
What is a standard hydrogen electrode? How is it prepared? Explain with a labelled diagram?
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: Standard hydrogen electrode is the basis for potential calculation in electrochemistry. The potential value of a standard hydrogen electrode is 0. Identify the atom getting oxidised or reduced to write the cell reaction and then be able to draw the cell diagram.
Complete step by step answer:
Standard Hydrogen Electrode also called as SHE in short is an electrode used for calculating potential value of different atoms/ions as it acts as a basis line in the electrochemical reactivity series.
Standard electrode potential(SHE) is set to be zero at a temperature of 298K. The pressure of the hydrogen gas present in this half-cell equals 1 bar. Platinum is generally used as an electrode in Standard Hydrogen Electrode.
The reaction takes place at redox half-cell of SHE is:
\[2{{H}^{+}}(aq)+2{{e}^{-}}\to {{H}_{2}}(g)\]
Let us now discuss the construction of the SHE.
For this, platinum electrode is generally used which is covered with finely powdered platinum black. A hydrogen blow is required for this.
A solution of acid having ${{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}}$molarity of 1 mole per cubic decimetre is taken in a beaker. The SHE should be properly sealed to prevent the interference of oxygen.
The other half cell of the entire Galvanic cell must be attached to the Standard Hydrogen Electrode through a reservoir in order to create an ionic conductive path.
This can be done through a direct connection, through a narrow tube, or even through the use of salt bridge.
Let us have a look at the diagram of SHE:
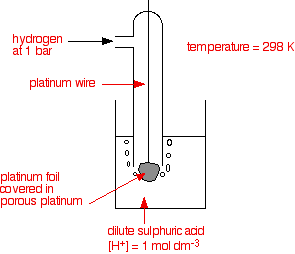
Note: The standard condition of this SHE is only attained at a particular temperature and pressure. The temperature of 298K and pressure of 1 bar is required for a Standard Hydrogen Electrode. This is also called as Standard temperature and pressure (STP) which is often used in various chemical reactions and processes to avoid errors in calculation due to external factors.
Complete step by step answer:
Standard Hydrogen Electrode also called as SHE in short is an electrode used for calculating potential value of different atoms/ions as it acts as a basis line in the electrochemical reactivity series.
Standard electrode potential(SHE) is set to be zero at a temperature of 298K. The pressure of the hydrogen gas present in this half-cell equals 1 bar. Platinum is generally used as an electrode in Standard Hydrogen Electrode.
The reaction takes place at redox half-cell of SHE is:
\[2{{H}^{+}}(aq)+2{{e}^{-}}\to {{H}_{2}}(g)\]
Let us now discuss the construction of the SHE.
For this, platinum electrode is generally used which is covered with finely powdered platinum black. A hydrogen blow is required for this.
A solution of acid having ${{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}}$molarity of 1 mole per cubic decimetre is taken in a beaker. The SHE should be properly sealed to prevent the interference of oxygen.
The other half cell of the entire Galvanic cell must be attached to the Standard Hydrogen Electrode through a reservoir in order to create an ionic conductive path.
This can be done through a direct connection, through a narrow tube, or even through the use of salt bridge.
Let us have a look at the diagram of SHE:

Note: The standard condition of this SHE is only attained at a particular temperature and pressure. The temperature of 298K and pressure of 1 bar is required for a Standard Hydrogen Electrode. This is also called as Standard temperature and pressure (STP) which is often used in various chemical reactions and processes to avoid errors in calculation due to external factors.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




