
(A) What are the longitudinal waves and transverse waves? Explain with the help of labelled diagrams.
(B) Give two examples each of longitudinal and transverse waves.
Answer
564k+ views
Hint: The wave is defined as the propagation of disturbance through the vibration of particles of a medium. Depending on the manner of propagation of the disturbance, there are two types of transmission of the disturbance leading to two types of waves: Longitudinal and Transverse waves.
Complete step by step answer:
A. Longitudinal and Transverse waves.
Depending on the method of the wave propagation, there are two types of waves: Longitudinal and Transverse waves.
Longitudinal waves:
In longitudinal waves, the propagation of energy is through a series of compression and rarefaction. The particles of the medium undergo a series compression to rarefaction, which transmit the energy in the direction as propagation of the energy. Here, we can see that the direction of the particles of the medium is the same as that of the direction of wave propagation. The longitudinal waves occur in fluid medium where the particles are free to move about and the elasticity is low.
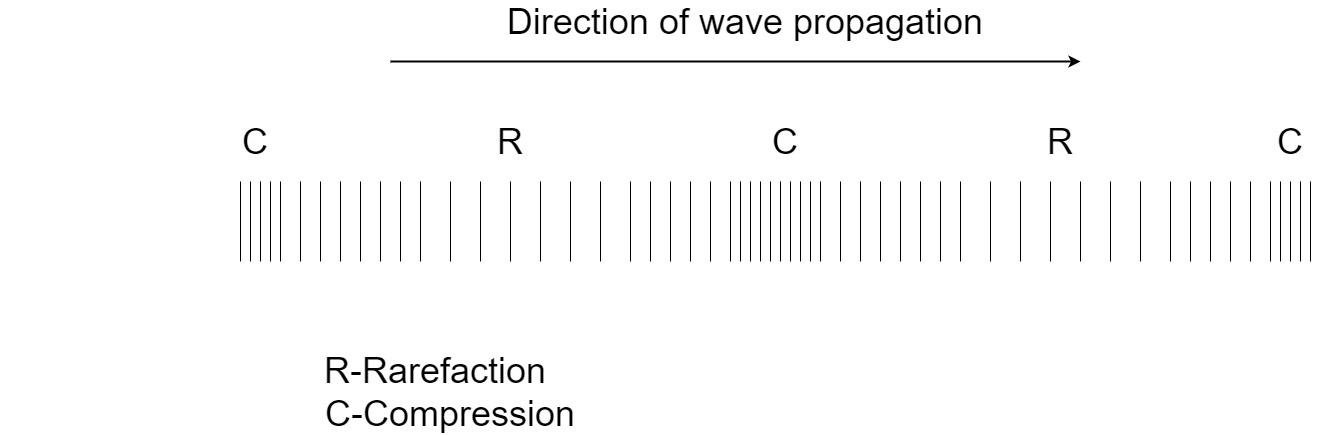 Transverse waves:
Transverse waves:
In transverse waves, the propagation of energy occurs through a series of actual upper and lower displacements of the particles of the medium, forming positions known as crest and trough. The formation of crest and trough are in the perpendicular direction of that of the propagation of the energy. The transverse waves occur in solid medium where the particles have high elasticity to return to their original form and position after the disturbance has occurred.
