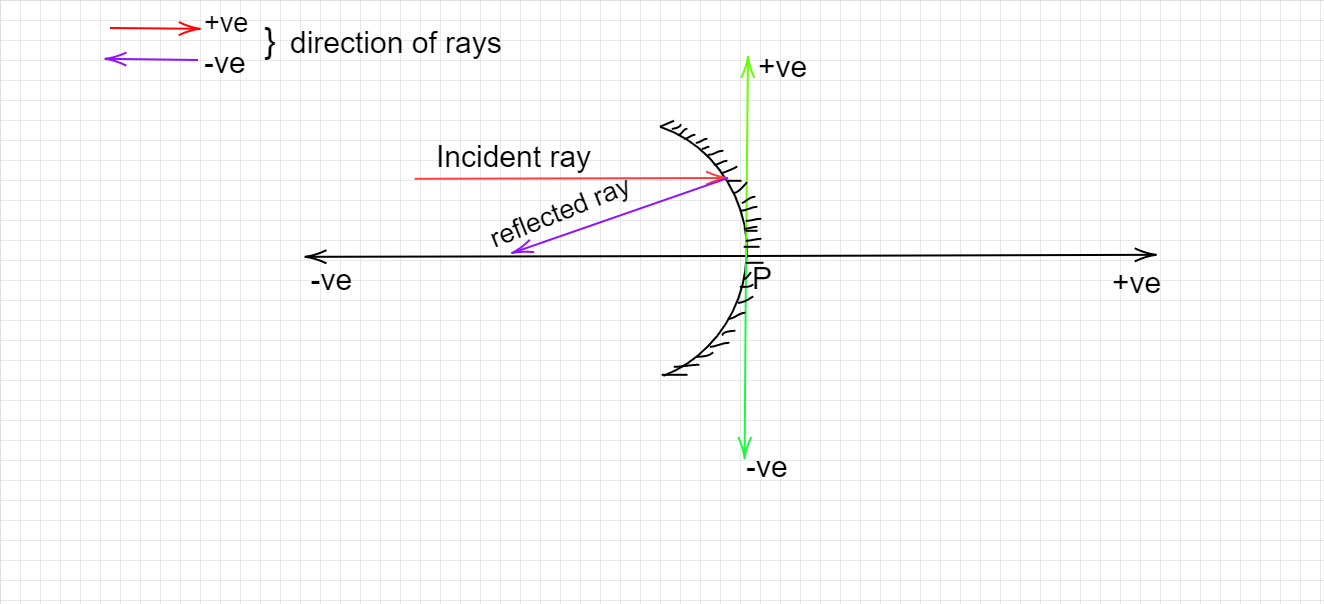
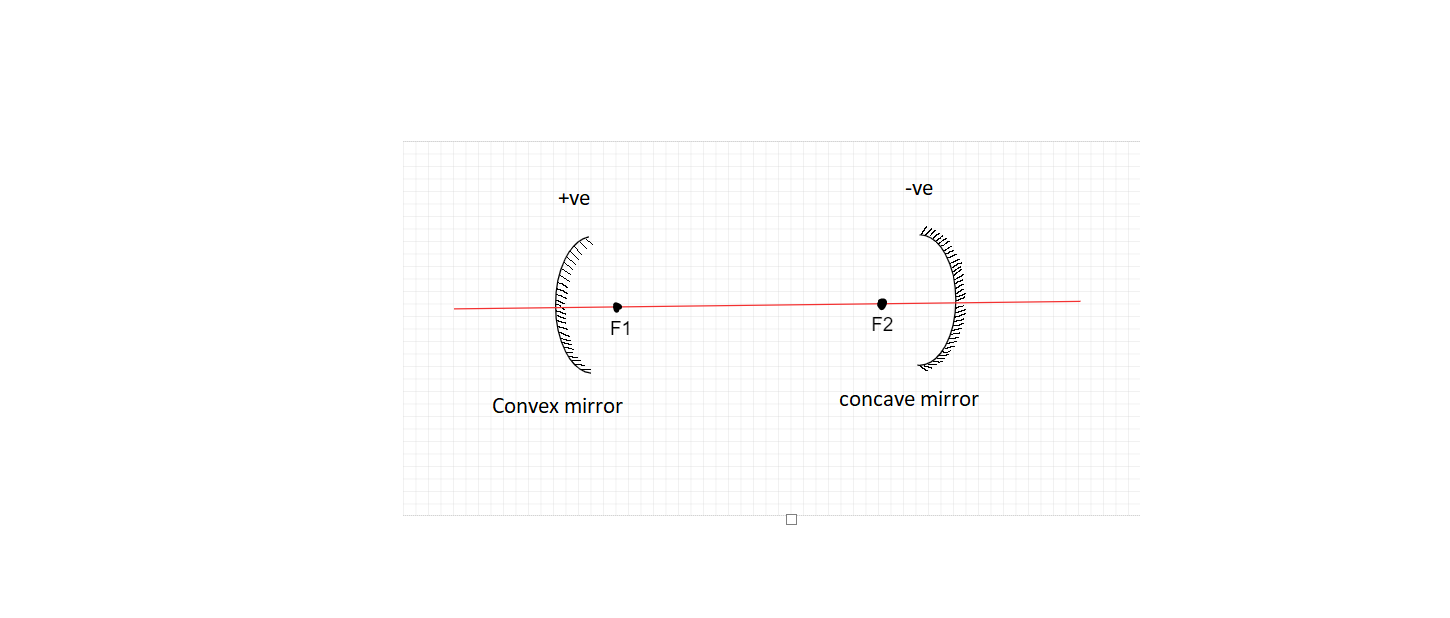
Thus for a spherical mirror, if its focus is negative, It lies on the left side of the pole. Looking at the focus of both convex and concave mirrors we observe, the focus of a convex mirror is positive, while that of a concave mirror is negative, thus the mirror in the question is concave.
Now for the sign convention for lenses, it is a bit trickier because lenses can have 2 foci, so the properties of the lens are taken into account.
A convex lens acts as a converging lens, it can focus parallel rays to a focus, which is on the right side of the lens, thus it has a positive focus.
A concave lens on the other hand is diverging in nature, if parallel rays are allowed to pass through a concave lens, they never intersect. They can be only traced back virtually, and the focus is thus on the left side of the optical centre, thus negative.
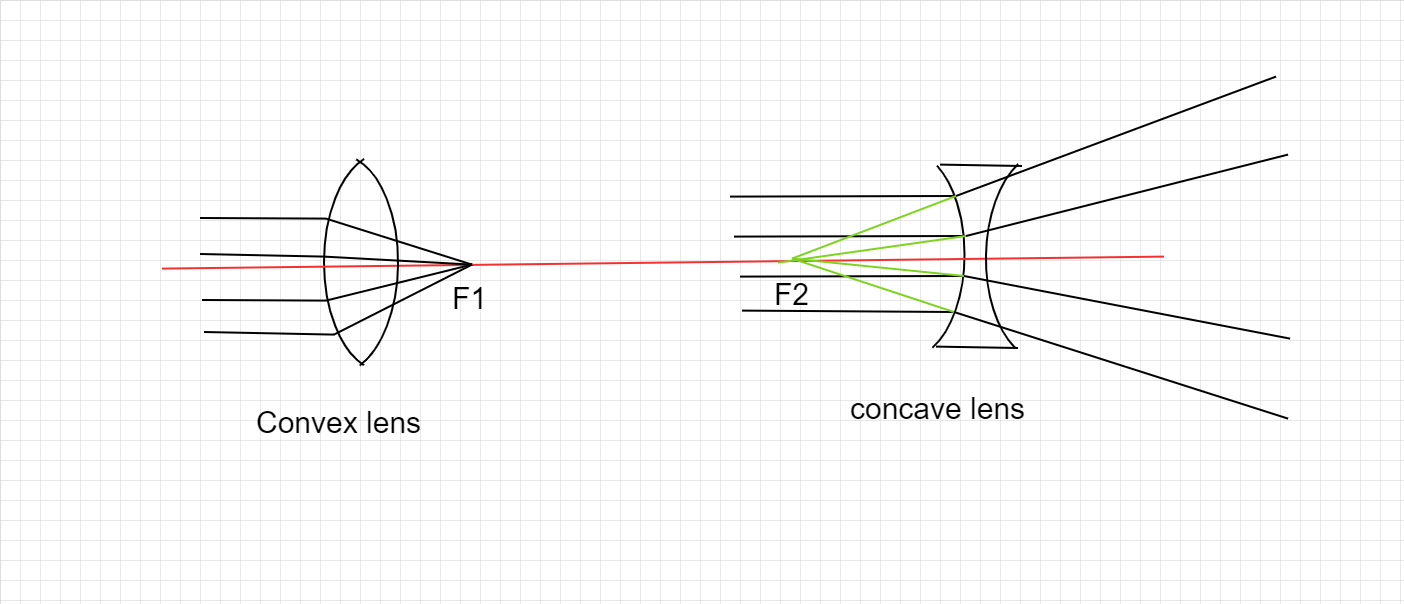
So the mentioned lens in the question is concave.
Therefore option (A) is correct.
Note
Another way to find the focus of these lenses is by using the lens formula and mirror formula. Assume an object on the left side of the lens, and draw the ray diagram to get the image and object distances with appropriate signs. This will give the sign of the focus.
The lens formula even works in cases when the converging-diverging concept fails, for example in the case of an air bubble inside water acting as a concave lens.
As per the Cartesian sign convention used for optics, all distances are measured from the pole of the mirror or the optical centre of the lens. The direction of the incident light is taken as positive and all other rays in the same direction are taken positive too.
Complete step by step answer
