
a) Write partial structure of:
i).Neoprene
ii).Terylene (Dacron)
iii).Nylon – 6
b) Explain the preparation of Buna-N with equation
Answer
579k+ views
Hint: The formation of a three-dimensional network through continuous linking of a single molecule or more, forms a polymer. It can take place simply through addition of the molecules, loss of water molecules, or combining of two or more molecules simultaneously.
Complete answer:
The polymerisation is a process through which the single units (monomers) are linked together into a long three-dimensional chain to form polymers.
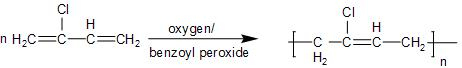
- In the Neoprene, it is obtained by the linking of the chloroprene or $\text{2-chloro-1,3-butadiene}$, which is the single monomer to an n-membered three-dimensional network. This involves the addition of the monomers, so it is known as the addition polymerisation.
The partial structure is shown in brackets, as given below:
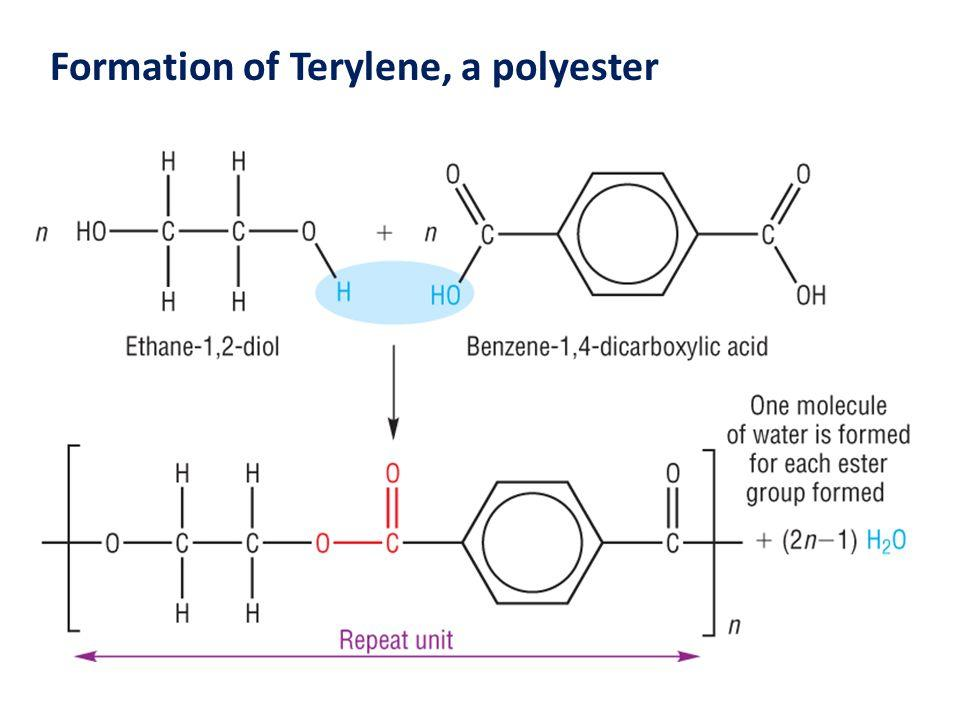
- In the Terylene, it involves the linking of two monomers simultaneously one after the other, along with the loss of water during the linkage into the n-network. Thus, it is known as the condensation polymerisation. The two monomers involved are ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid.
The partial structure is a shown in brackets, as given below:
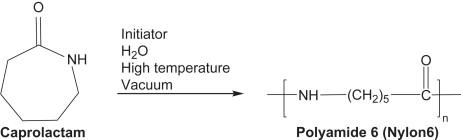
- In the case of Nylon-6, it is formed by the polymerisation of the caprolactam monomer through the ring opening process in the presence of acid (catalyst) and vapour. The partial structure is given in brackets as given below:
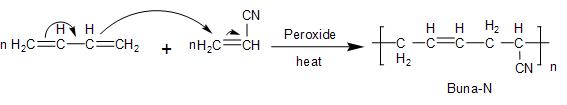
- Similarly, the Buna- N polymer also involves the polymerisation process of a mixture of $\text{1,3-butadiene}$ and $\text{acrylonitrile}$ in the presence of the peroxide catalyst. Thus, it is a process of two polymer additions known as copolymerisation. The reaction takes place as follows:
Note:
It can be seen that the polymerisation process involves various methods of linking like simple addition, loss of water molecule, ring opening and growth, or combining of two molecules.
Complete answer:
The polymerisation is a process through which the single units (monomers) are linked together into a long three-dimensional chain to form polymers.
- In the Neoprene, it is obtained by the linking of the chloroprene or $\text{2-chloro-1,3-butadiene}$, which is the single monomer to an n-membered three-dimensional network. This involves the addition of the monomers, so it is known as the addition polymerisation.
The partial structure is shown in brackets, as given below:

- In the Terylene, it involves the linking of two monomers simultaneously one after the other, along with the loss of water during the linkage into the n-network. Thus, it is known as the condensation polymerisation. The two monomers involved are ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid.
The partial structure is a shown in brackets, as given below:

- In the case of Nylon-6, it is formed by the polymerisation of the caprolactam monomer through the ring opening process in the presence of acid (catalyst) and vapour. The partial structure is given in brackets as given below:

- Similarly, the Buna- N polymer also involves the polymerisation process of a mixture of $\text{1,3-butadiene}$ and $\text{acrylonitrile}$ in the presence of the peroxide catalyst. Thus, it is a process of two polymer additions known as copolymerisation. The reaction takes place as follows:

Note:
It can be seen that the polymerisation process involves various methods of linking like simple addition, loss of water molecule, ring opening and growth, or combining of two molecules.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




