
A true breeding black fowl is crossed with a true breeding white fowl, and all the progeny fowls are neither black nor white. Is this an example of Mendelian inheritance?
Answer
487.8k+ views
Hint: The Mendelian kind of inheritance need not apply to all traits. Some traits do not follow Mendelian inheritance. Incomplete dominant traits, codominant traits, and polygenic traits do not follow Mendelian patterns of inheritance, which is a simple one. They follow complex patterns of inheritance. A trait can be controlled with two alleles on a gene, yet the two alleles may have different kinds of relationship when crossed.
Complete answer:
When a true-breeding black fowl is crossed with a real breeding white fowl and everyone else, the progeny fowl are intermediate between the black and white. They are neither white nor black. This is an example of Mendelian inheritance. This phenomenon is called incomplete dominance. The other names are intermediate inheritance and partial dominance. It comes into force when the true-breeding parents are crossed to produce an intermediate or heterozygous offspring.
In incomplete dominance, the alleles or variants are not expressed as recessive or dominant. The dominant allele is depicted in a reduced ratio.
An allele is not completely dominant over a recessive allele. The heterozygous phenotype of offspring is in-between the homozygous phenotypes.
Another example is when a red flower is crossed with a white flower, a pink flower is obtained as an offspring instead of the red flower.
When black fowl is crossed with white fowl, the grey fowl is obtained as an offspring. The grey color is intermediate between white and black due to the phenomenon of incomplete dominance.
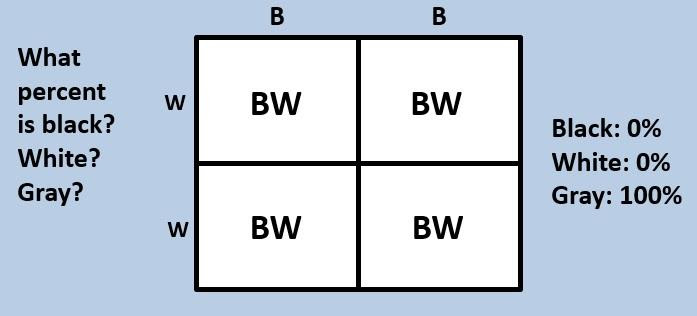
Fig.$1$: F$1$ Generation showing all offspring as grey
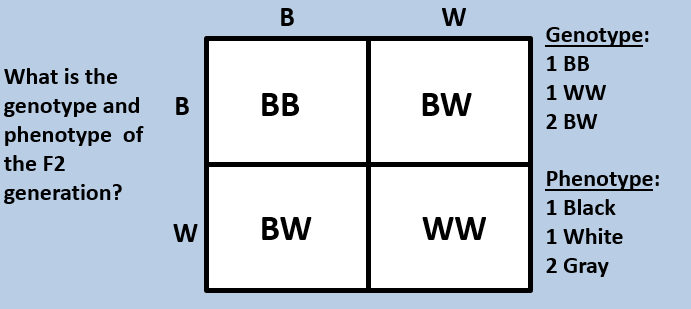
Fig.$2$: F$2$ Generation showing genotypic and phenotypic ratios
The phenotypic ratio is $1$: $2$: $1$ (black: gray: white)
The genotypic ratio is $1$: $2$: $1$ (black: gray: white)
Note:
Genes play a significant role in the determination of characteristics of an organism. However, the phenotype of an individual is influenced by other factors as well for many traits. Environmental factors like food availability and sunlight can affect the expression of genes in the phenotype of individuals. Though genes play an important role in attaining height, poor nutrition can prevent an individual from achieving full genetic potential.
Complete answer:
When a true-breeding black fowl is crossed with a real breeding white fowl and everyone else, the progeny fowl are intermediate between the black and white. They are neither white nor black. This is an example of Mendelian inheritance. This phenomenon is called incomplete dominance. The other names are intermediate inheritance and partial dominance. It comes into force when the true-breeding parents are crossed to produce an intermediate or heterozygous offspring.
In incomplete dominance, the alleles or variants are not expressed as recessive or dominant. The dominant allele is depicted in a reduced ratio.
An allele is not completely dominant over a recessive allele. The heterozygous phenotype of offspring is in-between the homozygous phenotypes.
Another example is when a red flower is crossed with a white flower, a pink flower is obtained as an offspring instead of the red flower.
When black fowl is crossed with white fowl, the grey fowl is obtained as an offspring. The grey color is intermediate between white and black due to the phenomenon of incomplete dominance.

Fig.$1$: F$1$ Generation showing all offspring as grey

Fig.$2$: F$2$ Generation showing genotypic and phenotypic ratios
The phenotypic ratio is $1$: $2$: $1$ (black: gray: white)
The genotypic ratio is $1$: $2$: $1$ (black: gray: white)
Note:
Genes play a significant role in the determination of characteristics of an organism. However, the phenotype of an individual is influenced by other factors as well for many traits. Environmental factors like food availability and sunlight can affect the expression of genes in the phenotype of individuals. Though genes play an important role in attaining height, poor nutrition can prevent an individual from achieving full genetic potential.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