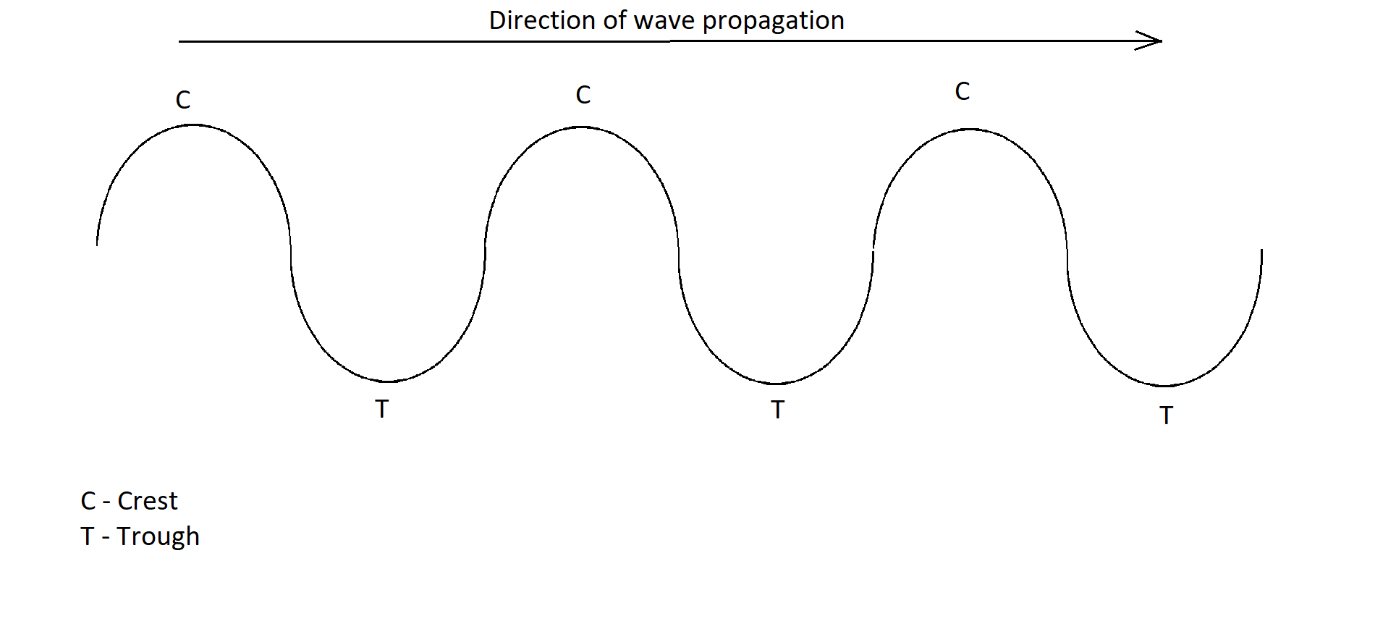 B. Examples of longitudinal and transverse waves.
B. Examples of longitudinal and transverse waves.
Longitudinal waves:
i) Sound waves propagating in fluids
ii) Ultrasound waves
iii) Compression springs
Transverse waves:
i) Ripples on the surface of water
ii) Electromagnetic waves
iii) Vibrations in a guitar string
Note: In sports like football, basketball etc, the fans use a method of cheering their team known as Mexican wave. The Mexican wave is an effect that resembles a wave where successive sections of the crowd raise their arms and lower them, synchronising them which appears in the form of a wave. This wave is another brilliant example of a transverse wave.
Complete step by step answer:
A. Longitudinal and Transverse waves.
Depending on the method of the wave propagation, there are two types of waves: Longitudinal and Transverse waves.
Longitudinal waves:
In longitudinal waves, the propagation of energy is through a series of compression and rarefaction. The particles of the medium undergo a series compression to rarefaction, which transmit the energy in the direction as propagation of the energy. Here, we can see that the direction of the particles of the medium is the same as that of the direction of wave propagation. The longitudinal waves occur in fluid medium where the particles are free to move about and the elasticity is low.

In transverse waves, the propagation of energy occurs through a series of actual upper and lower displacements of the particles of the medium, forming positions known as crest and trough. The formation of crest and trough are in the perpendicular direction of that of the propagation of the energy. The transverse waves occur in solid medium where the particles have high elasticity to return to their original form and position after the disturbance has occurred.

Longitudinal waves:
i) Sound waves propagating in fluids
ii) Ultrasound waves
iii) Compression springs
Transverse waves:
i) Ripples on the surface of water
ii) Electromagnetic waves
iii) Vibrations in a guitar string
Note: In sports like football, basketball etc, the fans use a method of cheering their team known as Mexican wave. The Mexican wave is an effect that resembles a wave where successive sections of the crowd raise their arms and lower them, synchronising them which appears in the form of a wave. This wave is another brilliant example of a transverse wave.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