In ray optics, directions are taken with respect to the incident ray and the pole of the mirror(P) (or optical centre in case of a lens). So if something lies, above the P it is positive, and vice versa. While for the horizontal sign convention, if the incident ray moves in the right direction, the left from the pole/ optical centre is taken as negative and vice versa.

Thus for a spherical mirror, if its focus is negative, It lies on the left side of the pole. Looking at the focus of both convex and concave mirrors we observe, the focus of a convex mirror is positive, while that of a concave mirror is negative, thus the mirror in the question is concave.

Now for the sign convention for lenses, it is a bit trickier because lenses can have 2 foci, so the properties of the lens are taken into account.
A convex lens acts as a converging lens, it can focus parallel rays to a focus, which is on the right side of the lens, thus it has a positive focus.
A concave lens on the other hand is diverging in nature, if parallel rays are allowed to pass through a concave lens, they never intersect. They can be only traced back virtually, and the focus is thus on the left side of the optical centre, thus negative.

So the mentioned lens in the question is concave.
Therefore option (A) is correct.
Note
Another way to find the focus of these lenses is by using the lens formula and mirror formula. Assume an object on the left side of the lens, and draw the ray diagram to get the image and object distances with appropriate signs. This will give the sign of the focus.
The lens formula even works in cases when the converging-diverging concept fails, for example in the case of an air bubble inside water acting as a concave lens.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




