
An example of dibasic acid is:
a.) Orthophosphoric acid
b.) Orthophosphoric acid
c.) Hypophosphorous acid
d.) Pyrophosphoric acid
Answer
597.9k+ views
Hint: In order to solve the given problem first we will understand the basic concept behind the classification of an acid is monobasic, dibasic and tribasic etc. Further we will see the chemical symbol of each of the acids given in the option and on the basis of their structure we will classify them and select the dibasic acid.
Complete step by step solution: We know that the general property of acid is mainly due to the presence of hydrogen in them. Not a single acid can exist without the presence of hydrogen atom.
The acids are classified on the basis of their basicity. Basicity is defined as the number of hydrogen ions present in the molecule of acids which are ionisable. Sometimes there may be many hydrogen atoms present in the molecule but they may not be ionisable so the basicity should not be calculated on the basis of the number of hydrogen atoms present in the molecule.
Classification of acids on the basis of basicity is as follows:
Monobasic acids: - There is only one ionisable hydrogen atom present in each molecule of monobasic acids. Example- Hydrochloric acid, Hydrobromic acid.
Dibasic acids: - There are two ionisable hydrogen atoms present in each molecule of dibasic acids. Example- Sulphuric acid, Oxalic acid.
Tribasic acids: - There are three ionisable hydrogen atoms present in each molecule of tribasic acids. Example- phosphoric acid.
Tetrabasic acids: - There are four ionisable hydrogen atoms present in each molecule of monobasic acids. Example- Silicic acid.
Now let us see the chemical structure of acid to find the dibasic acid.
Orthophosphoric Acid:
The molecular formula for orthophosphorous acid is ${H_3}P{O_3}$ .
Structure of Orthophosphoric Acid
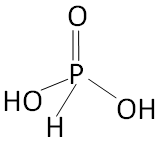
The basicity of the molecule is the number of acidic hydrogen atoms. To be acidic, hydrogen must be bound to a highly electronegative atom such as oxygen or fluorine.
As we can see from the structure of Orthophosphorous acid that there are two hydrogen atoms attached to two different oxygen atoms in the molecule which is ionisable. So the basicity of Orthophosphorous Acid is two.
Hence, an example of dibasic acid is Orthophosphorous acid
So, the correct answer is option A.
Note: In order to solve such problems related to basicity of the acids students must draw the structure of acids before classifying them on the basis of basicity. Students must keep in mind the concept of ionisable hydrogen and should count only the ionisable hydrogen present in the compound and not all the hydrogen to calculate the basicity. Orthophosphoric acid, commonly known as phosphoric acid, the phosphorous's most essential oxygen acid, was used to produce fertilizer phosphate salts. This is also used in dental cements, in albumin derivatives preparation and in the sugar and silk industries.
Complete step by step solution: We know that the general property of acid is mainly due to the presence of hydrogen in them. Not a single acid can exist without the presence of hydrogen atom.
The acids are classified on the basis of their basicity. Basicity is defined as the number of hydrogen ions present in the molecule of acids which are ionisable. Sometimes there may be many hydrogen atoms present in the molecule but they may not be ionisable so the basicity should not be calculated on the basis of the number of hydrogen atoms present in the molecule.
Classification of acids on the basis of basicity is as follows:
Monobasic acids: - There is only one ionisable hydrogen atom present in each molecule of monobasic acids. Example- Hydrochloric acid, Hydrobromic acid.
Dibasic acids: - There are two ionisable hydrogen atoms present in each molecule of dibasic acids. Example- Sulphuric acid, Oxalic acid.
Tribasic acids: - There are three ionisable hydrogen atoms present in each molecule of tribasic acids. Example- phosphoric acid.
Tetrabasic acids: - There are four ionisable hydrogen atoms present in each molecule of monobasic acids. Example- Silicic acid.
Now let us see the chemical structure of acid to find the dibasic acid.
Orthophosphoric Acid:
The molecular formula for orthophosphorous acid is ${H_3}P{O_3}$ .
Structure of Orthophosphoric Acid

The basicity of the molecule is the number of acidic hydrogen atoms. To be acidic, hydrogen must be bound to a highly electronegative atom such as oxygen or fluorine.
As we can see from the structure of Orthophosphorous acid that there are two hydrogen atoms attached to two different oxygen atoms in the molecule which is ionisable. So the basicity of Orthophosphorous Acid is two.
Hence, an example of dibasic acid is Orthophosphorous acid
So, the correct answer is option A.
Note: In order to solve such problems related to basicity of the acids students must draw the structure of acids before classifying them on the basis of basicity. Students must keep in mind the concept of ionisable hydrogen and should count only the ionisable hydrogen present in the compound and not all the hydrogen to calculate the basicity. Orthophosphoric acid, commonly known as phosphoric acid, the phosphorous's most essential oxygen acid, was used to produce fertilizer phosphate salts. This is also used in dental cements, in albumin derivatives preparation and in the sugar and silk industries.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




