
ABCD is a square of side \[2m\]. Charges of \[5nC, + 10nC\] and \[ - 5nC\] are placed at corners A, B and C respectively. What is the work done in transferring a charge of \[5\mu C\] from D to the point of intersection of the diagonals.
Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: Here side of the square is given. By using side, firstly we will find the diagonal value. Then we will find the value of potential at point O and D due to all other three charges that are given in this particular question. Then we use the work done formula which is the product of charge and the potential difference (\[W = v.q\] ).
Complete step by step answer:
Given that, Side of Square ABCD\[ = 2m\]
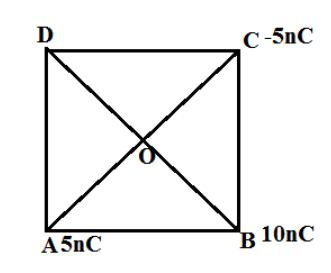
Three charges are given which are placed at the corner of the square (as shown).
Now we can see,
AC=BD=\[\sqrt {{{(2)}^2} + {{(2)}^2}} \] \[ = \sqrt {4 + 4} \]
=\[2\sqrt 2 \] \[ = 2.28m\]
Now, AO=BO=CO=\[\dfrac{{2.828}}{2} = 1.414m\]
Potential at O, \[{V_o} = \]\[\dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\left[ {\dfrac{{{q_1}}}{{AO}} + \dfrac{{{q_2}}}{{BO}} + \dfrac{{{q_3}}}{{CO}}} \right]\]
Potential at D, \[{V_D} = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\left[ {\dfrac{{{q_1}}}{{AD}} + \dfrac{{{q_2}}}{{BD}} + \dfrac{{{q_3}}}{{CD}}} \right]\]
Now, we know
Work done\[ = q\left[ {{v_O} - {v_D}} \right]\]
Charge \[q\] is given and we can find potential at point O and D .
So, W\[ = 5 \times {10^{ - 6}} \times 9 \times {10^9} \times \left[ {5 \times {{10}^{ - 9}}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{AO}} - \dfrac{1}{{AD}}} \right] + 10 \times {{10}^{ - 9}}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{BO}} - \dfrac{1}{{BD}}} \right]} \right]\]
\[\Rightarrow W = 45 \times {10^{ - 6}} \times {10^9} \times {10^{ - 9}}\left[ {5 \times \left( {\dfrac{1}{{1.414}} - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right) + 10 \times \left( {\dfrac{1}{{1.414}} - \dfrac{1}{{2.828}}} \right)} \right]\]
\[ \Rightarrow W = 450 \times {10^{ - 6}} \times \left( {\dfrac{1}{{1.414}} - \dfrac{1}{{2.828}}} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow W = \dfrac{{450 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}}}{{1.414}}\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right) = 159.12 \times {10^{ - 6}}Joules\]
So, \[159.12 \times {10^{ - 6}}joules\] work is done transferring a charge of \[5\mu C\] from D to the point of intersection of diagonals.
Note: Potential difference between two points is the total amount of work is done to transfer a unit charge from one point to another. \[v = \dfrac{w}{q}\]
Here,\[v\] is the potential ,\[w\] is the work done and q is the charge. After knowing the value of potential and charge, we can easily find how much work is done. Work done is calculated in \[joules\] . When \[1 coulomb\] of charge is transferred and potential difference is \[1volt\] then the work done is said to be \[1joule.\]
Complete step by step answer:
Given that, Side of Square ABCD\[ = 2m\]

Three charges are given which are placed at the corner of the square (as shown).
Now we can see,
AC=BD=\[\sqrt {{{(2)}^2} + {{(2)}^2}} \] \[ = \sqrt {4 + 4} \]
=\[2\sqrt 2 \] \[ = 2.28m\]
Now, AO=BO=CO=\[\dfrac{{2.828}}{2} = 1.414m\]
Potential at O, \[{V_o} = \]\[\dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\left[ {\dfrac{{{q_1}}}{{AO}} + \dfrac{{{q_2}}}{{BO}} + \dfrac{{{q_3}}}{{CO}}} \right]\]
Potential at D, \[{V_D} = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\left[ {\dfrac{{{q_1}}}{{AD}} + \dfrac{{{q_2}}}{{BD}} + \dfrac{{{q_3}}}{{CD}}} \right]\]
Now, we know
Work done\[ = q\left[ {{v_O} - {v_D}} \right]\]
Charge \[q\] is given and we can find potential at point O and D .
So, W\[ = 5 \times {10^{ - 6}} \times 9 \times {10^9} \times \left[ {5 \times {{10}^{ - 9}}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{AO}} - \dfrac{1}{{AD}}} \right] + 10 \times {{10}^{ - 9}}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{BO}} - \dfrac{1}{{BD}}} \right]} \right]\]
\[\Rightarrow W = 45 \times {10^{ - 6}} \times {10^9} \times {10^{ - 9}}\left[ {5 \times \left( {\dfrac{1}{{1.414}} - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right) + 10 \times \left( {\dfrac{1}{{1.414}} - \dfrac{1}{{2.828}}} \right)} \right]\]
\[ \Rightarrow W = 450 \times {10^{ - 6}} \times \left( {\dfrac{1}{{1.414}} - \dfrac{1}{{2.828}}} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow W = \dfrac{{450 \times {{10}^{ - 6}}}}{{1.414}}\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right) = 159.12 \times {10^{ - 6}}Joules\]
So, \[159.12 \times {10^{ - 6}}joules\] work is done transferring a charge of \[5\mu C\] from D to the point of intersection of diagonals.
Note: Potential difference between two points is the total amount of work is done to transfer a unit charge from one point to another. \[v = \dfrac{w}{q}\]
Here,\[v\] is the potential ,\[w\] is the work done and q is the charge. After knowing the value of potential and charge, we can easily find how much work is done. Work done is calculated in \[joules\] . When \[1 coulomb\] of charge is transferred and potential difference is \[1volt\] then the work done is said to be \[1joule.\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




