
What are insulators \[?\] Define on the basis of atomic structure \[?\]Give four examples of insulators \[?\]
Answer
558k+ views
Hint: We have to know about insulators and the atomic structure of insulators. Insulators have no capacity to carry current because of its atomic structure. Insulators do not have free electrons. Insulators do not let electrons flow very easily. These electrons are not free to move.
Complete answer:
Those materials or substances which contain very less amount of free electrons or no free electrons are called insulators. Insulators cannot carry current. Electrons cannot flow from one end to another end of the material of any insulators.
Valence's band of insulators is fully inhabited with electrons due to their covalent bonds. An insulator contains eight valence electrons. The atomic bonds in it depend on the electron pairs which are shared by any non-metals. There is no free charge or free electron carriers to start the current flow. Here is the band model of insulator
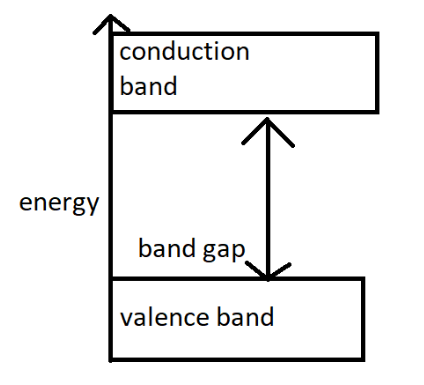
If we want to activate the conductivity then electrons have to move from valence band to conduction bands. For insulators electrons are in valence band. And the gap between those bands is huge for insulators. The four examples of insulators are wood, sealing wax, mica, air. But there are many more insulators in this world. Which are rubber, oil, air, diamond, dry cotton etc.
Note: We can get confused between semiconductors and insulators, but we have to keep that in mind that the band gap between conduction band and valence band of insulators is very huge. But for semiconductors, the gap between two bands is less than the insulators. So semiconductors sometimes can be converted into conductors.
Complete answer:
Those materials or substances which contain very less amount of free electrons or no free electrons are called insulators. Insulators cannot carry current. Electrons cannot flow from one end to another end of the material of any insulators.
Valence's band of insulators is fully inhabited with electrons due to their covalent bonds. An insulator contains eight valence electrons. The atomic bonds in it depend on the electron pairs which are shared by any non-metals. There is no free charge or free electron carriers to start the current flow. Here is the band model of insulator

If we want to activate the conductivity then electrons have to move from valence band to conduction bands. For insulators electrons are in valence band. And the gap between those bands is huge for insulators. The four examples of insulators are wood, sealing wax, mica, air. But there are many more insulators in this world. Which are rubber, oil, air, diamond, dry cotton etc.
Note: We can get confused between semiconductors and insulators, but we have to keep that in mind that the band gap between conduction band and valence band of insulators is very huge. But for semiconductors, the gap between two bands is less than the insulators. So semiconductors sometimes can be converted into conductors.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




