
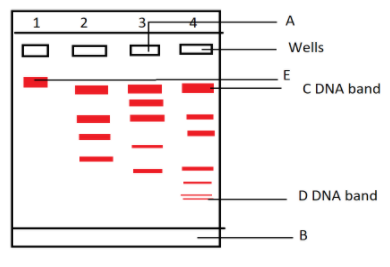
a) Why have DNA fragments in band 'D' moved farther away in comparison to those in band 'C'
b) Identify the anode end in the diagram.
c) What does E represent in the above diagram?

Answer
534k+ views
Hint: The given diagram represents the process of gel electrophoresis. In this process, the fragmented bands of the DNA are separated on the agarose gel on the basis of size of the fragment under the electrical field. The DNA moves towards the positive electrode as DNA is negatively charged. The heavier fragment will move slowly as compared to the lighter one.
Complete answer:
To answer this question, we must know about the process of gel electrophoresis.
The gel electrophoresis is the process by which DNA fragments are separated on the agarose gel under the electrical field. The DNA sample is loaded on different wells labelled as 1,2,3,4 in the given figure. The separation of the DNA is based on the size. The heavier fragment will stay at the top whereas the lighter ones move faster towards the bottom.
a) In the given diagram, band C is relatively of higher size as compared to band D. The thinner band can move easily and faster through the gel matrix as compared to the thicker or larger band. Thus, band D is located on the bottom.
b) Anode is the positive end of the electrical system. AS the DNA is negatively charged, it moves towards the positive end under the influence of the electrical field. So the end B is the anode.
c) During electrophoresis a standard DNA or marker DNA (whose size is already known) is loaded in first well so that the size of the test DNA fragments can be identified. So, E is the standard or the marker DNA.
Note: The gel electrophoresis is an important tool for separating the different DNA fragments. It finds application in investigating the genes associated with certain illnesses, in DNA fingerprinting, in polymerase chain reaction and also in DNA profiling.
Complete answer:
To answer this question, we must know about the process of gel electrophoresis.
The gel electrophoresis is the process by which DNA fragments are separated on the agarose gel under the electrical field. The DNA sample is loaded on different wells labelled as 1,2,3,4 in the given figure. The separation of the DNA is based on the size. The heavier fragment will stay at the top whereas the lighter ones move faster towards the bottom.
a) In the given diagram, band C is relatively of higher size as compared to band D. The thinner band can move easily and faster through the gel matrix as compared to the thicker or larger band. Thus, band D is located on the bottom.
b) Anode is the positive end of the electrical system. AS the DNA is negatively charged, it moves towards the positive end under the influence of the electrical field. So the end B is the anode.
c) During electrophoresis a standard DNA or marker DNA (whose size is already known) is loaded in first well so that the size of the test DNA fragments can be identified. So, E is the standard or the marker DNA.
Note: The gel electrophoresis is an important tool for separating the different DNA fragments. It finds application in investigating the genes associated with certain illnesses, in DNA fingerprinting, in polymerase chain reaction and also in DNA profiling.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




