
A student moves $\sqrt {2{\text{x}}} $ km east from his residence and then moves x km north. He then goes x km north east and finally he takes a turn of $90^\circ $ towards the right and moves a distance x km and reaches his school. What is the shortest distance of school from his residence?
A)$\left( {2\sqrt 2 + 1} \right){\text{x }}$ Km B) $3{\text{x}}$ Km C) $2\sqrt 2 {\text{x}}$ Km D) $3\sqrt 2 {\text{x}}$ Km
Answer
593.1k+ views
Hint: The formula used to solve this question is of Pythagoras theorem because a right angled triangle will form when the student takes a turn of $90^\circ $ towards his right. So, the formula for Pythagoras theorem is ${{\text{H}}^2}{\text{ = }}{{\text{P}}^2}{\text{ + }}{{\text{B}}^2}$ where H is the hypotenuse, P is the perpendicular and B is the base of the triangle. Once you find the value of hypotenuse you can easily find the shortest distance.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given, a student moves east from his residence (A) to point (B) = $\sqrt {2{\text{x}}} $ Km=AB
Now he moves north BC=x Km then moves north east CD=x km then he takes $90^\circ $ turn toward his right and moves distance DE=x km. Clearly E is the point of his school. Now we have to find the distance from A to E.i.e.AE as it is the shortest distance of school from his residence.
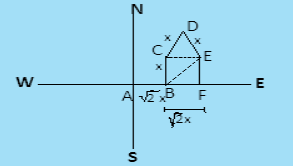
From the figure, it is clear that BF=CE and BC=FE
Now, in$\Delta {\text{CDE}}$, CD=x Km and DE=x Km. Also, $\angle {\text{D}} = 90^\circ $ . Then by Pythagoras theorem we can find CE.
By Pythagoras theorem, in a right angled theorem
$ \Rightarrow $ ${{\text{H}}^2}{\text{ = }}{{\text{P}}^2}{\text{ + }}{{\text{B}}^2}$$ = {\text{C}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ = C}}{{\text{D}}^2}{\text{ + D}}{{\text{E}}^2}$
$
\Rightarrow {\text{C}}{{\text{E}}^2} = {{\text{x}}^2}{\text{ + }}{{\text{x}}^2} = 2{{\text{x}}^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{CE}} = \sqrt {2{{\text{x}}^2}} = {\text{x}}\sqrt 2 \\
$
Since we know that CE=BF then CE$ = {\text{x}}\sqrt 2 = $ BF and we know that BC\[ = {\text{x}} = \] FE. From the diagram it is clear that, ${\text{AF = AB + BF = }}\sqrt 2 {\text{x + }}\sqrt 2 {\text{x}} = 2\sqrt 2 {\text{x}}$. Now we have to find AE so we will construct a $\Delta {\text{AFE}}$ which is a right angled triangle, so by Pythagoras theorem,
$ \Rightarrow $ ${{\text{H}}^2}{\text{ = }}{{\text{P}}^2}{\text{ + }}{{\text{B}}^2}$=${\text{A}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ = A}}{{\text{F}}^2}{\text{ + F}}{{\text{E}}^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\text{AE = }}\sqrt {{{\left( {2\sqrt 2 {\text{x}}} \right)}^2} + {{\text{x}}^2}} $
On simplifying we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\text{AE = }}\sqrt {8{{\text{x}}^2} + {{\text{x}}^2}} = \sqrt {9{{\text{x}}^2}} = 3{\text{x}}$
Hence the correct answer is ‘B’.
Note: Here most students may make mistake in making the diagram thinking that C point is already in northeast and may draw point D parallel to point C like-
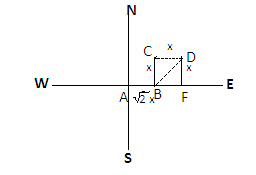
This will change the answer as the value will change. This diagram drawn is wrong as the student walks northeast from point C so the line will be drawn diagonally not horizontally.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given, a student moves east from his residence (A) to point (B) = $\sqrt {2{\text{x}}} $ Km=AB
Now he moves north BC=x Km then moves north east CD=x km then he takes $90^\circ $ turn toward his right and moves distance DE=x km. Clearly E is the point of his school. Now we have to find the distance from A to E.i.e.AE as it is the shortest distance of school from his residence.

From the figure, it is clear that BF=CE and BC=FE
Now, in$\Delta {\text{CDE}}$, CD=x Km and DE=x Km. Also, $\angle {\text{D}} = 90^\circ $ . Then by Pythagoras theorem we can find CE.
By Pythagoras theorem, in a right angled theorem
$ \Rightarrow $ ${{\text{H}}^2}{\text{ = }}{{\text{P}}^2}{\text{ + }}{{\text{B}}^2}$$ = {\text{C}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ = C}}{{\text{D}}^2}{\text{ + D}}{{\text{E}}^2}$
$
\Rightarrow {\text{C}}{{\text{E}}^2} = {{\text{x}}^2}{\text{ + }}{{\text{x}}^2} = 2{{\text{x}}^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{CE}} = \sqrt {2{{\text{x}}^2}} = {\text{x}}\sqrt 2 \\
$
Since we know that CE=BF then CE$ = {\text{x}}\sqrt 2 = $ BF and we know that BC\[ = {\text{x}} = \] FE. From the diagram it is clear that, ${\text{AF = AB + BF = }}\sqrt 2 {\text{x + }}\sqrt 2 {\text{x}} = 2\sqrt 2 {\text{x}}$. Now we have to find AE so we will construct a $\Delta {\text{AFE}}$ which is a right angled triangle, so by Pythagoras theorem,
$ \Rightarrow $ ${{\text{H}}^2}{\text{ = }}{{\text{P}}^2}{\text{ + }}{{\text{B}}^2}$=${\text{A}}{{\text{E}}^2}{\text{ = A}}{{\text{F}}^2}{\text{ + F}}{{\text{E}}^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\text{AE = }}\sqrt {{{\left( {2\sqrt 2 {\text{x}}} \right)}^2} + {{\text{x}}^2}} $
On simplifying we get,
$ \Rightarrow {\text{AE = }}\sqrt {8{{\text{x}}^2} + {{\text{x}}^2}} = \sqrt {9{{\text{x}}^2}} = 3{\text{x}}$
Hence the correct answer is ‘B’.
Note: Here most students may make mistake in making the diagram thinking that C point is already in northeast and may draw point D parallel to point C like-

This will change the answer as the value will change. This diagram drawn is wrong as the student walks northeast from point C so the line will be drawn diagonally not horizontally.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




